Peer-Reviewed Publication MAYO CLINIC With age, cells can experience senescence, a state where they stop growing but continue releasing inflammatory and tissue-degrading molecules. When a person is young, the immune system responds and eliminates senescent cells, often referred to as zombie cells. However, zombie cells linger and contribute to various age-related health problems and diseases....
Tag: <span>Aging</span>
Magnesium’s pivotal role in slowing aging’s impact
By Dr. Priyom Bose, Ph.D.Feb 13 2024Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Aging is associated with many biological, physiological, and psychological changes, some of which include a decline in cognitive function, greying of hair, frailty, and increased risk of contracting certain diseases. Aging also increases the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular...
T cells can be reprogrammed to fight aging
Cold Spring Harbor LaboratoryThe fountain of youth has eluded explorers for ages. It turns out the magic anti-aging elixir might have been inside us all along. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Corina Amor Vegas and colleagues have discovered that T cells can be reprogrammed to fight aging, so to speak. Given the right...
Could a drug prevent hearing loss from loud music and aging?
Peer-Reviewed PublicationUNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN FRANCISCO Could a Drug Prevent Hearing Loss from Loud Music and Aging?Researchers have found a gene that links deafness to cell death in the inner ear in humans – creating new opportunities for averting hearing loss. A person’s hearing can be damaged by loud noise, aging and even certain...
New roles for autophagy genes in cellular waste management and aging
Autophagy genes help extrude protein aggregates from neurons in the nematode C. elegans Peer-Reviewed Publication BUCK INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH ON AGING Autophagy, which declines with age, may hold more mysteries than researchers previously suspected. In the January 4th issue of Nature Aging, it was noted that scientists from the Buck Institute, Sanford Burnham Prebys and...
What happens to teeth as you age? And how can you extend the life of your smile?
A healthy smile helps us live long, well and happy lives. But just like our bodies, our teeth succumb to age-related changes. So what happens to teeth as you age? And what can you do to ensure your smile lasts the distance?First, what are teeth made of? The tooth crown is covered by a hard...
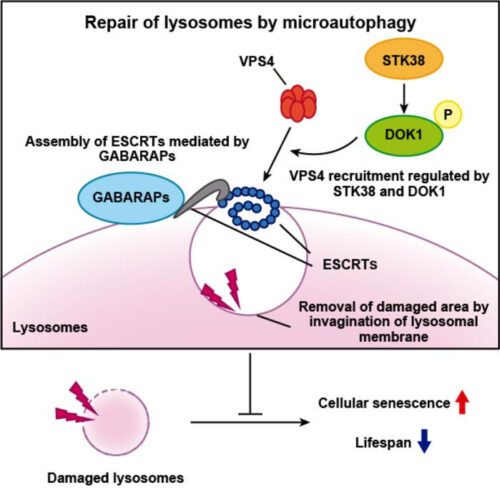
Microautophagy is essential for preventing aging
Researchers from Osaka University have shown for the first time that damaged lysosomes are repaired by a process called microautophagy, which is essential for preventing aging Peer-Reviewed Publication OSAKA UNIVERSITY OVERVIEW: LYSOSOMES ARE REPAIRED BY ESCRT-DRIVEN MICROAUTOPHAGY, AND STK38 AND GABARAPS ARE KEY REGULATORS OF THIS PROCESS BY RECRUITING ESCRTS TO LYSOSOMES. THESE REGULATORS ARE...
Researchers discover elevated spinal cord enzyme linked to motor neuron aging
by Justin Jackson , Medical Xpress Credit: CC0 Public Domain A research collaboration led by the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, investigated the role of CHIT1, a protein associated with microglia, in aging. In a paper, “CHIT1-positive microglia drive motor neuron aging in the primate spinal cord,” published in Nature, the group identifies...
Cancer stem cells trigger macrophage aging in mouse study
by Hokkaido University (Top) Cancer stem cells produce interleukin-6 (IL-6), which induces senescence in macrophages (Mφ). In turn, these produce arginase-1 and inactivate T cells. As a result, cancer cells are not killed by immune system cells, leading to tumor formation. (Bottom) Non-cancer stem cells do not produce IL-6. Macrophages do not age and T cells...
Blood factor can turn back time in the aging brain
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN FRANCISCO Blood Factor Can Turn Back Time in the Aging Brain Platelets are behind the cognitive benefits of young blood, exercise and the longevity hormone klotho In a remarkable convergence, scientists have discovered that the same blood factor is responsible for the cognitive enhancement that results from young blood transfusion, the...