ByREBECCA DYER (Marshall Pitman/Canva Pro)Using cannabis may cause changes in the human body’s epigenome, a study of over 1,000 adults suggests. The epigenome functions like a set of switches, activating or deactivating genes to change how our bodies function. “We observed associations between cumulative marijuana use and multiple epigenetic markers across time,” Lifang Hou, a...
Category: <span>Genetics</span>
Scientists discover new Achilles heel of leukemia cells
by Goethe University Frankfurt am Main Graphical abstract. Credit: iScience (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107844Leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children. Treatment involves intensive chemotherapy, which has severe side effects due to its non-specific mode of action. A team from the Department of Pediatrics and the Institute for Experimental Pediatric Hematology and Oncology at...
When cells touch, their genetics change: A new front in understanding cancer
by Olivia Trani, Virginia Commonwealth University Graphical abstract. Credit: Molecular Systems Biology (2023). DOI: 10.15252/msb.202311670The cells that make up our bodies are constantly communicating with each other, sometimes directly by physical touch. These interactions allow cells to respond to their neighbors, adapt to their surrounding environment and organize themselves into a fully functioning organism. Studying...
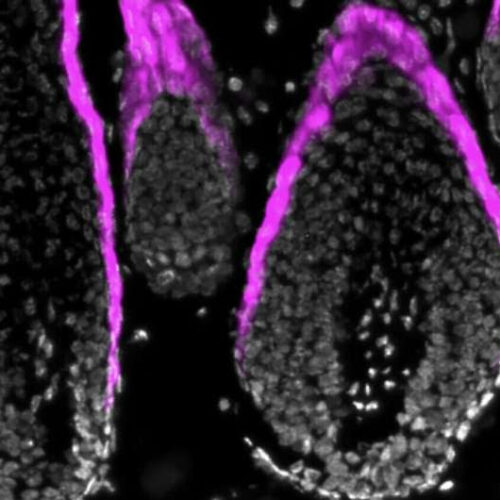
Discovery of hemoglobin in the epidermis sheds new light on our skin’s protective properties
by Elsevier Hemoglobin α (magenta) in mouse hair follicles during the growth phase of hair cycles. Credit: Umi Tahara, Takeshi Matsui, Keitaro Fukuda, and Masayuki AmagaiResearchers have shown for the first time that hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells where it binds oxygen, is also present in the epidermis, our skin’s outermost body...
Gene linked to persistent stuttering into adulthood uncovered
by Danielle Galvin, University of Melbourne Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new study led by University of Melbourne researchers has discovered a link between a new gene pathway and structural brain anomalies in some people who stutter into adulthood, opening up promising research avenues to enhance the understanding of persistent developmental stuttering. Published in the journal...
Genetic Therapies Bring Change to Neurology Clinics
Jim Kling PHOENIX – New therapies are on the horizon for genetic neuromuscular diseases, and this will raise both hopes for patients and challenges for neurologists. Following successful genetic treatments for ALS, hereditary amyloidosis, and spinal muscular atrophy, therapies for conditions like Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) neuropathy are set to change neurology practice, according to Nicolas Madigan,...
New research advances understanding of cancer risk in gene therapies
by University of York Landscape of somatic mutations in SCD. a, Dot-plot showing the number of mutations per HSPC for each patient plotted against the patient age at the time of sampling. SNV mutation burdens of individual HSPC colonies from before GT, with correction for coverage, are displayed per patient. Mean mutation burdens per individual are...
Gene finding provides new insights into pancreas development and helps search for type 1 diabetes cure
by University of Exeter Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Understanding how the human pancreas develops is crucial to allow scientists to make insulin producing–beta cells in the quest to cure type 1 diabetes. Now, scientists have made a unique and surprising discovery—a gene that is essential for making the pancreas in humans is not present in almost...
Microbubble gene therapy may protect against heart disease
by University of Hawaii at Manoa Credit: Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.07.032 Gene therapy has great promise for treating genetic diseases, and even for more common diseases such as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Over the past decade, the gene-editing technology CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)—a family of DNA sequences found...
Disrupting a single gene could improve CAR T cell immunotherapy, new study shows
by Jim Stallard, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain CAR T cell therapy, a powerful type of immunotherapy, has begun to revolutionize cancer treatment. Pioneered at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), the therapy involves engineering a patient’s T cells so they recognize and attack cancer cells. These CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T...