According to an international group of researchers including a team from the University of Liverpool, patients experience 30% fewer side effects when medication doses are tailored to their DNA. The group’s study, published in The Lancet, is the first to demonstrate the practical application of using a panel of genes to tailor drug prescription to...
Tag: <span>DNA</span>
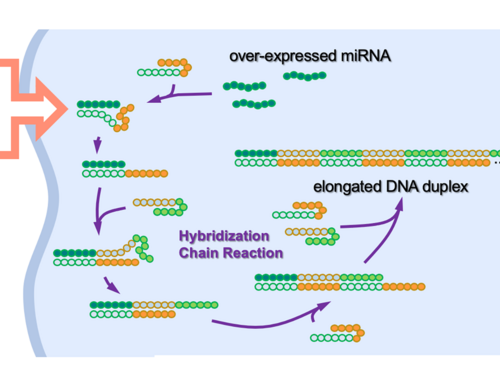
Artificial DNA kills cancer
UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO IMAGE: ONCOLYTIC DNA HAIRPIN PAIRS (OHPS) ARE INTRODUCED TO THE CANCER CELL. WHEN THE OHPS ENCOUNTER THE TUMOR-CAUSING OVEREXPRESSED MICRORNA (MIRNA), THEY UNRAVEL TO CONNECT WITH THE MIRNA AND EACH OTHER TO FORM LONGER DNA STRANDS. THESE ELONGATED STRANDS THEN TRIGGER AN IMMUNE RESPONSE, THE BODY’S BUILT-IN DEFENSE MECHANISM, WHICH INHIBITS FURTHER...
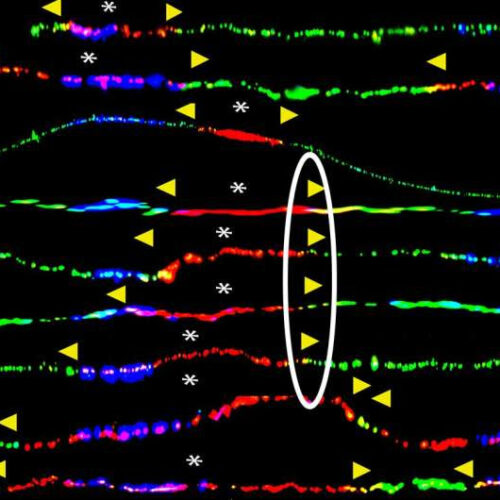
Faulty DNA repair may lead to BRCA-linked cancers
by Weill Cornell Medical College Stalled replication forks (yellow arrows) are detected at the BRCA1 gene in cells containing a BRCA1 germline mutation. Credit: Weill Cornell Medicine Error-prone DNA replication and repair may lead to mutations and cancer in individuals who inherit a mutant copy of the BRCA1 gene, according to a new study by...
Study of over five million people’s DNA reveals genetic links to height
by Queen Mary, University of London Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The study, published today (12 October) in Nature, is the largest ever genome-wide association study, using the DNA of over 5 million people from 281 contributing studies. It plugs a sizeable gap in our understanding of how our genetic differences account for differences in height. Over...
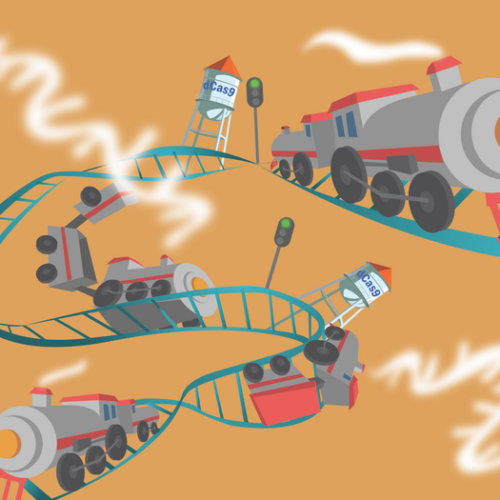
Synthetic tools conduct messages from station to station in DNA
RICE UNIVERSITY IMAGE: RICE UNIVERSITY BIOENGINEERS ARE USING DEACTIVATED CAS9 PROTEINS TO TARGET KEY SEGMENTS OF THE HUMAN GENOME AND SYNTHETICALLY TRIGGER THE TRANSCRIPTION OF HUMAN GENES. CREDIT: ILLUSTRATION BY SOFIA ESCOBAR/RICE UNIVERSITY HOUSTON – (July 18, 2022) – Rice University researchers have demonstrated that CRISPR-Cas9, increasingly famous as a gene-editing tool, can be employed in...
Matching drugs to DNA is ‘new era of medicine’
By James GallagherHealth and science correspondent Published19 hours ago IMAGE SOURCE, GETTY IMAGES We have the technology to start a new era in medicine by precisely matching drugs to people’s genetic code, a major report says. Some drugs are completely ineffective or become deadly because of subtle differences in how our bodies function. The British...
Fastest DNA sequencing technique helps undiagnosed patients find answers in mere hours
A research effort led by Stanford scientists set the first Guinness World Record for the fastest DNA sequencing technique, which was used to sequence a human genome in just 5 hours and 2 minutes. A new ultra-rapid genome sequencing approach developed by Stanford Medicine scientists and their collaborators was used to diagnose rare genetic diseases in an...
Research team identifies new mechanism for protecting DNA
Discovery offers hope to better understand how diseases like cancer, premature aging can be prevented. Researchers from Case Western Reserve University have identified a new mechanism by which a protein known for repairing damaged DNA also protects the integrity of DNA by preserving its structural shape. The discovery, involving the protein 53BP1, offers insight into understanding how...
Secondary structures in DNA are associated with cancer
by Lila Reynolds, Northwestern University Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new cancer study reports that DNA manifested as knot-like folds and third rungs between DNA’s two strands may drive cancer development, and an important regulatory enzyme could be associated with the formation of these unusual structures. Scientists from Northwestern Medicine and the La Jolla Institute for...
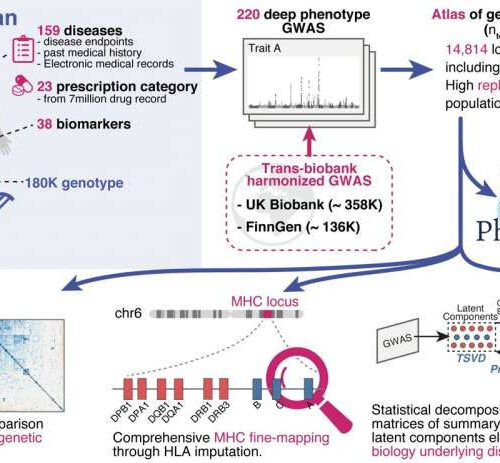
Redefining human diseases through the lens of DNA
by Osaka University Fig.1 Overview of this study. We performed 220 deep-phenotype genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in BioBank Japan, then performed trans-biobank meta-analyses with UK Biobank and FinnGen (ntotal = 628,000). As downstream analyses, we performed (i) cross-population comparisons of pleiotropy and genetic correlations, (ii) comprehensive HLA fine-mapping, and (iii) statistical decomposition of a matrix...