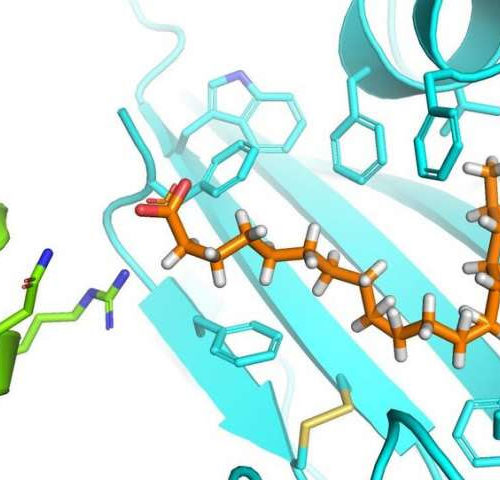
by University of Bristol A druggable pocket in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein that could be used to stop the virus from infecting human cells has been discovered by an international team of scientists led by the University of Bristol. The researchers say their findings, published today in the journal Science, are a potential ‘game changer’ in defeating the current...
A link between sensory neurons activation and the immune system
By Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Scientists at EPFL, ETHZ and Harvard Medical School/Boston Children’s Hospital have developed an implantable technology that enabled the discovery of an interaction between sensory neurons and immune cells. Pain is a protective mechanism, alerting us to danger by generating an unpleasant sensation. The warning message is carried to the spinal...
Study finds that children’s immune response protects against COVID-19
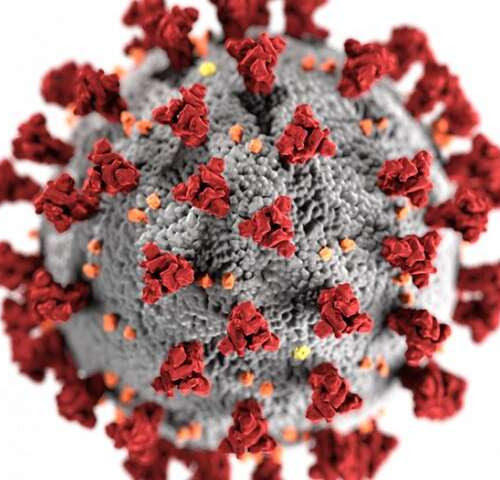
by Albert Einstein College of Medicine Image of the ultrastructural morphology exhibited by the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). The first study comparing the immune responses of adults and children with COVID-19 has detected key differences that may contribute to understanding why children usually have milder disease than adults. The findings also have important implications for vaccines...
Researchers discover potential cause of immunotherapy-related neurotoxicity
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania New research has uncovered the previously unknown presence of CD19—a B cell molecule targeted by chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell immunotherapy to treat leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma—in brain cells that protect the blood brain barrier (BBB). This discovery may potentially be the cause...
Researchers find diminished response by ‘killer’ T cells in elderly COVID-19 patients
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WASHINGTON, D.C. – September 21, 2020 – Although people of any age can become infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, elderly patients face a higher risk of severity and death than younger patients. New research comparing the immune response among age groups, published this week in mBio, an open-access journal of the...
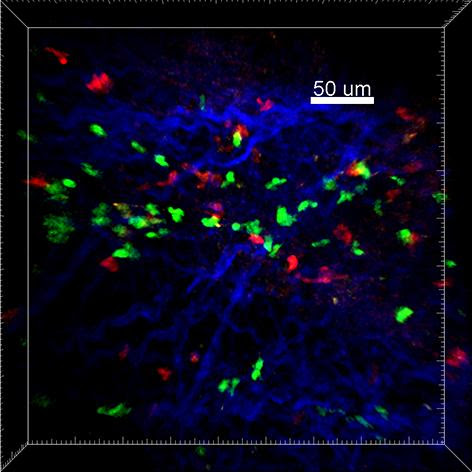
Regulatory T cells could lead to new immunotherapies aimed at treating multiple sclerosis
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE IMAGE: REGULATORY T CELLS (GREEN) SHOWN INTERACTING WITH PATHOGENIC TH17 CELLS (RED) NEAR COLLAGEN FIBERS (BLUE) IN THE SPINAL CORD IN A MODEL OF MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Irvine, CA – September 21, 2020 – In a new University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers have discovered how regulatory T cells (Treg) are instrumental in...
VCU study shows the experimental drug AR-12 could be a promising COVID-19 treatment
A team of scientists led by Paul Dent, Ph.D., at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center has discovered that an experimental cancer drug called AR-12 inhibits the SARS-CoV-2 virus, the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, from infecting cells and replicating. Their findings were published online today in the journal Biochemical Pharmacology, and steps are now being...
‘Bandage’ transplants bone-forming stem cells into bone fractures
New biomaterial transplants bone-forming stem cells into severe bone fractures It could reduce complications and infections from serious open fracture injuries After creating new bone to fix a fracture the biomaterial is absorbed by the body UK experts tested the material on mice and want to do clinical trials on humans A new type of bandage has been...
This revolutionary new coronavirus cure is already saving lives
A breakthrough coronavirus cure might soon be available, as researchers are studying a drug that could eliminate the virus, calm the immune response, and repair damaged tissue. The drug is described in different ways: Medicinal signaling cells (MSCs), mesenchymal lineage adult stem cells, or adipose-tissue derived mesenchymal stromal cells (AT-MSC). MSCs therapy proved to be very effective...
Senolytics: A New Weapon in the War on Aging
Anti-aging drugs that remove harmful cells from our bodies could treat a range of diseases that plague the elderly. By Nathaniel Scharping Getting old means fighting a war you’ll never win. Our bodies already battle for us every day, against bacteria and viruses, mutant cells, harmful chemicals and the slow rush of time itself. But...