by University of Hawaii at Manoa Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers have recently discovered that certain enzymes binded to each other may help lessen the risk of developing mesothelioma, a cancer of the lining of the lungs and abdomen. The study from University of Hawaiʻi Cancer Center’s Flavia Novelli, Michele Carbone, and Haining Yang was...
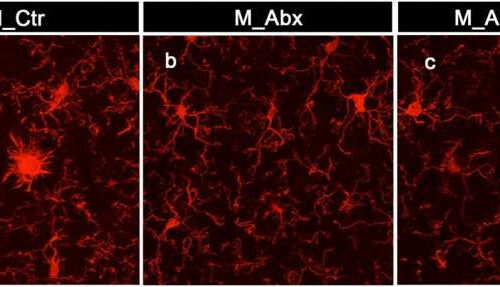
Immune cells in the brain play key role in relationship between gut microbes and b-amyloid deposits
by University of Chicago Medical Center Microglia in the brain of male mice with Alzheimer’s Disease have a “neurodegenerative” appearance and is associated with amyloid beta plaques in the brain (left) while treating the mice with antibiotics early in life leads to “neuroprotective” microglia and reduced amyloidosis (middle). The beneficial effects of antibiotics can be...
Unique brain channel combats epileptic seizures
by Colorado State University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Epilepsy, a chronic brain disorder that causes seizures, affects around 50 million people worldwide. New research from the lab of Department of Biomedical Sciences Professor Susan Tsunoda that was recently featured in the Journal of Neuroscience showed for the first time that a channel in the brain called dSlo2...
Scientists discover pathway that allows cancer to bypass oncology treatments
by City of Hope National Medical Center Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at City of Hope, a world-renowned cancer research and treatment organization, have identified a pathway that explains how mutated cancer cells can continue to replicate and become resistant to oncology therapies. Using whole genome sequencing technology, the scientists discovered a new mechanism for...
The largest ever study of the plasma proteome published
by deCODE genetics Dr. Kari Stefansson CEO of deCODE genetics and one of the senior authors on the paper. Credit: deCODE genetics In a study published today in Nature Genetics, scientists at deCODE genetics , a subsidiary of the pharmaceutical company Amgen, demonstrate how measuring the levels of a large number of proteins in plasma at...
Does cancer immunotherapy work differently in men vs. women?
by Thomas Jefferson University Credit: CC0 Public Domain A class of cancer immunotherapy called checkpoint inhibitors has revolutionized cancer treatment. It’s a new way to attack the disease by unleashing the immune system. However, not every patient benefits from the treatment, and it can cause severe, sometimes life-threatening, side effects in some. New research shows...
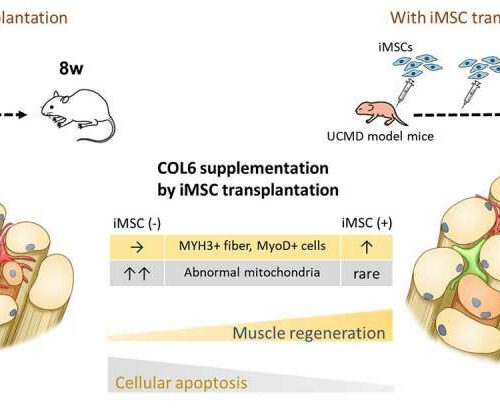
Stem cells promote recovery regeneration in mice with a rare muscle disease
by Kyoto University The Hidetoshi Sakurai laboratory shows how iPS cells can replenish collagen VI to regenerate muscles in mice suffering from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy. Credit: Kyoto University Muscle dystrophy describes a set of diseases that causes the weakening and loss of muscle. Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy is a rare disease that is the...
Landmark study into genetic disorder offers clues into links between metabolism and mental health
by Tanner Stening, Northeastern University A new study, published Wednesday, focused on a severe neurodevelopmental disorder referred to as 16p11.2 Deletion Syndrome, a condition often associated with autism, intellectual disability, language impairments, seizures, obesity, and movement disorders, among a range of other health problems. Credit: Ruby Wallau/Northeastern University Researchers at Northeastern and neighboring colleges say...
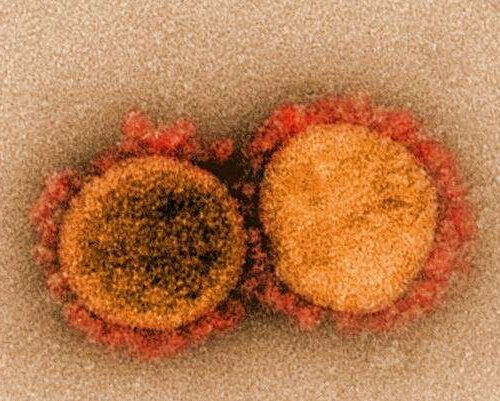
Study reports a novel broad-spectrum antiviral drug class with activity against SARS-CoV-2
by Georgia State University Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID The COVID-19 pandemic and resurgence of infections by other respiratory RNA viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children has caused an...
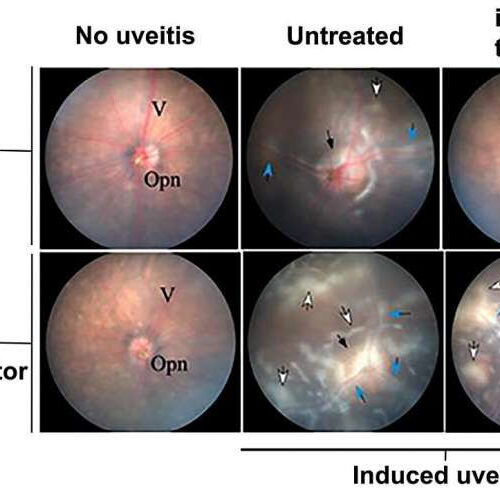
Discovering a new B cell that tempers autoimmunity
by National Institutes of Health Photographs of mouse retina showing the effect of uveitis treatment with i27-Bregs. The left column represents a normal retina. Photos in the middle and right column are retinal images from mice with uveitis, untreated or treated with i27-Bregs. The central spot is the optic nerve head. Note the absence of...