by Jennifer Brown, University of Iowa Calvin Carter and Sunny Huang (pictured in their lab at the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine) may have discovered a safe new way to manage blood sugar non-invasively using electromagnetic fields (EMFs). Their findings, published in Cell Metabolism, show that exposing diabetic mice to a combination of static...
Evidence of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and MND in brains of young people exposed to dirty air
by Lancaster University Researchers looking at the brainstems of children and young adults exposed lifelong to air pollution in Mexico City have discovered disturbing evidence of harm. Previous studies have linked fine particulate air pollution exposure with Alzheimer’s disease, and researchers have also reported evidence of air pollution-derived nanoparticles in the frontal cortex of the brain. But after examining...
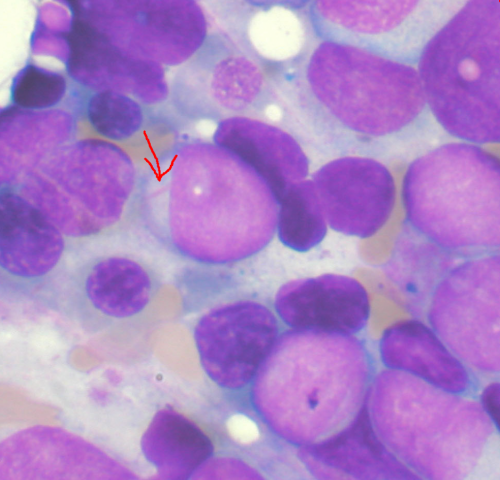
Researchers discover drug resistance mechanism in leukemia, identify treatment strategy
by Temple University Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia. Several blasts have Auer rods. Like packaging designed to create a protective environment around a product, the mix of cells and fluids immediately surrounding human bone marrow provides critical protective and nourishing conditions for hematopoietic—or bone marrow-originating—stem cells. Immune cells and other specialized components native to...
New research supports sofosbuvir in combination with other antivirals for COVID-19
by Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science This figure shows that there is substantially more cleavage of Remdesivir-RNA (g, h, i) than Sofosbuvir-RNA (a, b, c) by SARS-CoV-2 exonuclease. It is also apparent that Remdesivir-RNA (g, h, i) is cleaved by the exonuclease more rapidly than RNA extended with UMP (d, e, f). The...
‘Brain fog’ following COVID-19 recovery may indicate PTSD
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – LOS ANGELES HEALTH SCIENCES IMAGE: DR. ANDREW LEVINE A new report suggests that lingering “brain fog” and other neurological symptoms after COVID -19 recovery may be due to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), an effect observed in past human coronavirus outbreaks such as SARS and MERS. People who have recovered from COVID-19...
Study finds odor-sensing neuron regeneration process is adaptive
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO ANSCHUTZ MEDICAL CAMPUS AURORA, Colo. — Olfactory sensory neurons are nasal neurons that make use of hundreds of different types of odorant receptors to analyze odorous chemicals in our external world and send that information to our brain. These neurons have the unusual ability to undergo turnover throughout life – a process...
US Insulin prices 8 times higher than in other nations
RAND CORPORATION Insulin prices are more than eight times higher in the United States than in 32 high-income comparison nations combined, according to a new RAND Corporation study. The study compared how much different types of insulin sold in the U.S. would cost if bought at prices in other countries. The average price per unit...
Study identifies brain cells most affected by epilepsy and new targets for their treatment
by University of Copenhagen Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological diseases. It is caused by a malfunction in brain cells and is usually treated with medicines that control or counteract the seizures. Scientists from the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen and Rigshospitalet have now identified the exact neurons that are most affected...
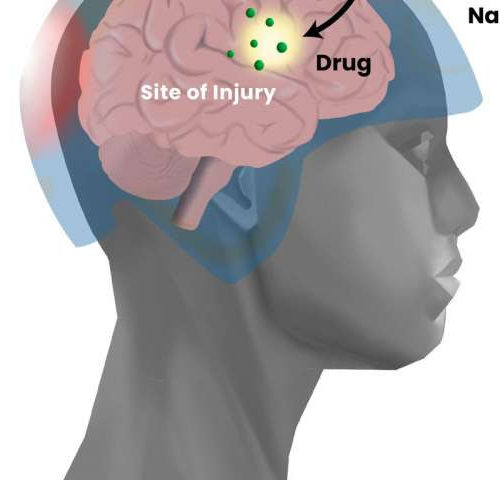
Development of precision drug delivery tool to treat traumatic brain injury
by Alexandra Demetriou, University of Southern California USC scientists have developed an experimental precision treatment for traumatic brain injury (TBI) that involves trapping therapeutic drugs in nanocage carriers before administering treatment. Near-infrared (NIR) light can safely penetrate the skull, and it can be used to “open” the nanocage to release drugs at the site of brain...
New therapeutic target identified for rare virus-associated lymphomas
by Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research Targeting a “cell survival” protein could be a valuable new approach to treating certain blood cancers associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), according to research resulting from a collaboration between scientists at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, Australia and the University of Birmingham, UK. The research team discovered that the protein BCL-XL...