Hebrew University of Jerusalem Hebrew University study proposes a new model suggesting that disrupted RNA editing within pancreatic beta cells might initiate an inflammatory response akin to early-stage type 1 diabetes. This new perspective challenges the long-held belief of viral involvement, offering potential implications for treatments and cures. A recent study by researchers at the...
Will superintelligent AI sneak up on us? New study offers reassurance
Improvements in the performance of large language models such as ChatGPT are more predictable than they appear. Matthew Hutson Some researchers think that AI could eventually achieve general intelligence, matching and even exceeding humans on most tasks.Credit: Charles Taylor/Alamy Will an artificial intelligence (AI) superintelligence appear suddenly, or will scientists see it coming, and have...
Updated guidelines issued for management of anaphylaxis
by Elana Gotkine In a practice parameter update published online Dec. 17 in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, new guidelines are presented for the diagnosis and management of anaphylaxis. David B. K. Golden, M.D.C.M., from the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, and colleagues focused on seven areas with new evidence to...
Pet ownership may slow cognitive decline in older adults living alone
by Lori Solomon Pet ownership is associated with slower rates of cognitive decline among older adults living alone, according to a study published online Dec. 26 in JAMA Network Open. Yanzhi Li, Ph.D., from Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, China, and colleagues explored the association of pet ownership with cognitive decline among 7,945 participants (mean...
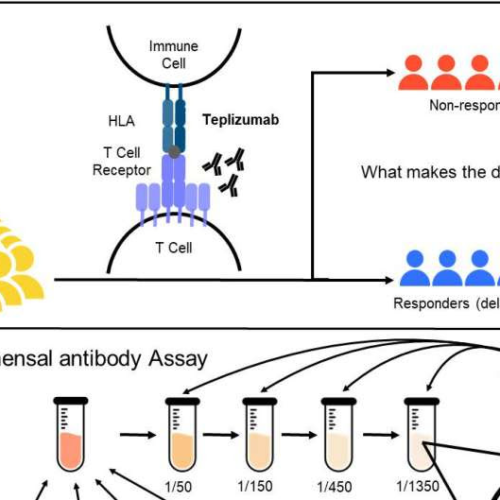
Gut microbes may determine patients’ response to a drug that delays onset of type 1 diabetes
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress Teplizumab delays type 1 diabetes (T1D) in at-risk individuals in TN10 trial, but participants respond differently to the treatment. Systemic, non-pathogenic antibody responses to gut bacteria can be quantified by anti-commensal antibody (ACAb) assay. Individuals with higher IgG2 responses to specific gut bacteria are more likely to get early...
Scientists use organoid model to identify potential new pancreatic cancer treatment
by Weill Cornell Medical College Perhexiline maleate induces cell death of human pancreatic cancer organoids. (Red: Cell death marker; Blue: DAPI). Credit: Xiaohua DuanA drug screening system that models cancers using lab-grown tissues called organoids has helped uncover a promising target for future pancreatic cancer treatments, according to a new study from researchers at Weill Cornell...
Researchers uncover unexpected molecular pattern in fragile X syndrome
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Credit: Cell (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.019Researchers have found new disrupted genes and an unexpected molecular pattern—dubbed BREACHes—related to fragile X syndrome (FXS), a genetic disorder estimated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to impact about 1 in 7,000 males about 1 in 11,000 females. The...
Artificial intelligence lowers the barrier to ultrasound brain disease treatment
by National Research Council of Science and Technology Simulation-Guided Navigation Systems Credit: Korea Institute of Science and TechnologyFocused ultrasound technology is a non-invasive treatment method that focuses ultrasound energy on a few millimeters of the brain, including deep regions, to treat neurological disorders without opening the skull. It has been applied to the treatment of various...
3D-printed chip showing body’s reaction to drugs could end need for animal tests
Andrew Gregory Health editor Scientists have developed a pioneering 3D-printed device that could speed up patient access to new medicines and eliminate the need for animal testing. Thousands of animals are used in the early stages of developing medicines worldwide every year, yet many drugs tested on animals do not end up showing any clinical...
Monoclonal Antibodies: A New Treatment for Long COVID?
Hallie Levine A treatment used to treat acute COVID-19 infection has also been found to be effective against long COVID, a new small study has found. The research, which assessed the benefits of monoclonal antibodies, suggests relief may finally be ahead for millions of Americans with long COVID for whom treatment has remained elusive. The...