Medscape Medical News > Features John Watson June 06, 2024 Celiac disease is a chronic, immune-mediated, systemic disorder caused by intolerance to gluten — a protein present in rye, barley, and wheat grains — that affects genetically predisposed individuals. Due to its wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, celiac disease resembles a multisystemic disorder. Its most...
Tag: <span>celiac disease</span>
Celiac disease: New findings on the effects of gluten
MAY 16, 2024 by Bielefeld University An electron transmission micrograph from the study shows the problematic peptide 33-mer DGP with spiky structures that can open the intestinal barrier. Credit: Bielefeld University Today is International Celiac Day. Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune condition that occurs in around 1% of the world’s population. It is triggered...
If a family member has celiac disease, you should get yourself tested
by University of Queensland Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainAn Australian-first study, published in the Medical Journal of Australia, has found significant prevalence of undiagnosed celiac disease among first degree relatives of people already diagnosed. The study findings support existing overseas recommendations for screening of first degree relatives for celiac disease. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder where...
Beyond the Gut: 7 Symptoms That May Mean You Have Celiac Disease
Written by Jennifer Robertson, MD, MSEd, NBHWC | Reviewed by Patricia Pinto-Garcia, MD, MPH Published on December 15, 2022 Key takeaways: The best-known symptoms of celiac disease include diarrhea, stomach pain, weight loss, and bloating. Celiac disease can cause symptoms beyond the gut. Most people with celiac disease experience additional symptoms, like headaches, rashes, mood...
Psoriasis tied to elevated risk for celiac disease
by Lori Solomon Individuals with psoriasis have double the odds of having celiac disease (CD) versus individuals without psoriasis, according to a research letter published online Feb. 9 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Marina Z. Joel, from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, and colleagues examined the association between psoriasis and...
Serological test signals viral triggers of diseases like diabetes and celiac disease
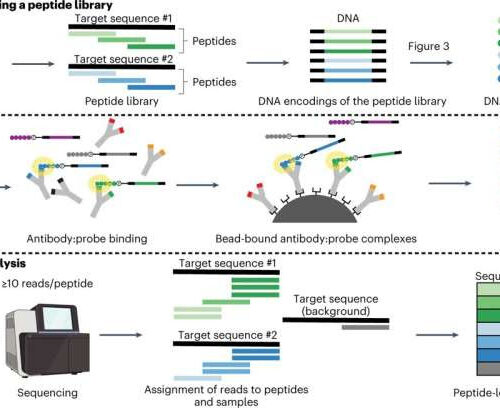
by Northern Arizona University Overview of protocol. a, Design of a peptide library begins with a set of target protein sequences. An informatic approach (such as the combined sliding-window/set-cover algorithm described in the ‘Design of peptide-encoding oligonucleotides’ section of ‘Experimental design’) is then used to design a library of peptides of a user-defined length that...
Not just ‘Gluten-sensitive’: What people with celiac disease want you to know
by Dennis Thompson Hayden Bishop can’t help but feel terribly self-conscious when she goes out to eat with friends and family. Bishop has celiac disease, a serious autoimmune disorder in which even the least exposure to gluten creates an antibody response that damages the small intestine, resulting in debilitating symptoms. Unfortunately, the gluten-free diet fad has led...
New drug shows real promise against celiac disease
by Amy Norton An experimental drug can prevent intestinal damage caused by celiac disease, an early trial has found—raising hopes that it could become the first medication for the serious digestive disorder. With celiac disease, the immune system attacks the lining of the small intestine when a genetically susceptible person eats gluten—a protein found in...
Celiac disease might be cured by restoring immune tolerance to gliadin
UNIVERSITY OF HELSINKI Celiac disease affects 0.3-2.4% of people in most countries world-wide, and approx. 2% in Finland. Celiac patients suffer from a variety of symptoms, typically intestinal complaints, such as diarrhea, but are often symptom-free. Immunologist Tobias Freitag co-developed and tested nanoparticles containing gliadin for the immunomodulatory treatment of celiac disease in Professor Seppo...
Bacterial link in celiac disease
MONASH UNIVERSITY Bacterial exposure has been identified as a potential environmental risk factor in developing coeliac disease, a hereditary autoimmune-like condition that affects about one in 70 Australians. It is estimated that half of all Australians are born with one of two genes that cause coeliac disease, and approximately one in 40 are likely to...
- 1
- 2