by University of Cambridge Credit: CC0 Public Domain Scientists have made a promising step towards developing a new drug for treating acute myeloid leukaemia, a rare blood disorder. In a study published today in Nature, Cambridge researchers report a new approach to cancer treatment that targets enzymes which play a key role in translating DNA into...
Weight loss surgery reduces brain pressure in patients with neurological condition
by University of Birmingham Credit: CC0 Public Domain Weight loss surgery is more effective than dieting to reduce brain pressure that can cause blindness in patients with a neurological condition, finds a study led by the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust (UHB). Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) is a debilitating condition that...
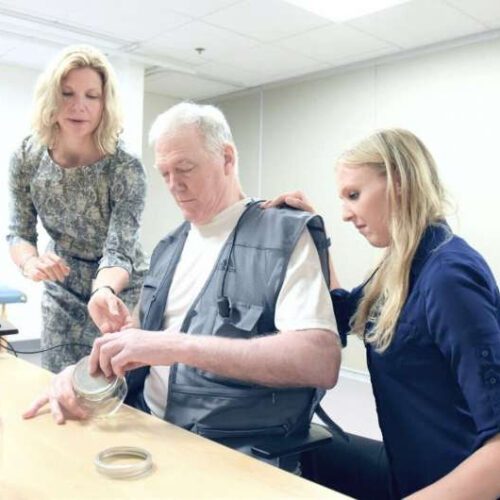
Results of study could be biggest rehab advance in decades for patients after stroke
by MGH Institute of Health Professions Dr. Teresa Kimberley (left) works with a vagus nerve stimulation patient (center) and a grad assistant at the Brain Recovery Lab on the MGH Institute of Health Professions campus in Boston. Credit: John Shaw Results of a study co-authored by MGH Institute of Health Professions researcher Teresa Kimberley, Ph.D.,...
Genomic study points to new treatment approaches for advanced small-cell lung cancer
by Ohio State University Medical Center Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new study of advanced small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center—Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC—James) has identified molecular patterns linked to patients developing resistance to certain therapies. This study, published in the journal JTO...
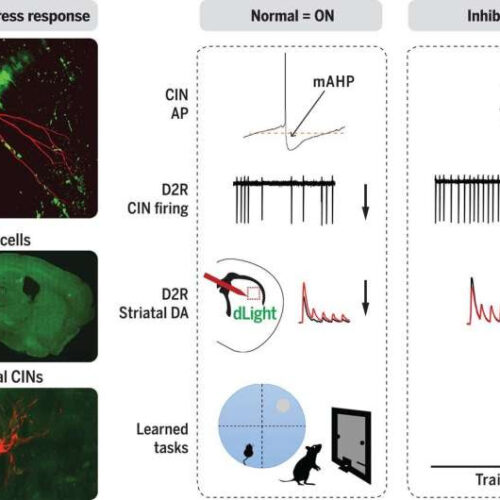
Two-color reporter shows cholinergic neurons engage ISR to modulate dopamine levels
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Using a two-color viral reporter of ISR activation state, striatal CINs were distinguished from other cell types by showing steady-state ISR activation. ISR inhibition altered CIN excitability, inverted the sign of dopamine modulation of CIN firing rate and evoked dopamine release, and increased movement vigor in learned tasks. mAHP,...
Drug derived from Kentucky-grown plant shows promise for ovarian cancer treatment
by Jenni Ho, University of Kentucky Researcher Kristen Hill, Ph.D., views ovarian cancer cells treated with Artemesia annua extracts. Credit: UK HealthCare Marketing A new study from University of Kentucky Markey Cancer researchers shows that Artemisia annua, a plant that has been traditionally used for its anti-malaria components, shows promise in treating ovarian cancer. The study,...
IS 1 VACCINE DOSE ENOUGH IF YOU’VE HAD COVID-19?
The findings, published in Science Immunology, suggest only a single vaccine dose may be needed to produce a sufficient antibody response. Researchers found that those who did not have COVID-19—called COVID naïve—did not have a full immune response until after receiving their second vaccine dose, reinforcing the importance of completing the two recommended doses for achieving strong levels...
Feeling confinement in the gut
Resolving a missing link of research, Canadian researchers find significant microbiome changes in crew who spent 520 days in isolation to simulate a mission to Mars Crew members who took part in the Mars500 experiment showed significant changes in their gut microbiota from their 520 days in confinement, according to a new study by scientists...
Researchers identify the proteins that cause intestinal disease
TEL-AVIV UNIVERSITY IMAGE: PROF. TAL PUPKO CREDIT: TEL AVIV UNIVERSITY Researchers from Tel Aviv University have created an artificial intelligence platform that can identify the specific proteins that allow bacteria to infect the intestines – a method that paves the way for the creation of smart drugs that will neutralize the proteins and prevent disease,...
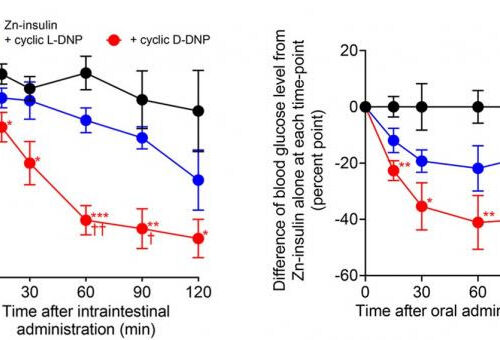
Toward painless oral insulin administration
KUMAMOTO UNIVERSITY IMAGE: LEFT: BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS CONTINUED TO DECREASE FROM 15 TO 60 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION. THIS DECREASE IN BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS PERSISTED UNTIL AT LEAST 120 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION. RIGHT: A DECREASE IN BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS WAS OBSERVED 15 MINUTES AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION, AND THE HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT PERSISTED UNTIL 120 MINUTES AFTER ADMINISTRATION....