by University Health Network Credit: CC0 Public Domain Princess Margaret scientists have revealed how stem cells are able to generate new blood cells throughout our life by looking at vast, uncharted regions of our genetic material that hold important clues to subtle biological changes in these cells. The finding, obtained from studying normal blood, can be...
New mechanism of pain control revealed
by Kyushu University Marked as concentrated yellow here, a unique population of astrocytes in the dorsal horn of the mouse spinal cord have been found to play a role in controlling pain. Credit: Kyushu University Researchers in Japan have revealed a previously unknown mechanism for pain control involving a newly identified group of cells in...
Survival protein may prevent collateral damage during cancer therapy
by Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research The cell survival protein BCL-XL may protect kidneys from damage caused by cancer therapies. Credit: Art of Science, Dr Michael Roy WEHI researchers have identified a protein that could protect the kidneys from ‘bystander’ damage caused by cancer therapies. The “cell survival protein,” called BCL-XL, was required in...
Quantum nanodiamonds may help detect disease earlier
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON IMAGE: AN ARTIST’S CONCEPTION OF NANODIAMONDS USED FOR IN VITRO DIAGNOSTICS. CREDIT: ELLA MARU STUDIO/ UCL The quantum sensing abilities of nanodiamonds can be used to improve the sensitivity of paper-based diagnostic tests, potentially allowing for earlier detection of diseases such as HIV, according to a study led by UCL researchers in...
Real-world neuroscience experiments show diversity in learning new motor skills
by Alana Cullen, Imperial College London Credit: Imperial College London Researchers at Imperial College London have shown how the whole body changes while learning new movement-based skills. By using a new data-driven approach to analyse full-body movement during motor learning in the real world, the researchers both demonstrated the involvement of the whole body in the learning process and identified...
Study is the first to link microbiota to dynamics of the human immune system
by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (From left) Researchers Emily Fontana, Luigi Amoretti, Joao Xavier, Roberta Wright, and Jonas Schluter in the lab. Credit: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center researchers have uncovered an important finding about the relationship between the microbiota and the immune system, showing for the first time that...
Protein commonly screened for in pregnancy is linked to gestational diabetes
by Jim Fessenden, University of Massachusetts Medical School Stained tissue showing changes in blood vessels in fat tissue between nonpregnant and pregnant women. Credit: R. Rojas-Rodriguez et al., Science Translational Medicine (2020) Laboratory research and analysis of epidemiological data by Silvia Corvera, MD, and Tiffany Moore Simas, MD, MPH, MEd, and colleagues show that low levels...
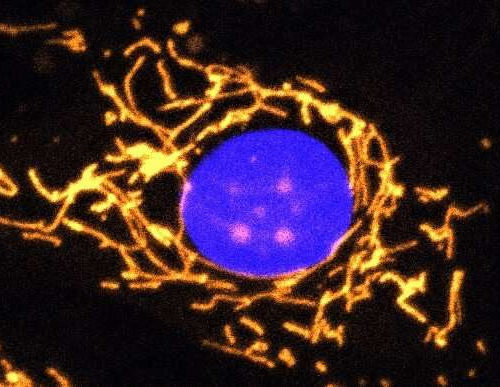
Scientists develop new gene therapy for eye disease
by Trinity College Dublin A fluorescent microscope image with mitochondria highlighted in gold. This healthy cell shows a highly elaborate and well-connected network of mitochondria. Credit: Professor Jane Farrar and Dr Daniel Maloney, Trinity College Dublin Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have developed a new gene therapy approach that offers promise for one day treating an...
Viruses shown to evolve as a result of different immune responses in different ethnic populations
Posted Today Differences in the cellular immune system in different human populations are now known to influence a virus’s evolution. A virus will adapt and may ultimately form subtypes to escape common antiviral immune responses. For the first time, in a paper published in Virus Evolution, Professor Astrid Iversen of the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences at...
Altered ‘coat’ disguises fatal brain virus from neutralizing antibodies
Posted Today A genetic modification in the ‘coat’ of a brain infection-causing virus may allow it to escape antibodies, according to Penn State College of Medicine researchers. They say testing people for this and other viral mutations may help identify patients at risk for developing a fatal brain disease. Dr. Aron Lukacher, professor and chair of the Department...