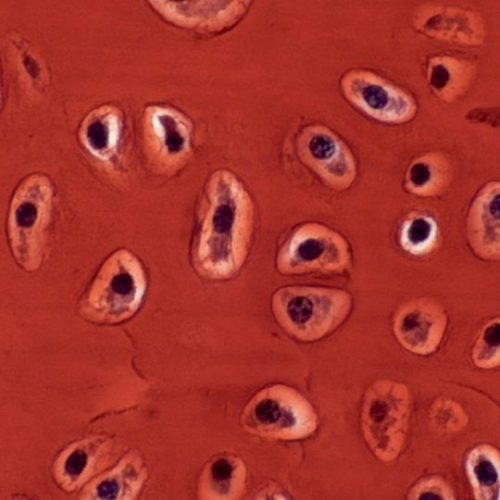
Researchers have found that adult skates have the ability to spontaneously repair injured cartilage, using a type of cartilage stem cell. Human cartilage has very limited capacity for repair, and the finding may lead to new stem cell treatments for human cartilage injuries. Published in the journal eLife, the study identified a new type of...
Tag: <span>Molecular therapy</span>
Scientists edge closer to treatment for myotonic dystrophy
by University of Nottingham untreated and treated with kinase inhibitors. Following treatment with inhibitors targeting CDK12 nuclear foci in DM1 cells are reduced. Credit: Dr. Ami Ketley , the University of Nottingham Scientists at the University of Nottingham have taken a step closer towards developing a treatment for the long-term genetic disorder, myotonic dystrophy. In...
A new therapeutic target against diseases caused by lipid accumulation in cells
by University of Barcelona Researchers from the University of Barcelona (UB) and the August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) found a new molecular mechanism involved in the regulation of cholesterol movement in cells, an essential process for proper cell functioning. The study, published in the journal Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, also identifies...
Scientists discover how the molecule-sorting station in our cells is formed and maintained
New mechanism to explain how the cell organelle that sorts and distributes substances entering a cell is formed and maintained TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE The cells in our body are workshops that continuously operate to produce and process substances to keep us going. When a substance enters a cell for processing, it is surrounded by...
Molecular gatekeepers that regulate calcium ions key to muscle function
CHILDREN’S NATIONAL HOSPITAL Calcium ions are essential to how muscles work effectively, playing a starring role in how and when muscles contract, tap energy stores to keep working and self-repair damage. Not only are calcium ions vital for the repair of injured muscle fibers, their controlled entry into the mitochondria, the cell’s energy powerhouses, spells...
Microbiome: Untapped source of novel antimicrobials
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress Just as Gold Rush prospectors once mined the Northern California hills for the shiny precious metal, “bioprospectors” are searching for a new prize: potential antimicrobial molecules—and they are hunting them down in the human microbiome. For nearly two decades scientists have been lifting the veil of mystery from the...
New study explains the molecular mechanism for the therapeutic effects of cilantro
Herbs, including cilantro, have long been used as folk remedies UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE Herbs, including cilantro, have a long history of use as folk medicine anticonvulsants. Until now, many of the underlying mechanisms of how the herbs worked remained unknown. In a new study, researchers uncovered the molecular action that enables cilantro to...
Researchers work on scientific foundation for new forms of therapy in neurodegenerative processes
Protective proteins that mitigate the destruction of nerve cells after a stroke can be administered into the brain through the nose, as Heidelberg University researchers demonstrated using a mouse model. The team led by Prof. Dr. Hilmar Bading at the Interdisciplinary Center for Neurosciences (IZN) is laying the scientific groundwork for new forms of therapy...
Molecular therapy set to protect at-risk patients against heart attack and stroke
A blood clot forming in the carotid artery. Even a single dose of a specific ribonucleic acid molecule, known as a small interfering RNA (siRNA), offers patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease long-lasting protection against high LDL cholesterol – one of the main risk factors for heart attack and stroke. This is the...