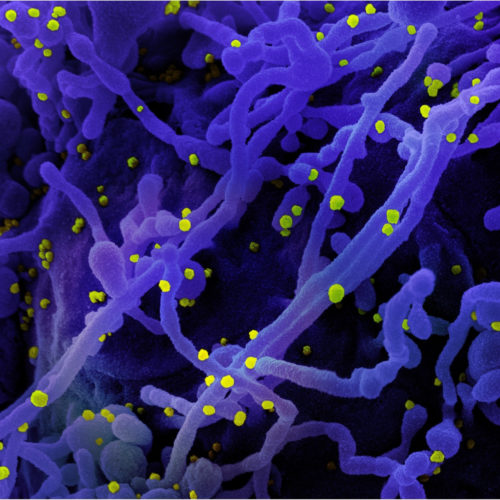
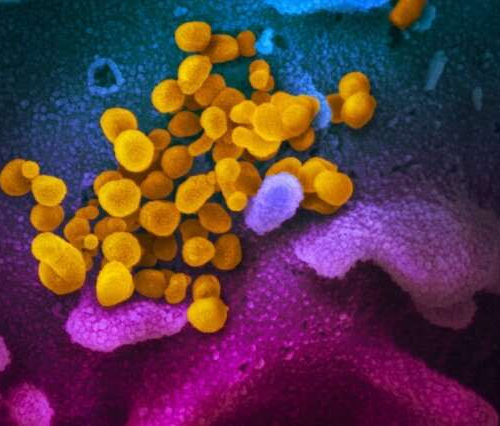
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc A study conducted by researchers at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg has shown that the antidepressant agent fluoxetine may be an effective drug for the early treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) among at-risk groups. Jochen Bodem and colleagues found that the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine significantly inhibited viral...
Tag: <span>COVID-19</span>
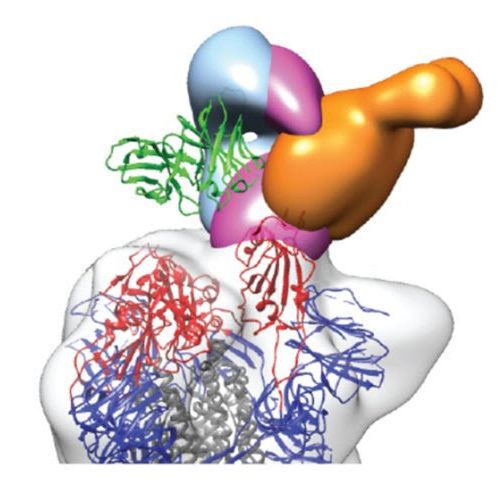
Researchers identify potent antibody cocktail with potential to treat COVID-19
by Deborah Kotz, University of Maryland School of Medicine Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) evaluated several human antibodies to determine the most potent combination to be mixed in a cocktail and used as a promising anti-viral therapy against the virus that causes COVID-19. Their research, conducted in collaboration with scientists...
HIV and TB increase death risk from COVID-19, study finds—but not by much
By Linda NordlingJun. 15, 2020 , 4:30 PM Science’s COVID-19 reporting is supported by the Pulitzer Center. CAPE TOWN, SOUTH AFRICA—Living with HIV or active tuberculosis (TB) increases a person’s likelihood of dying from COVID-19, preliminary data from South Africa show. However, the effect is small compared with other known risk factors such as old...
Smartphone app uses voice recordings to detect fluid in the lungs
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF CARDIOLOGY Sophia Antipolis – 19 June 2020: Voice analysis by a smartphone app identifies lung congestion in heart failure patients, allowing early intervention before their condition deteriorates. The small study is presented today on HFA Discoveries, a scientific platform of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 “Speech is personal and as such,...
How cells’ ‘lava lamp’ effect could make cancer drugs more powerful
Discovery that synthetic compounds form concentrated droplets inside cells could shake up drug development — including the hunt for coronavirus treatments. Fluorescently tagged molecules of the cancer drug cisplatin clump up inside droplets in cells.Credit: Isaac Klein/Whitehead Institute There’s a long-standing assumption in the pharmaceutical industry that when drug molecules enter a cell, they spread...
COVID-19 immunology study reveals universally effective antibodies
A study of 149 people who have recovered from COVID-19 show that although the amount of antibodies they generated varies widely, most individuals had generated at least some that were intrinsically capable of neutralizing the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The findings are published in the journal Nature. Antibodies vary widely in their efficacy. While many may latch...
Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after infection, study suggests
Berkeley Lovelace Jr. @BERKELEYJR Coronavirus antibodies may last only two to three months after a person becomes infected with Covid-19, according to a new study published Thursday in Nature Medicine. Researchers in the Wanzhou District of China compared the antibody response of 37 asymptomatic people with that of 37 symptomatic people. The researchers found people...
By tricking mice into sensing fake smells, scientists decode how the brain recognizes scent
By JULIET ISSELBACHERJUNE 18, 2020 New research untangles the complex code the brain uses to distinguish between a vast array of smells, offering a scientific explanation for how it separates baby powder from bleach, lemon from orange, or freshly cut grass from freshly brewed coffee. A single scent can trigger a complex chain of events...
Up to 45 percent of SARS-CoV-2 infections may be asymptomatic
by The Scripps Research Institute An extraordinary percentage of people infected by the virus behind the ongoing deadly COVID-19 pandemic never show symptoms of the disease, according to the results of a Scripps Research analysis of public datasets on asymptomatic infections. The findings, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, suggest that asymptomatic infections may account...
Study says vitamin-magnesium combo may reduce severity of COVID-19 in seniors
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MD The COVID-19 pandemic that began in late December 2019 has spread to over 188 countries and territories, causing over 6.5 million cases and 385,000 deaths. With no effective therapeutic COVID-19 drug or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine in sight, researchers are exploring different strategies to limit its...