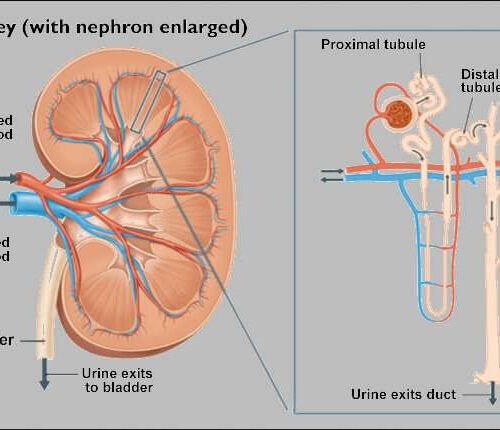
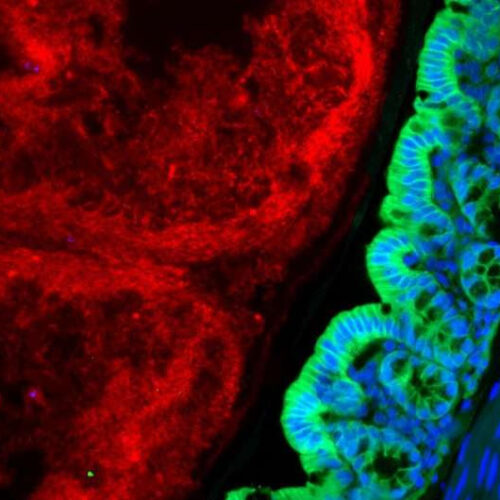
by University of Washington School of Medicine COVID-19 was found to directly invade proximal tubule cells in kidney organoids. Credit: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Up to 25 percent of patients’ COVID-19 cases involve acute kidney injury—the kidneys’ equivalent of a heart attack. Clinicians have suspected that such injuries are a...
Category: <span>Inflammation</span>
Link between intestinal inflammation and microbiome
by Kiel University Microscopic image of intestinal tissue. Green: epithelial cells which produce HK2. Red: bacteria inside the intestine. Credit: Saskia Weber-Stiehl, IKMB, Kiel University Around 500 to 1,000 different types of bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms colonize our intestines. All of them together form the intestinal microbiome. As we now know, these microbes play...
New therapy for acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis could potentially save lives
by Adam Pope, University of Alabama at Birmingham Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers with the University of Alabama at Birmingham Marnix E. Heersink School of Medicine have published a new study in PLOS ONE detailing a new therapy for acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or AE-IPF, that could potentially be lifesaving. Recent research studies have suggested...
Rheumatoid arthritis finding may lead to new inflammation blockers
by Sara Tiner, Mayo Clinic Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Mayo Clinic researchers have linked the T cell dysfunction seen in rheumatoid arthritis with a metabolic deficiency, reported in a new Nature Immunology publication. In “helper” T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, low levels of a specific amino acid lead to cellular miscommunication, but supplying it may provide...
Exercise increases the body’s own ‘cannabis’ which reduces chronic inflammation, says new study
by University of Nottingham Credit: CC0 Public Domain Exercise increases the body’s own cannabis-like substances, which in turn helps reduce inflammation and could potentially help treat certain conditions such as arthritis, cancer and heart disease. In a new study, published in Gut Microbes, experts from the University of Nottingham found that exercise intervention in people with arthritis, did not...
CRISPR screen identifies new anti-inflammatory drug target
by Vanderbilt University Medical Center Credit: CC0 Public Domain A metabolic enzyme that has been studied in cancer biology and is important for T cell function may offer a new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics, Vanderbilt researchers have discovered. They report Nov. 11 in the journal Immunity that inhibiting or genetically deleting the enzyme, called MTHFD2,...
Researchers identify pathway critical for the development and prevention of intestinal inflammation
by Dresden University of Technology Small intestinal crypts of IBD patients with unchanged (left) and mutated (right) XIAP gene. Paneth cells are labeled in red and nuclei of all cells in a crypt are labeled in blue. The patients with mutated XIAP gene have smaller number of Paneth cells. Credit: Anne Strigli Inflammatory bowel diseases...
New therapeutic molecule yields new hope for Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients
by University of Montreal Histopathology of gastrocnemius muscle from patient who died of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy, Duchenne type. Cross section of muscle shows extensive replacement of muscle fibers by adipose cells. Credit: Public Domain A research team led by Nicolas Dumont, a researcher at CHU Sainte-Justine and professor at the Université de Montréal, has discovered...
Newly discovered skin cell may underlie inflammatory skin disease
by Robin Marks, University of California, San Francisco Microscope image of skin fascia showing TIFFs labeled in green. Selected TIFFs are labeled in pink to visualize their star-like shape. Credit: Rosenblum Lab The surprise discovery of a new type of cell explains how distress to the skin early in life may prime a person for...
How chronic intestinal inflammation can cause cancer
by Frederike Buhse, Kiel University Microscopic image of inflamed intestinal tissue; on the right, the DNA repair mechanism is disrupted, resulting in increased tumor-promoting growth. Credit: IKMB, Kiel University Chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are inflammations of the gastrointestinal tract which flare up in phases and are accompanied by bloody bowel movements, diarrhea and severe impairment...