by Medical University of Vienna Previously unknown molecular connection between an inflammatory signalling molecule and one of the main oncogenes identified. Credit: Medical University of Vienna A team of MedUni Vienna researchers led by Johannes A. Schmid at the Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, has managed to identify a...
Category: <span>Inflammation</span>
Gentle stroll on treadmill helps prevent liver cancer
by Newcastle University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Regular gentle exercise could play a role in reversing liver damage that can lead to cancer, suggests a new study. Scientists at Newcastle University showed that aerobic exercise in mice reduced the levels of inflammation in the liver that develops with ageing, which reversed liver damage and prevented tumours from developing, with only one mouse...
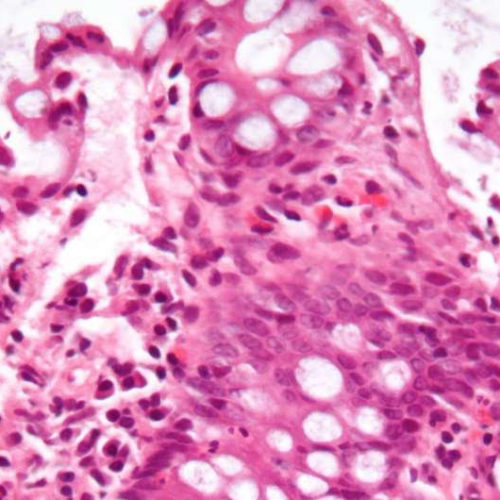
Scientists switch on tissue repair in inflammatory bowel disease
by KU Leuven Micrograph showing inflammation of the large bowel in a case of inflammatory bowel disease. Colonic biopsy. Credit: Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 A method that instructs immune system cells to help repair damaged tissues in the intestine has been developed by researchers at KU Leuven and Seoul National University. This opens the way for more effective treatment...
Uncovering a link between inflammation and heart disease
by Laura Castañón, Tufts University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Inflammation is part of an immune response to fight off pathogens and clear infections. But patients with cardiac disease often have chronic inflammation that damages their hearts, even with no infection present. In a recent study published in Circulation, immunologists at Tufts University School of Medicine in collaboration...
NIH study shows hyaluronan is effective in treating chronic lung disease
NIH/NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES IMAGE: THE RESEARCH SHOWS THAT INHALING HYALURONAN INTERFERES AT ALMOST EVERY STEP OF THE COPD CYCLE, MAKING IT A POTENT TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE. CREDIT: STAVROS GARANTZIOTIS, M.D. Researchers at the National Institutes of Health and their collaborators found that inhaling unfragmented hyaluronan improves lung function in patients suffering...
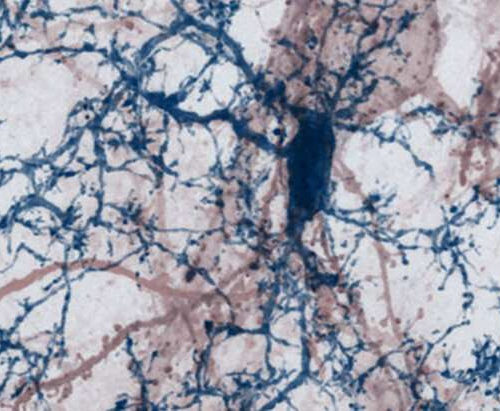
Inflammatory reactions in multiple sclerosis lead to synapse loss in the cerebral cortex
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich A nerve cell with its dendritic processes studded by synaptic spines (red) being contacted by brain-resident microglia cell (blue) in a mouse brain. Credit: Misgeld & Kerschensteiner Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the central nervous system, in which nerve cells are attacked by the patient’s...
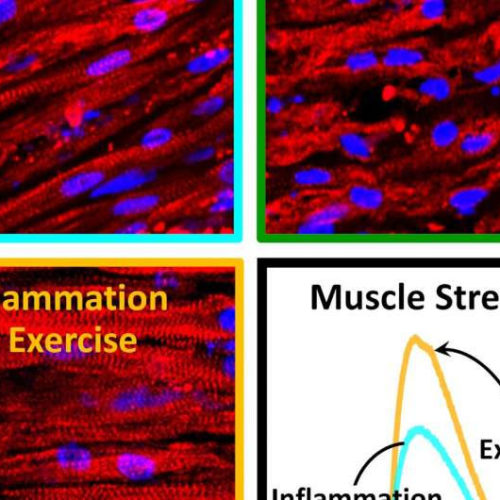
Exercising muscle combats chronic inflammation on its own
by Duke University School of Nursing Long, thin, well-defined muscle fibers (top left) are in shambles after prolonged inflammation (top right), but maintain their structure (bottom left) and strength (bottom right) when exercised during the inflammation. Credit: Zhaowei Chen, Duke University Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that human muscle has an innate ability to...
Inflamed environment is Clostridioides difficile paradise
by North Carolina State University A medical illustration of Clostridioides difficile bacteria, formerly known as Clostridium difficile, presented in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) publication entitled, Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. Credit: CDC A new study from North Carolina State University shows that the inflammation caused by Clostridioides difficile (C....
Opening a new door into kinder, gentler therapies for chronic inflammation
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress A structural model of TNFR2 and the antibody agonist. Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) Credit: H. Torrey et al., Science Signaling (2020) A naturally occurring antibody capable of stimulating the body’s immune-suppressing regulatory T cells has been discovered by a team of Harvard scientists, a finding...
Study: e-cigarettes trigger inflammation in the gut
Chemicals used for vaping break down zipper-like junctions between cells in the gut, leading to chronic inflammation and potential for other health concerns UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO IMAGE: IN THE BOTTOM FRAMES, BURST CELL JUNCTIONS IN THE GUT LINING CAN BE SEEN AFTER BEING EXPOSED TO E-CIGARETTE CHEMICALS AS COMPARED TO HEALTHY CELLS...