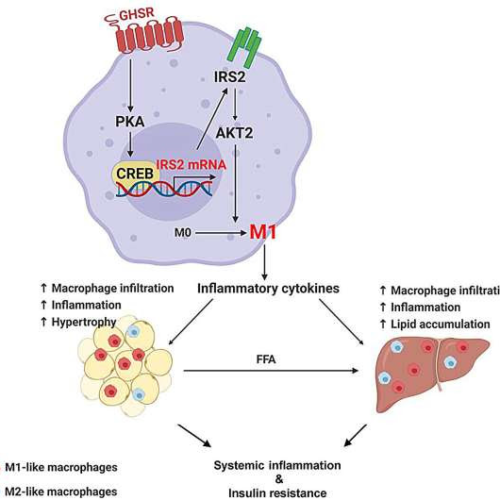
by Laura Muntean, Texas A&M University Credit: Molecular Metabolism (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101852A team comprised primarily of Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists has made an important discovery that could lead to a novel treatment for obesity and obesity-associated diseases or conditions. Details of the discovery can be found in the study “Nutrient-sensing growth hormone secretagogue receptor in...
Year: <span>2024</span>
Research into the nature of memory reveals how cells that store information are stabilized over time
by University at Buffalo Dheeraj Roy, Ph.D., assistant professor in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics in the Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences at UB, is a senior author on a new paper that explains aspects of how memory works at the cellular level. Credit: Sandra Kicman/Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical SciencesThink of...
Ketamine fueled actor Matthew Perry’s death, but new study says it may help others
by Eric Williamson, University of Virginia 10 ml vial of 1000 mg ketamine. Credit: Psychonaught/WikipediaKetamine has been in the headlines recently, implicated in the high-profile death of “Friends” actor Matthew Perry in October. But can the powerful drug also be helpful to those suffering from opioid addiction? A University of Virginia study shows evidence it can....
Wireless drug patch shows promise as chronic disease treatment delivery system
by David DeFusco, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine Spatiotemporal on-demand patch for wireless, active control of drug delivery. a Schematic illustration highlighting the construction of a wirelessly controlled spatiotemporal on-demand patch (SOP) for high-precision drug delivery. The SOP features two main components: (i) an array of drug-loaded microneedles protected by active...
How vaccines that target specific forms of cancer are showing great promise
by Tanner Stening, Northeastern University Mansoor Amiji, University Distinguished Professor in the Departments of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Chemical Engineering at Northeastern. Credit: Matthew Modoono/Northeastern UniversityOne of the great promises in the field of cancer immunotherapy is the emergence of cancer vaccines. Unlike traditional vaccines that are tailored to infectious diseases, cancer vaccines work by teaching the...
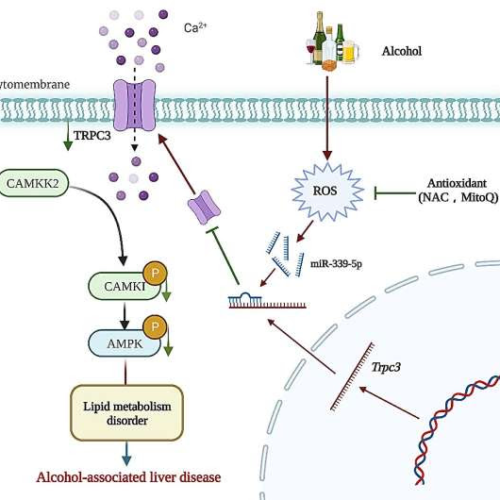
Hepatic TRPC3: An emerging regulator of alcohol-associated liver disease
by Higher Education Press The proposed model of hepatic TRPC3-regulated ALD. Credit: Qinchao Ding, Rui Guo, Liuyi Hao, Qing Song, Ai Fu, Shanglei Lai, Tiantian Xu, Hui Zhuge, Kaixin Chang, Yanli Chen, Haibin Wei, Daxi Ren, Zhaoli Sun, Zhenyuan Song, Xiaobing Dou, Songtao LiExcessive alcohol intake is strongly associated with alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) which...
How emotions influence what adolescents eat
by Rasmus Cloes, Leibniz-Institut für Präventionsforschung und Epidemiologie – BIPS Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A new study by the Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology—BIPS has investigated how emotional states influence the eating habits of children and adolescents and which interventions help to change unhealthy eating habits. The research focuses on the role of...
Caffeine: How quitting can benefit your health
by Adam Taylor, The Conversation Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Caffeine is the most consumed psychoactive compound in the world. Even if you don’t drink coffee or tea, you probably still regularly consume caffeine since it’s found in everything from fizzy drinks and cold remedies to decaf coffee and chocolate. When caffeine is consumed, it’s rapidly absorbed...
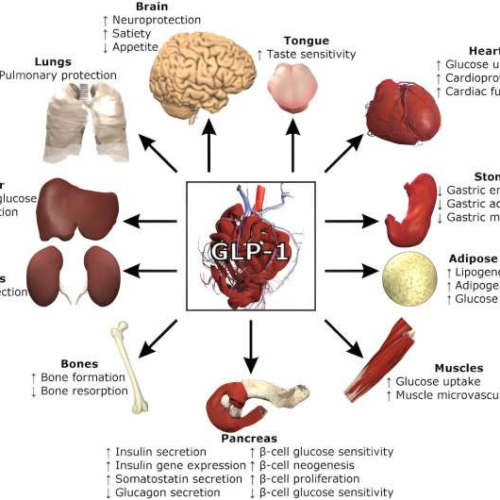
Your body has a built-in system that works like weight loss meds: Food and your gut microbiome
by Christopher Damman, The Conversation GLP-1 serves many functions in the body. Credit: Lthoms11/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SAWegovy, Ozempic and Mounjaro are weight loss and diabetes drugs that have made quite a splash in health news. They target regulatory pathways involved in both obesity and diabetes and are widely considered breakthroughs for weight loss and blood sugar...
‘Exhalation’ system improves symptoms for most common form of chronic sinus infections
by Meagan Raeke, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Mechanism of action of the EDS-FLU.EDS-FLU delivers medication using an EDS. The sealed-palate, bidirectional, “burst” biomechanics created by the EDS during use deposit topically acting anti-inflammatory high and deep in sinonasal drainage tracts and sinuses. The patient inserts the nosepiece into 1 nostril and...