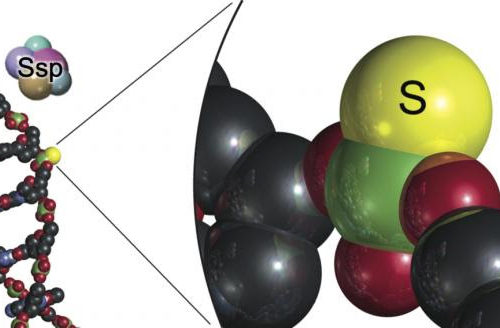
Groundbreaking discovery explains why some bacteria have been able to defend against phage therapy, and opens new ways for the medical community to overcome existing challenges Singapore, 6 May 2020 – Researchers from Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, have discovered a new anti-phage defence mechanism found in some...
Tag: <span>DNA</span>
Interleukin-12 electroporation may sensitize ‘cold’ melanomas to immunotherapies
by American Association for Cancer Research Combining intratumoral electroporation of interleukin-12 (IL-12) DNA (tavokinogene telseplasmid, or TAVO) with the immune checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab (Keytruda) led to clinical responses in patients with immunologically quiescent advanced melanoma, according to results from a phase II trial published in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for...
A portable, reusable test for COVID-19
by University of Utah “Testing, testing, testing.” It’s a mantra that health officials have been constantly promoting because screening people for COVID-19 is the best way to contain its spread. In the U.S., however, that crucial necessity has been hampered due to a lack of supplies. But University of Utah electrical and computer engineering professor...
Research team develops vaccine platform applicable to viruses
by National Research Council of Science & Technology Bang Eun-kyoung(left) from the KIST’s Center for Neuro-Medicine are discussing the efficacy of RNA stabilizer containing zinc complex. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) MERS, which struck South Korea in a 2015 outbreak, was caused by a coronavirus, the same family of viruses that is...
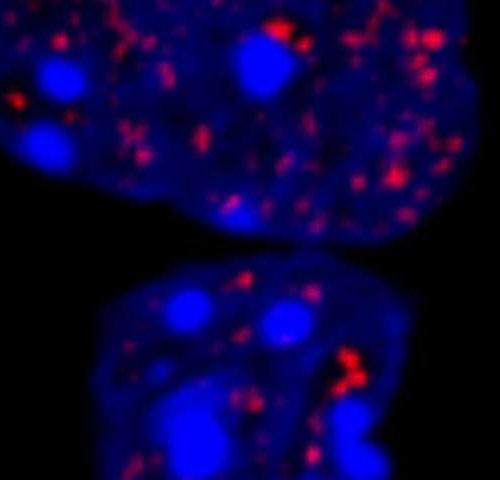
Unexpectedly potent protein droplets help explain hereditary diseases
by Max Planck Society Microscopic image of cell nuclei of cultured cells. HOXD13 condensates are labelled in red. The DNA is stained in blue. Credit: MPI f. Molecular Genetics/ Shaon Basu Repeats of individual building blocks within proteins are the cause of many hereditary diseases, but how such repeats actually cause disease is still largely...
Portable, reusable coronavirus sensor produces results within a minute
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc “Testing, testing, testing.” It’s a mantra that health officials have been constantly promoting because screening people for COVID-19 is the best way to contain its spread. In the U.S., however, that crucial necessity has been hampered due to a lack of supplies. But University of Utah electrical and computer engineering...
Molecules identified that reverse cellular aging process
By Nick Lavars Central to a lot of scientific research into aging are tiny caps on the ends of our chromosomes called telomeres. These protective sequences of DNA grow a little shorter each time a cell divides, but by intervening in this process, researchers hope to one day regulate the process of aging and the...
Scientists uncover a gene that doubles the risk of developing several neurodegenerative diseases
by HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology Richard M. Myers, PhD, and Nicholas Cochran, PhD, in the Myers Lab at HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology. Credit: HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology Scientists at the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), and the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB), have identified a new risk factor...
Scientists recreate DNA damage caused by toxins from smoking
CREDIT: PHIL ROBERTS Researchers from the University of York have recreated how toxins from smoking cause unique patterns of DNA damage. The discovery could help scientists better understand the cause of bladder cancer and the link to smoking. The causes of bladder cancer remain largely unknown, however smoking is seen as the main risk factor...
Breast cancer drug slows prostate cancer progression in major trial
By Nick Lavars Scientists are reporting some promising findings from a large prostate cancer trial, where patients were administered a drug typically used to treat breast cancer. The drug proved more effective than standard hormone treatments at applying the brakes to the disease, with the scientists hopeful it can lead to approval this year of...