by Queen Mary, University of London Immunohistochemistry for alpha-synuclein showing positive staining (brown) of an intraneural Lewy-body in the Substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Credit: Wikipedia Including genetic markers in addition to well known risk factors improves tests to predict Parkinson’s disease, according to a study led by Queen Mary University of London. Parkinson’s disease is...
Reprogramming brain cells enables flexible decision-making
by University of Zurich Humans and animals have the ability to constantly adapt to new situations. Credit: Frank Brüderli; Universität Zürich Greetings without handshakes, mandatory masks in trains, sneezing into elbow crooks—the COVID-19 pandemic dramatically illustrates how important it can be for humans to shed habitual behaviors and to learn new ones. Animals, too, must be...
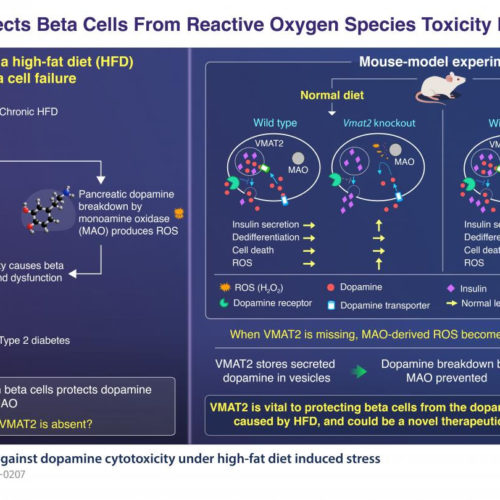
A ferry protein in the pancreas protects it from the stress induced by a high-fat diet
TOKYO INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY IMAGE: VMAT2 CONTROLS THE AMOUNT OF DOPAMINE IN BETA-CELLS THEREBY PROTECTING PANCREATIC BETA-CELLS FROM EXCESSIVE OXIDATIVE STRESS. Every time we eat, the glucose level in our body goes up. This spurs our pancreatic machinery into action and through intricate physiological mechanisms, appropriate amounts of insulin are produced, our blood glucose levels...
Injectable hydrogel could someday lead to more effective vaccines
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY Vaccines have curtailed the spread of several infectious diseases, such as smallpox, polio and measles. However, vaccines against some diseases, including HIV-1, influenza and malaria, don’t work very well, and one reason could be the timing of antigen and adjuvant presentation to the immune system. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Sciencedeveloped an...
Experimental, precision strategy targets unique cancer protein found in certain acute myeloid leukemia cases
Lab study shows promise of aiming genetically engineered T-cell therapy at a gene fusion. Precision immunotherapies that aim the power of the body’s soldier cells at cancer have revolutionized the care of certain types of leukemia. But not all types — yet. New research by a team from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center is helping...
Researchers develop tissue engineering platform technology for joint tissue regeneration
A research team led by Professor Kim Gyo-beom of Dongguk University’s Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering has developed the latest technology for joint tissue regeneration via simultaneous delivery of therapeutic growth factors and adi-pose derived stem cells into the body. The work was published in the Journal of Controlled Release (Impact Factor: 7.727, JCR...
Study uncovers new markers present on melanoma tumors
by Emily Henderson, B.Sc.Sep 16 2020 A collaborative study led by Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute and the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute (ONJCRI) has uncovered new markers (HLA-associated peptides) that are uniquely present on melanoma tumors and could pave the way for therapeutic vaccines to be developed in the fight against melanoma. Despite all improvements...
Anxiety disorders are linked to inflamed thyroid glands
Although antianxiety medications target the nervous system, one new study suggests that anxiety disorders may stem more from the endocrine system. A recent study looked at the relationship between anxiety and the thyroid gland. Most people have brief periods of anxiety from time to time, such as when they experience stressful situations in which the outcome is...
New gene implicated in neuron diseases
SCRIPPS RESEARCH INSTITUTE IMAGE: CLAUDIO JOAZEIRO, PHD, IS A PROFESSOR IN THE SCRIPPS RESEARCH DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE JUPITER, FL — Failures in a quality control system that protects protein-building fidelity in cells can lead to motor neuron degeneration and related diseases, according to a new study from an international team co-directed by Scripps Research...
A ‘cell-less’ therapy may regenerate heart tissue without cell transplant risks
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCE IMAGE: AN EXOSOME DERIVED FROM HEART CELLS GROWN FROM HUMAN INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM CELLS. THIS MATERIAL RELATES TO A PAPER THAT APPEARED IN THE SEP. 16, 2020, ISSUE OF SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL. Ling Gao and colleagues have developed a strategy that uses exosomes – tiny membrane-bound sacs secreted by cells –...