by Institute of Science and Technology Austria Stem cells divide at the bottom of the intestinal crypts and the resulting cells are pushed upwards to the top pf the villi where they are discarded. Credit: © Shutterstock A special layer of cells that coats the insides of the small and large intestines takes in nutrients and...
Tag: <span>Gut</span>
In Colitis Patients, Skin Conditions May Originate in the Gut
A new study by UC San Francisco researchers reveals how gut inflammation can disrupt not only the digestive system, but also the skin. It’s a tale in which the main players are specialized immune cells and the bacterial communities – called microbiomes – that dwell within the gut and skin. Scientists have become increasingly aware that disturbances to the...
Fragile balance in the gut
LEIBNIZ INSTITUTE FOR NATURAL PRODUCT RESEARCH AND INFECTION BIOLOGY – HANS KNOELL INSTITUTE IMAGE: CANDIDA ALBICANS (YELLOW) FORMING HYPHAE ON DIFFERENTIATED INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS (NUCLEI IN BLUE AND F-ACTIN IN PURPLE). CREDIT: RAQUEL ALONSO-ROMAN / LEIBNIZ-HKI The presence of probiotics such as lactic acid bacteria changes the environment in the intestine and forces the yeast...
New study finds that the gut can hold important clues about concussions
by Houston Methodist Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A recently published study by Houston Methodist scientists suggests telltale signs of concussions might be found in the gut. By taking blood, stool and saliva samples from 33 Rice University football players, the researchers were able to examine the diagnostic potential of the gut’s microbiome. They say their...
How the gut communicates with the brain
by Flinders University Credit: Pixabay How the ‘second brain’ – the enteric nervous system in our gut—communicates with our first brain has been one of the most challenging questions faced by enteric neuroscientists, until now. New research from Flinders University has discovered how specialized cells within the gut can communicate with both the brain and spinal...
How food intake modifies the gut
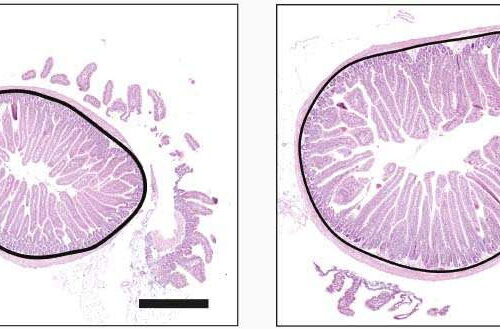
by University of Geneva Sections of mouse intestine. Up, a normal gut circumference (in black) and villi (pink convolutions). Bottom, expanded gut after overeating-induced obesity with a bigger circumference and longer villi. Credit: UNIGE / Mirko Trajkovski With more than 10% of the world’s population obese and 40% overweight, obesity constitutes one of the most...
Following your gut: The remarkable role of intestinal cells
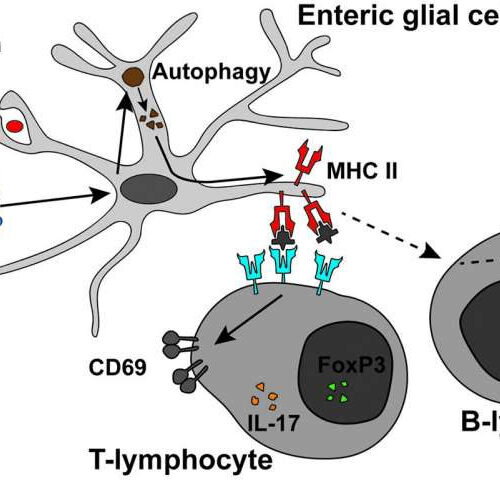
by Michigan State University This image is a 3-D volume rendering of a myenteric ganglion with enteric glia labeled in blue and MHC-II labeled in red. Credit: Aaron Chow and the Gulbransen Lab Food is essential for life—a daily source of calories and comfort. But for the more than 3 million adults in the United States...
Scientists reveal how vitamin A enters immune cells in the gut
by UT Southwestern Medical Center Dietary vitamin A becomes retinol, which is internalized into cells by LRP1 and promotes adaptive immunity in the intestine. Credit: Hooper Lab using BioRender.com / UT Southwestern Medical Center Immunologists and geneticists at UT Southwestern Medical Center have discovered how vitamin A enters immune cells in the intestines—findings that could offer...
Gut and heart signals affect how we see ourselves
by Anglia Ruskin University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain New research has discovered that the strength of the connection between our brain and internal organs is linked to how we feel about our appearance. Published in the journal Cortex, the study is the first to investigate, and first to identify, the association between body image and the brain’s processing of...
Gut to brain: Nerve cells detect what we eat
MAX-PLANCK-GESELLSCHAFT IMAGE: FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY IMAGE OF GENETICALLY DISTINCT NEURONS IN THE NODOSE GANGLION. CREDIT: MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR METABOLISM RESEARCH The gut and the brain communicate with each other in order to adapt satiety and blood sugar levels during food consumption. The vagus nerve is an important communicator between these two organs. Researchers from the Max...