by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have found more evidence that dry fasting (fasting without food or liquid intake) from dawn to dusk can play an important role in overall health. In a new study published in Metabolism Open, researchers found that fasting from dawn to dusk for four...
Tag: <span>Immune cells</span>
Researchers discover how immune cells prevent cognitive decline
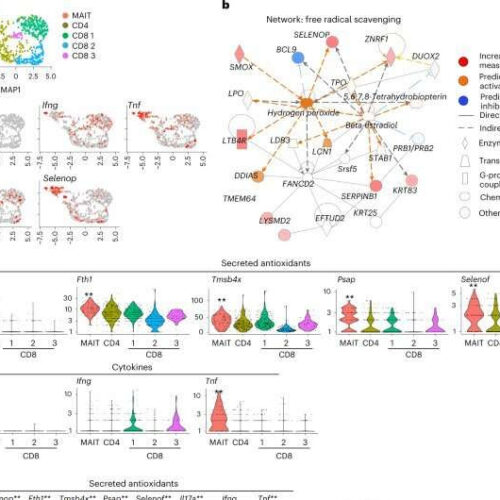
by Rutgers University MAIT cells express genes encoding secreted antioxidant molecules. Credit: Nature Immunology (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01349-1 Could the underproduction of poorly understood immune cells contribute to Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive decline? A Rutgers study in Nature Immunology suggests it may—and that increasing these cells could reverse the damage. Rutgers researchers deactivated the gene that produces...
Drug triggers immune cells to attack prostate cancer
by Julia Evangelou Strait, Washington University School of Medicine A drug compound stimulates immune cells to attack prostate tumors, according to new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Shown is a human prostate cancer organoid, a small 3D structure that serves as a model of prostate tumors. When the organoid is...
Immune cells in ALS patients can predict the course of the disease
by Karolinska Institutet Progression rate of newly diagnosed ALS patients. ALS patients were stratified by the proportion of T cell subsets in the blood (A) and cerebrospinal fluid (B) at the time of diagnosis. The longitudinal evolution of ALS functional rating scale-revised (ALSFRS-R) in relation to the baseline categories of T cell subsets is plotted...
Reprogramming of immune cells shown to fight off melanoma
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL IMAGE: ILLUSTRATION SHOWING HOW MINIATURE ARTIFICIAL PROTOCELLS LOADED WITH ANTI-MICRORNA-223 CARGO CAN REPROGRAM CANCER-ASSOCIATED MACROPHAGES IN LARVAL AND ADULT ZEBRAFISH LEADING THEM TO BE MORE PRO-INFLAMMATORY AND THUS ABLE TO DRIVE MELANOMA SHRINKAGE CREDIT: PACO LOPEZ CUEVAS A new way of reprogramming our immune cells to shrink or kill off cancer cells...
Potential melanoma target bypasses therapeutic resistance to immune checkpoint blockers
by Jeff Hansen, University of Alabama at Birmingham Constitutive activation of JAK1/2 in IFNγR1KO melanoma cells. a Identification of a JAK1/2-centric network of activated protein tyrosine kinases in IFNγR1KO cells by kinomic analysis. Input nodes (kinases) with large blue circles around them and smaller red circles on the top right corner indicate increased activity in IFNγR1KO cells. Arrowheads denote...
New checkpoint gene demonstrates ability to supercharge immune cells against cancer
by University of Minnesota Medical School Graphical abstract. Credit: Med (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.medj.2022.07.008 University of Minnesota researchers and their collaborators at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) investigated the role of a new intracellular checkpoint gene in regulating T-cell function against solid tumors. Known as CISH, the team published results in Med that show the checkpoint gene plays a key...
Immune cells engineered to battle cancer can be turned ‘on’ or ‘off’
by Boston University Credit: CC0 Public Domain The billions of immune cells that help protect us from diseases do amazing things, but sometimes they need a little boost. For decades, scientists have been trying to figure out ways to engineer living immune cells to better combat aggressive diseases, like cancer. One big, relatively recent advancement in...
New method detects gut microbes that activate immune cells
by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Cedars-Sinai investigators have developed a method to help identify which human gut microbes are most likely to contribute to a slew of inflammatory diseases like obesity, liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer and some neurological diseases. The technique, described in the peer-reviewed journal Science Translational Medicine, uses a protein...
Fast-acting immune cells provide powerful protection against stroke
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH IMAGE: XIAOMING HU, M.D., PH.D. CREDIT: XIAOMING HU PITTSBURGH, Aug. 1, 2022 – A unique subset of white blood cells confers fast-acting and lasting protection against ischemic stroke in mice, University of Pittsburgh neurologists and immunologists reported in the Journal of Clinical Investigation today. This study identified a novel subset of CD8+ regulatory-like T cells, or...