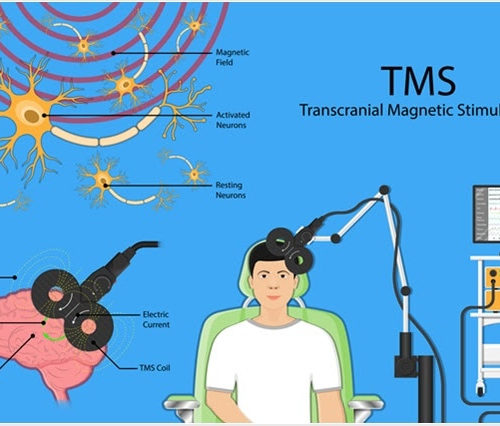
Major depression is one of the most common mental illnesses facing Americans. For some, the disorder can be effectively treated by conventional approaches, like talk therapy and antidepressants. For others, however, their symptoms persist through several different treatments, affecting their quality of life. New, alternative methods of treatment can offer hopes for these people. Transcranial...
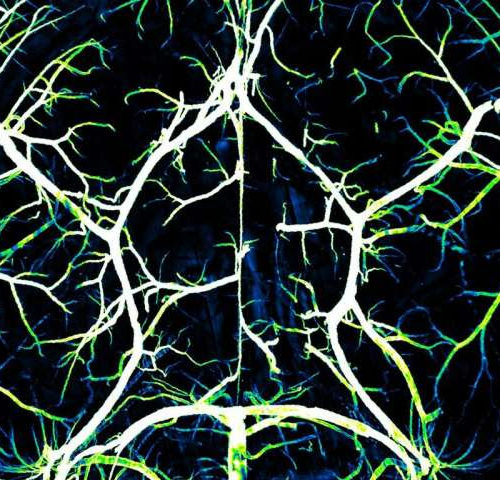
How the brain and its arteries communicate to supply blood to areas of heightened neural activity
by Harvard Medical School The brain is a ravenous organ. A three-pound adult human brain consumes about a fifth of the body’s energy, yet it cannot store energy on its own and requires constant nourishment from the cardiovascular system. The organ’s energy needs fluctuate greatly depending on neural activity, and sufficient blood must be delivered...
MRI findings predict shoulder stiffness for rotator cuff tears
Joint capsule edema and thickness at the axillary recess prove useful in predicting stiff shoulder in patients with small to large (< 5 cm) full-thickness rotator cuff tears AMERICAN ROENTGEN RAY SOCIETY Leesburg, VA, February 19, 2020–Two MRI findings–joint capsule edema and thickness at the axillary recess, specifically–proved useful in predicting stiff shoulder in patients...
New evidence that shows how the brain makes decisions
by Caitlin McDermott-Murphy, Harvard University Today, the internet is a sensory free-for-all: Pop-up ads burst into articles every few paragraphs, stealing the screen with lollipop colors and music, shouting product information from unseen corners. The human body is not so different. Every fingernail, elbow, nostril, and eyebrow is constantly vying for the brain’s attention. “Right...
Research uncovers new path for melanoma detection and treatment
by Edith Cowan University A new way to spot melanoma cells circulating in the blood has the potential to significantly improve the monitoring of cancer patients and guide future treatment. Edith Cowan University’s Melanoma Research Group, in collaboration with Harvard Medical School and clinicians at Western Australian hospitals, has pioneered a new technique to detect...
Single HPV vaccine dose may be effective against cervical cancer: study
by Wiley New research indicates that a single dose of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine is as effective as multiple doses for preventing preinvasive cervical disease, which can later develop into cervical cancer. The findings are published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society (ACS). HPV is the most common...
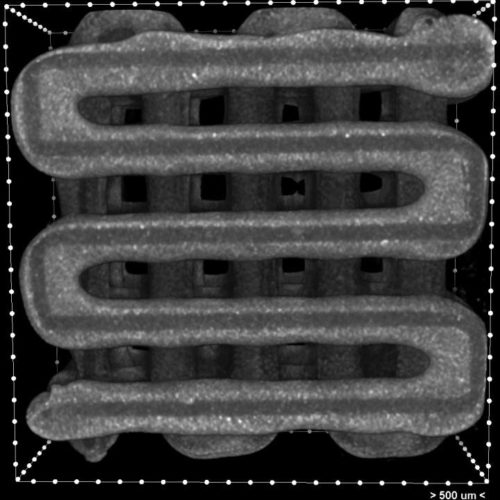
Grooves hold promise for sophisticated healing
Rice University bioengineers 3D-print implants to seed multiple layers of tissue RICE UNIVERSITY HOUSTON – (Feb. 4, 2020) – Who ever said bioengineers can’t get their groove on? The Rice University team led by Antonios Mikos says otherwise with its development of a groovy method to seed sophisticated, 3D-printed tissue-engineering scaffolds with living cells to...
Researchers successfully test coin-sized smart insulin patch, potential diabetes treatment
UCLA biomedical engineers, in collaboration with UNC School of Medicine and MIT researchers, led preclinical experiments for a new device to automatically manage glucose levels and deliver needed insulin quickly UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA HEALTH CARE UCLA bioengineers and colleagues at UNC School of Medicine and MIT have further developed a smart insulin-delivery patch that...
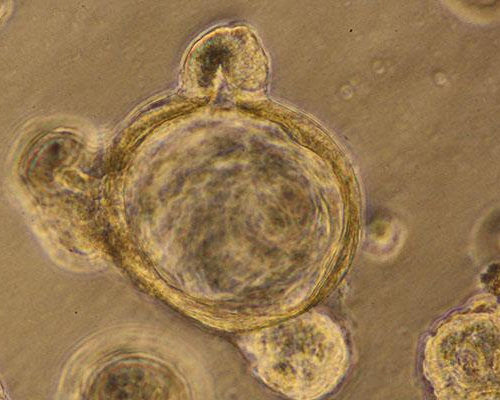
Human gut-in-a-dish model helps define ‘leaky gut,’ and outline a pathway to treatment
3D human gut organoids reveal molecular system that keeps intestinal linings sealed, demonstrate how the system breaks down and how it can be strengthened with the diabetes drug metformin UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO Once a vague scapegoat for a variety of ills, increasing evidence suggests a condition known as “leaky gut” — in...
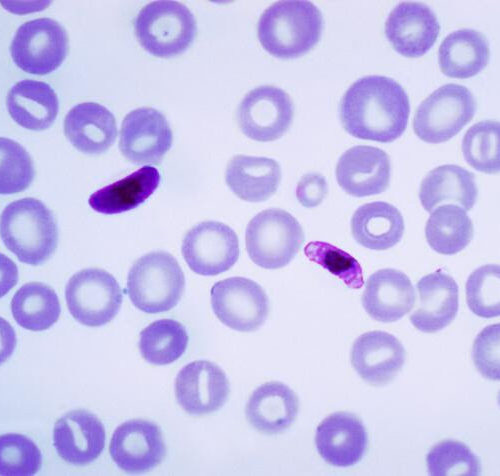
Discovery paves path forward in the fight against the deadliest form of malaria
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH HEALTH Scientists have identified a key molecule involved in the development of cerebral malaria, a deadly form of the tropical disease. The study identifies a potential drug target and way forward toward alleviating this condition for which few targeted treatments are available. In studies with mice, investigators discovered that the EphA2 protein...