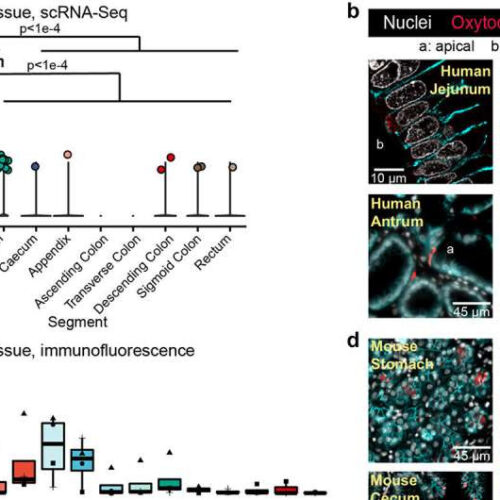
by Baylor College of Medicine Oxytocin expression and production in the epithelium of the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. a) log normalized counts of oxytocin expression in human intestinal epithelial cells reported by the scRNA-Seq data from the Gut Cell Atlas.Citation32 Significance values reflect the number of rarefactions (of 10,000) in which the comparison had a...
Tag: <span>Gut bacteria</span>
Study links specific gut bacteria to increased risk of severe malaria
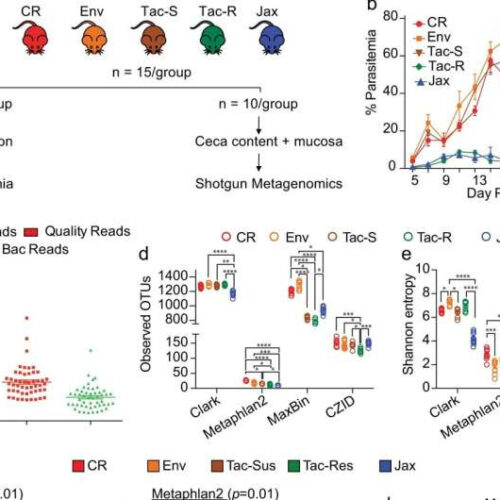
by Indiana University Shotgun metagenomics revealed distinct gut microbiota composition and genetic potential within and between the hyperparasitemia resistant and susceptible mice. a C57BL/6 mice were acquired from four different vendors (N = 15/group): Charles River Laboratories (CR), Envigo (Env), Taconic Biosciences (Tac), and Jackson Laboratory (Jax). Mice from Taconic Biosciences were obtained from two different facilities with...
Study shows engineered gut bacteria can treat hypertension
The finding from scientists at The University of Toledo opens new doors in the pursuit of harnessing our body’s own microbiome to regulate blood pressure Peer-Reviewed Publication UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO DR. BINA JOE, A DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR AND CHAIR OF THE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY IN THE UTOLEDO COLLEGE OF MEDICINE AND LIFE SCIENCES,...
Gut bacteria may help protect against heart disease, gout
The gut microbiome may influence heart health, research shows. Laura Herrera/Stocksy Over the past few years, researchers have discovered more details on how the body’s gut microbiome affects its overall health. An unhealthy gut microbiome, for example, has been linked to a variety of diseases. Researchers from the University of Wisconsin–Madison have now identified specific bacteria in the...
Helping ‘good’ gut bacteria and clearing out the ‘bad’ — all in one treatment
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome or restore populations of “good bacteria” after a heavy course of antibiotics. But now, they could also be used as an effective treatment strategy for certain intestinal diseases, such as Crohn’s disease. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a microgel delivery system for probiotics that keeps...
Common Gut Bacteria Linked to Parkinson’s Disease
Megan Brooks May 12, 2023 A common gut bacteria may play a role in the development of Parkinson’s disease (PD) by causing aggregation of the alpha-synuclein protein, a key feature in the pathology of PD, a small study suggests. Environmental factors as well as genetics are also suspected to play a role in PD etiology, although the exact cause...
Scientists identify compounds that reduce the harmful side effects of antibiotics on gut bacteria
by European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases A medical illustration of Clostridioides difficile bacteria, formerly known as Clostridium difficile, presented in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) publication entitled, Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. Credit: CDC Antibiotics help to fight bacterial infections, but they can also harm the...
GUT BACTERIA DISCOVERY COULD BRING NEW PROBIOTICS
The microbes that inhabit the gut are critical for human health. Understanding the factors that encourage the growth of beneficial bacterial species—known as “good” bacteria—in the gut may enable medical interventions that promote gut and overall human health. Specifically, the team discovered that one of the most abundant beneficial species found in the human gut...
Gut bacteria may play a role in diabetes
by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Correlations among abundance levels of 12 species associated with insulin homeostasis traits or dysglycemia. Correlation coefficients are displayed, with shades of red representing positive values and shades of blue representing negative values. The two clusters of species are outlined with squares. *P < 0.05 and >0.01; **P < 0.01 and ≥0.0001;...
COVID-19 virus increases risk for other infections by disrupting normal mix of gut bacteria
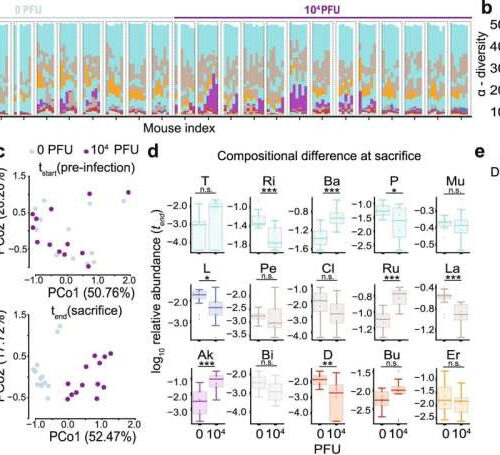
by NYU Langone Health SARS-CoV-2 infection causes gut microbiome alterations in mice. K18-hACE2 mice were infected intranasally with 0 or 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2. Fecal samples for microbiome analyses were collected daily from day 0 (before infection) until sacrifice; mice were sacrificed on days 5–7. Results show pooled data from three independent experiments with n = 3–5 mice...