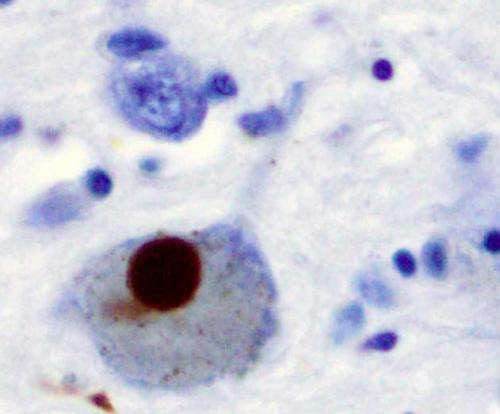
Charlampos “Haris” Tzoulis with groundbreaking research on Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease. Credit: Ingvild Festervoll Melien A study performed by researchers from the University of Bergen, Norway, and the University of Vienna, Austria, shows damage of the mitochondria—the cell’s microscopic powerhouses—in the brains of people with Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease. The researchers found that the mitochondrial power generator (known as...
Tag: <span>Parkinson’s disease</span>
Parkinson’s disease may start in the gut
by Karolinska Institutet Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the University of North Carolina in the USA have mapped out the cell types behind various brain disorders. The findings are published in Nature Genetics and offer a roadmap for the development of new therapies to target neurological and psychiatric disorders. One interesting finding was...
Smart contact lenses that diagnose and treat diabetes
CREDIT: SEI KWANG HAHN (POSTECH) Diabetes is called an incurable disease because once it develops, it does not disappear regardless of treatment in modern medicine. Having diabetes means a life-long obligation of insulin shots and monitoring of blood glucose levels. But what if you could control the secretion of insulin just by wearing contact lenses?...
Parkinson’s discovery implicates “second brain” in the gut
By Nick Lavars A growing body of evidence is forging a stronger and stronger connection between the onset of Parkinson’s disease and the gut. Scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have thrown further weight behind this theory, with an investigation of cellular behavior in the nervous...
Ultra-precision nano-sensor could detect iron disorders
Chronic iron imbalances – having either too little or too much iron in the blood – can result in medical conditions ranging from anaemia and haemochromatosis through to more severe diseases, such as cancer, Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease. Haemochromatosis is one of Australia’s most common hereditary diseases and the Australian Bureau of Statistics estimates...
New research gives further evidence that autoimmunity plays a role in Parkinson’s disease
by La Jolla Institute for Immunology roducing brain cells of patients with Parkinson’s disease. T cells that react to alpha-synuclein are most abundant when patients are first diagnosed with the disease. Credit: La Jolla Institute for Immunology A new study co-led by scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) adds increasing evidence that...
Belgian scientists identify ATP10B as novel risk gene for Parkinson’s disease
VIB (THE FLANDERS INSTITUTE FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY) Screening DNA of Parkinson’s patients in the Christine Van Broeckhoven laboratory (VIB-UAntwerpen Center for Molecular Neurology) identified a new risk gene for Parkinson’s disease. Mutations in ATP10B resulted in loss of ATP10B protein. The function of the ATP10B gene was revealed by the Peter Vangheluwe lab (KU Leuven, Laboratory...
Is Appendectomy Linked to Parkinson’s Disease?
By Osman Shabir, M.Sc. Reviewed by Dr. Mary Cooke, Ph.D. Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder clinically characterized by resting tremor, bradykinesia (slow movements), dyskinesia (impairment of movement), dystonia (stiffness of muscles including facial muscles), a stooped posture, sexual and urinary dysfunction, drooling, and in some cases psychiatric symptoms including psychosis, dementia, and depression Pathologically,...
Biomarker for Parkinson’s disease may originate in the gut
by Lori Dajose, California Institute of Technology Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder, impairing the motor functions of millions of elderly people worldwide. Often, people with PD will experience disturbances in gastrointestinal function, such as constipation, years before motor symptoms set in. Postmortem examinations of the brains of people with PD have shown...
New insights into the processes that cause Parkinson’s disease
by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne In a breakthrough for Parkinson’s disease, scientists at EPFL have reconstructed the process by which Lewy bodies form in the brain of patients. The study offers new insights into how Parkinson’s disease begins and evolves, and opens up a set of potential new treatment targets. The brains of patients...