by Amy Mone, Johns Hopkins University Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center in Baltimore, working with colleagues in the Netherlands, developed a blood test that can predict recurrence of gastric cancer in patients after surgery. A description of their test, which is still experimental, was published online Jan. 27 in the journal Nature...
Artificial nerve cells could cure chronic diseases
by CORDIS With its promise to bring new insights into the diagnosis and treatment of conditions as varied as cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, bioelectronic medicine is now in the spotlight. Bringing together various fields like biochemistry, molecular medicine, neuroscience, immunology, electrical and mechanical engineering, computer science and mathematics, bioelectronic medicine focuses on electrical signaling...
Team examines the link between cognition and hearing or vision loss
by Concordia University There is a long-established and widely recognized link between declines in sensory acuity—particularly hearing and vision—and cognition. Data from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA), involving tens of thousands of participants across the country aged 45 to 85, backs this up. A recent study led by Montreal researchers asks why this...
Six patients with rare blood disease are doing well after gene therapy clinical trial
by Sarah C.p. Williams, University of California, Los Angeles UCLA researchers are part of an international team that reported the use of a stem cell gene therapy to treat nine people with the rare, inherited blood disease known as X-linked chronic granulomatous disease, or X-CGD. Six of those patients are now in remission and have...
The future of human healing lies in the brain of a starfish
by Adam Dove, Carnegie Mellon University, Department of Chemical Engineering The incredible benefits of stem cell therapy have been widely known for decades. It can alleviate the pain of arthritis, and help patients heal exponentially faster after surgery. But stem cell therapies are prohibitively expensive—to the tune of $100,000 to $200,000 per patient. Because of...
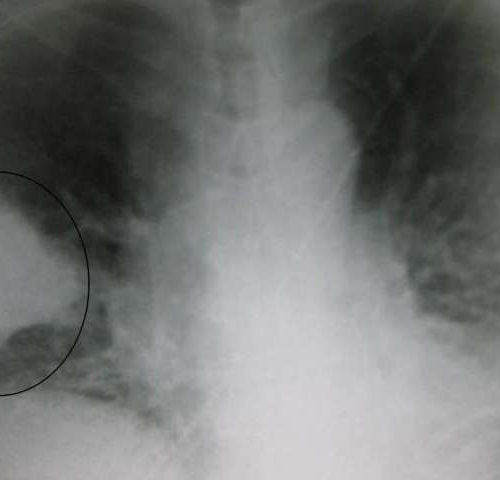
Pneumonia recovery reprograms immune cells of the lung
by Boston University School of Medicine A black and white X-ray picture showing a triangular white area on the left side. A circle highlights the area. Credit: James Heilman, MD./Wikipedia Researchers have determined that after lungs recover from infection, alveolar macrophages (immune cells that live in the lungs and help protect the lungs against infection)...
Research offers promise for treating schizophrenia
by Allyson Mann, University of Georgia Research by a University of Georgia psychologist shows that targeting one particular symptom of schizophrenia has a positive effect on other symptoms, offering significant promise for treating an aspect of schizophrenia that currently has no pharmaceutical options. A team led by Gregory Strauss published a study confirming that successfully...
Scientists create listeriosis-immune mice by turning off gene in myeloid cells
The study provides exciting material for understanding the mechanisms of the immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. ITMO UNIVERSITY An international research team which includes specialists from ITMO University has conducted a series of experiments with the goal of studying the immune system and identifying the genes and proteins involved in the response to certain harmful...
Researchers identify mechanism that triggers a rare type of muscular dystrophy
by Autonomous University of Barcelona A study led by the IBB-UAB has identified the molecular mechanism through which a protein carrying genetic mutations associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1G accelerates its tendency to form amyloid fibrils and triggers the appearance of the disease. The research, published in Cell Reports, will pave the way for...
Gut bacteria linked to personality
Dr Katerina Johnson of Oxford University’s Department of Experimental Psychology has been researching the science of that ‘gut feeling’ – the relationship between the bacteria living in the gut (the gut microbiome) and behavioural traits. In a large human study she found that both gut microbiome composition and diversity were related to differences in personality,...