AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF SCIENCE IMAGE: A SCHEMATIC SHOWING THE BIMODAL NEUROMODULATION DEVICE. WIRELESS HEADPHONES DELIVERED SOUNDS, WHILE A SMALL ELECTRODE ARRAY STIMULATED THE TONGUE WITH DIFFERENT PATTERNS. THIS MATERIAL RELATES TO A PAPER THAT APPEARED. A device that stimulates the ears and tongue substantially reduced the severity of tinnitus symptoms in 326...
MIT SCIENTISTS MAKING KEY PROGRESS ON UNIVERSAL FLU VACCINE
BY DAN ROBITZSKI MIT scientists just made important progress toward a universal flu vaccine — an inoculation against all influenza viruses at once. When we’re vaccinated against a flu, our immune system generates antibodies that target a protein on the virus called hemagglutinin (HA). It turns out that the difference between a seasonal flu shot...
Fusing cytokines with antibodies found to be effective at treating brain tumors in mice
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress Graphical abstract of immunocytokines for the treatment of glioblastoma. A team of researchers from University Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology and biotechnology company Philochem, has found fusing cytokines with antibodies to be an effective treatment for glioblastoma in mice. In their paper published...
Genetic study reveals ancestry-specific risk factors for coronary artery disease
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress A large team of researchers affiliated with a host of institutions across Japan has identified multiple loci associated with ancestry-specific risk factors for coronary artery disease. In their paper published in the journal Nature Genetics, the group describes their analysis of genetic information from several publicly available databases and its results. Coronary...
Coronavirus antibodies last at least three months after infection, study suggests
by University of Toronto Coronavirus antibodies can last at least three months after a person becomes infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a new study published Thursday in Science Immunology. Coronavirus antibodies can last at least three months after a person becomes infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a new study...
Inhibiting epileptic activity in the brain
by University of Illinois at Chicago The DUSP4 protein is located on the border between epileptic and non-epileptic brain tissue Epileptic seizures often originate in small, localized areas of the brain where neurons abnormally fire in unison. These electrical impulses disrupt proper brain functioning and cause seizures. But what makes regions where seizures start different from...
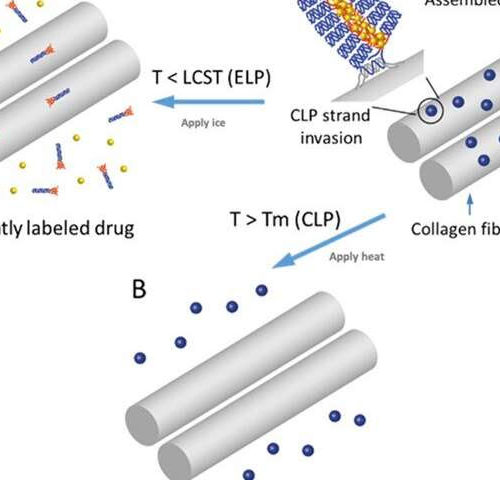
Researchers advance drug delivery systems to treat connective tissue disorders
by Karen B. Roberts, University of Delaware University of Delaware Professor Kristi Kiick is leading collaborative research to create new drug delivery systems with the potential to improve treatment for diseases that affect connective tissues, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, which is an autoimmune disease. The UD researchers have devised tiny cargo-carrying systems many times smaller than a human...
Research pinpoints sources of atrial fibrillation
by Amy Colgan, The Ohio State University People who suffer from persistent atrial fibrillation in the heart may find relief from a new treatment approach discovered by researchers at The Ohio State University Davis Heart and Lung Research Institute. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heartbeat, or a condition in which the atria fail to contract in a strong, rhythmic way....
Potential COVID-19 vaccines not affected by dominant “G-strain”
by University of York 3D print of a spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19–in front of a 3D print of a SARS-CoV-2 virus particle. The spike protein (foreground) enables the virus to enter and infect human cells. On the virus model, the virus surface (blue) is covered with spike proteins (red) that enable...
New study sheds light on the best drug choices for some patients with advanced breast cancer
by Institute of Cancer Research Breast cancer cells. Patients with metastatic breast cancer carrying a particular mutation fare better on one form of hormone therapy than another and can be identified using a blood test, according to a new study. In a combined analysis of two major Phase III clinical trials, called SoFEA and EFECT, researchers were able to show...