by Elana Gotkine Applying low-frequency bladder vibration (LFBV) to patients with spinal cord injury (SCI)/neurogenic bladder who developed urinary tract infections (UTIs) during rehabilitation is associated with a reduction in urinary leukocytes and urinary bacteria on day 10, according to a study recently published in International Urology and Nephrology. Yingying Zhang, from The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow...
Tag: <span>Spinal cord</span>
Spinal cord electrical stimulation restores neural function in clinical trial
by University of Pittsburgh Credit: CC0 Public Domain A new drug-free, minimally invasive intervention targets the root cause of progressive loss of neural function in spinal muscle atrophy (SMA), an inherited neuromuscular disease. An intervention, which involves electrical stimulation of the sensory spinal nerves, can gradually reawaken functionally silent motor neurons in the spinal cord and...
Fast-acting sub-perception therapy spinal cord stimulation found to reduce back pain
by Lori Solomon Patients with chronic pain treated with the novel Fast-Acting Sub-Perception Therapy (FAST) spinal cord stimulation (SCS) systems may achieve significant and durable pain relief for up to 12 months of follow-up, according to a study presented at the 23rd Annual Pain Medicine Meeting, a meeting of the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain...
Spinal cord stimulation vs medical management for chronic back and leg pain
JAMA Network OpenPeer-Reviewed Publication JAMA Network About The Study: This systematic review and network meta-analysis found that spinal cord stimulation therapies for treatment of chronic pain in back and/or lower extremities were associated with greater improvements in pain compared with conventional medical management. These findings highlight the potential of spinal cord stimulation therapies as an effective...
In experiment, electrical stimulation of the spinal cord helps a patient with Parkinson’s to walk
By Matthew Herper Marc, a 62-year-old who has had Parkinson’s for 30 years, received an experimental treatment that appeared to notably improve his ability to keep his balance and walk without freezing up. An experimental treatment that delivers an electrical current to the spinal cord appeared to notably improve the ability of a man with Parkinson’s...
Novel tool could help neuroscientists crack the secrets of spinal cord
Reviewed by Lily Ramsey, LLM Aug 7 2023 The spinal cord is harder to access and study than even the brain. The challenges posed by its mobility and anatomical structure have made understanding exactly how it functions difficult. Rice University engineers will work with collaborators to optimize an array of nanoelectronic threads, or NETs ⎯...
Novel research demonstrates new method of spinal cord tissue repair
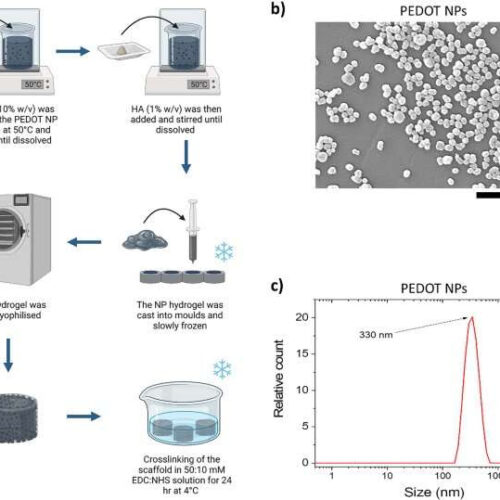
by University of Limerick a Synthesis schematic of gel:HA:PEDOT-NPs scaffolds. Incorporation of PEDOT NPs into Gel:HA hydrogel and processing by means of lyophilisation develops porous scaffolds, (image created with BioRender.com). b SEM images of synthesized PEDOT NPs. c DLS measurement of PEDOT NPs in the hydrodynamic state. Credit: Biomaterials Research (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s40824-022-00310-5 Unique new material developed...
Motor units in the spinal cord might be far more flexible than we thought
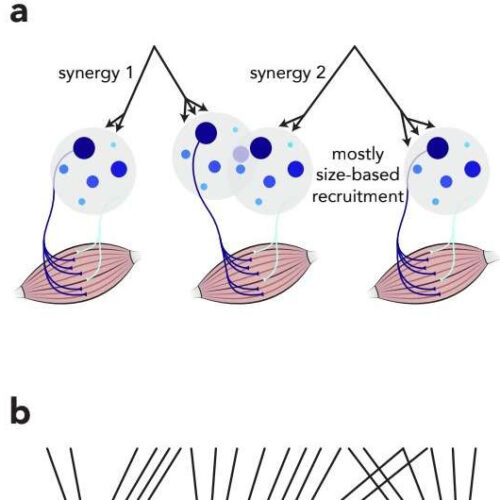
by Ingrid Fadelli, Medical Xpress Credit: Marshall et al, Nature Neuroscience (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-022-01165-8 When humans and other mammals perform voluntary movements, a series of neural processes take place. The cerebral cortex, the outer region of the brain, sends signals to motor units (i.e., neurons) in the spinal cord, which in turn activate individual muscles. Past neuroscience...
Improved understanding of early spinal cord development paves the way for new treatments
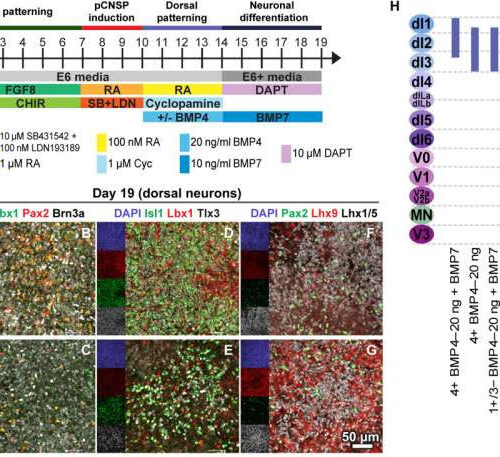
by Rebekah McBride, University of Wisconsin-Madison Addition of BMP7 during neuronal differentiation further dorsalizes postmitotic population. (A) Timeline of dorsal differentiation from H120-NMPs, with BMP7 added during neuronal differentiation phase from days 14 to 19. (B to G) Immunostaining in day 19 postmitotic cultures shows that DAPT treatment rapidly converts progenitors to dorsally shifted postmitotic phenotypes...
Epigenetic treatment in mice improves spinal cord regeneration after injury
by Public Library of Science Shown is an increased density of synapses (green) that contact motoneurons (purple) in the spinal cord of an injured animal after treatment with the small molecule TTK21-These are important for motor function. Credit: Franziska Mueller (CC-BY 4.0, creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) Currently, spinal cord injury does not have any effective treatments; physical rehabilitation can...