by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine Portrait of Kathrin de la Rosa. Credit: Pablo Castagnola, MDC A few years ago, Professor Kathrin de la Rosa and her colleagues in the lab of the Swiss immunologist Antonio Lanzavecchia made an unusual discovery. The team found antibodies in the blood of malaria patients that had been...
Could long COVID be linked to herpes viruses? Early data offer a hint
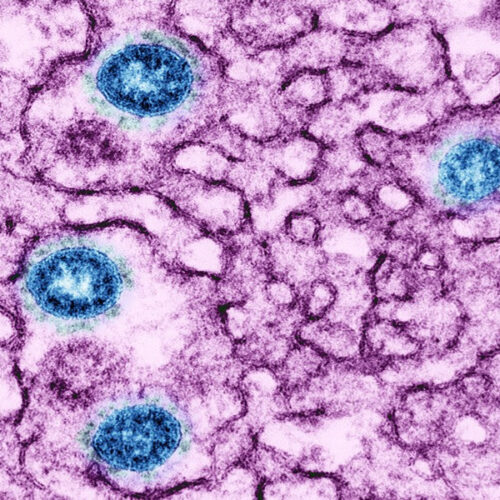
Emily Waltz Particles of the SARS-CoV-2 virus (blue) inside an infected cell.Credit: NIH/SPL Researchers looking for biological drivers and markers of long COVID have linked the syndrome to herpes viruses, as well as to reduced levels of a stress hormone1. The exploratory study drew both praise and criticism from scientists contacted by Nature. “A major weakness...
Could tiny blood clots cause long COVID’s puzzling symptoms?
Cassandra Willyard Illustration by David Parkins When Lara Hawthorne, an illustrator in Bristol, UK, began developing strange symptoms after having COVID-19, she hoped that they weren’t due to the virus. Her initial illness had been mild. “I’ve been triple vaccinated. I felt quite protected,” she says. But months later, she was still sick with a...
COATING KEEPS KILLING VIRUSES AND BACTERIA FOR MONTHS
As reported in the journal Matter, the coating proved deadly to SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19), E. coli, MRSA, and a variety of other pathogens. It killed 99.9% of microbes even after months of repeated cleaning, abrasion, and other punishment on real-world surfaces like keyboards, cell phone screens, and chicken-slathered cutting boards. The coating...
Invasive strategy does not improve survival in kidney disease patients with ischemia
by European Society of Cardiology Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain In patients with advanced chronic kidney disease and chronic coronary disease, an invasive strategy does not reduce the five-year risk of death compared to a conservative strategy. That’s the finding of late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session on 29 August at ESC Congress 2022. Previous trials...
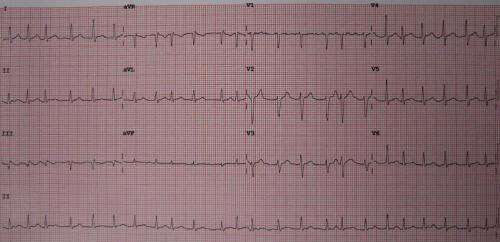
Atrial fibrillation screening using smartphones increases detection and treatment
by European Society of Cardiology A 12 lead ECG showing atrial fibrillation at approximately 150 beats per minute. Credit: James Heilman, MD/Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 Atrial fibrillation screening using conventional smartphones more than doubles the detection and treatment rate in older people compared to routine screening, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session on 28...
New weapon targets antibiotic resistance
A new class of motorized molecules that kill specific bacteria shows promise to curb the threat of antibiotic resistance to human health. Rice University scientists led a team developing light-activated hemithioindigo (HTI) molecules that destroy Gram-positive bacteria and the biofilms they form. The molecules enhance the local generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that chemically attack and destroy drug-resistant cells. The new molecules...
What is Hyperthymesia?
Hyperthymesia is a real (not fictional) condition associated with how human memory works. People with hyperthymesia can remember an incredibly large number of their life experiences, often with many slightest details. This condition is considered abnormal – even when most of us probably would want to have such a superior memory performance. Hyperthymesia, or highly superior autobiographical...
Using Light-Up Skullcaps, Neurologist Is Pioneering an Autism Test for Babies
If you’re looking for a touching story about babies, you’re in the right place. And this one starts like every newborn’s tale begins: with drooling. Baby Aspen – tiny, drowsy, with big eyelashes – and new mom Mara Roman were asked to donate, collected in tubes like those used for COVID-19 saliva testing. “Just do...
Modified nucleotides used in COVID-19 vaccines work as designed
The remarkable effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 has generated much interest in synthetic mRNA therapeutics for treating and preventing disease. But some basic science questions have remained about whether the modified nucleotides used in the vaccines faithfully produce the protein products they are designed to make. The synthetic mRNAs used in the COVID-19 vaccines incorporate the...