Advances in 3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, are capturing attention in the health care field because of their potential to improve treatment for certain medical conditions. A radiologist, for instance, might create an exact replica of a patient’s spine to help plan a surgery; a dentist could scan a broken tooth to make a...
Bench Scientists Discover a New T-cell
Posted by Kathleen Hoffman Something unusual happened when Professor Andrew Sewell and the T-Cell Modulation Group at the University of Cardiff put the blood of a healthy donor in a petri dish with some cancer cells. What grew in the blood was a T-cell that no one had seen before. This T-cell attacked the cancer cells...
A small switch with a big impact
UNIVERSITY OF WÜRZBURG T cells play a key role in the human immune system. They are capable of distinguishing diseased or foreign tissue from the body’s own, healthy tissue with great accuracy; they are capable of triggering the actions necessary to fight off the troublemakers. The details of this immune response are manifold and the...
Diagnosing COVID-19 in just 30 minutes
POHANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (POSTECH) IMAGE: THE REACTION IS COMPOSED OF FOUR MAIN COMPONENTS: A SET OF PROBES, SPLINTR LIGASE, T7 RNA POLYMERASE AND A FLUOROGENIC DYE. IN THE PRESENCE OF TARGET RNA, HYBRIDIZATION, LIGATION, TRANSCRIPTION. The year 2020 can be summarized simply by one word – COVID-19 – as it was the...
Promising breath-test for cancer
FLINDERS UNIVERSITY IMAGE: FLINDERS UNIVERSITY CANCER RESEARCHER DR. ROGER YAZBEK. The global quest to use a person’s breath analysis for rapid, inexpensive and accurate early-stage testing for cancer and other diseases has taken a leap forward. In a new paper in the British Journal of Cancer, Flinders University researchers have reported significant progress in developing a method to...
80-year-old antibiotic redesigned for new medical uses
UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO IMAGE: PINK COLOR HIGHLIGHTS THE LOCATIONS OF SIX AMINO ACIDS THAT WERE ALTERED IN THE SYNTHESIZED VERSIONS OF THE GRAMICIDIN A MOLECULE. A TEAM FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO DEPARTMENT OF. Physicians and scientists have long searched the natural world for chemicals that can improve human health. However, evolutionary selection optimized natural...
A multishot lens less camera in development could aid in disease diagnosis
Researchers at Penn State are developing a new type of imaging that does not require a lens and uses reconfigurable particle-based masks to take multiple shots of an object. The technology is expected to have used in lower-cost and faster disease diagnosis and the enhancement of optical microscopy and may lead to thinner cellphone technology. The research is supported by...
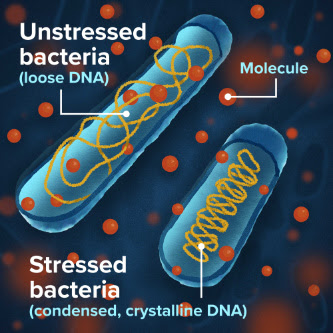
A route to better antibiotics: understanding ‘stressed bacteria’
Doctors often treat ear infections, strep throat, and urinary tract infections with antibiotics that kill the bacteria causing these infections. Sometimes, however, bacteria mount strong responses to stressors such as antibiotics, allowing these “stressed” bacteria to survive. This is especially the case when a person takes multiple antibiotics. Understanding the mechanisms behind bacteria’s responses is...
Sensor Rapidly Detects SARS-CoV-2, Antibodies, and Inflammatory Markers
Researchers at Caltech have developed a low-cost multiplex test that can rapidly provide three different types of data on COVID-19. The test can detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2, antibodies against the virus (potentially indicating a level of immunity), and inflammatory markers that could indicate the severity of COVID-19. Using blood or saliva, the test can provide...
Nanoparticles can turn off genes in bone marrow cells
Using specialized nanoparticles, MIT engineers have developed a way to turn off specific genes in cells of the bone marrow, which play an important role in producing blood cells. These particles could be tailored to help treat heart disease or to boost the yield of stem cells in patients who need stem cell transplants, the researchers say....