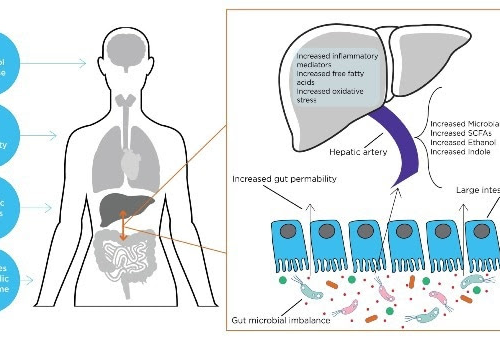
Content by Owlstone Medical LtdReviewed by Louis Castel The gut-liver axis is the term used to describe the two-way relationship between the gut microbiome and the liver. This relationship stems from the integration of signals produced by various factors such as diet, genetics, and the environment. The liver and the gastrointestinal tract are connected by...
Category: <span>biological sciences</span>
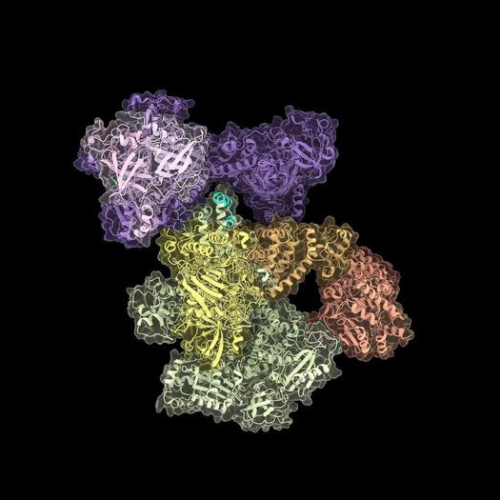
“One ring to rule them all”: How actin filaments are assembled by formins
MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE OF MOLECULAR PHYSIOLOGY IMAGE: FORMINS ARE MADE OF TWO IDENTICAL PARTS (RED, ORANGE) THAT ENCIRCLE THE ACTIN (GREY) FILAMENT IN A RING-LIKE CONFORMATION.CREDIT: MPI OF MOLECULAR PHYSIOLOGY Joining forces “Our discovery allows us to interpret decades of biochemical studies on formins through new lenses, which answers many long-standing, open questions in this...
Scientists develop new strategy for treating tendon–bone injuries
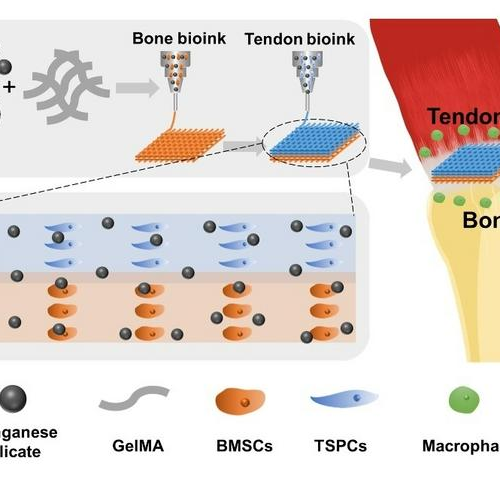
CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS IMAGE: SCHEMATIC ILLUSTRATION OF THE IMMUNOMODULATORY MULTICELLULAR SCAFFOLDS BASED ON MANGANESE SILICATE (MS) NANOPARTICLES FOR INTEGRATED TENDON-TO-BONE REGENERATION view moreCREDIT: DU LIN AND WU CHENGTIE According to a study published in Science Advances, a research group led by Prof. WU Chengtie from the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese...
Vitamin A’s Role in Skin Influences Wound Repair and Hair Growth
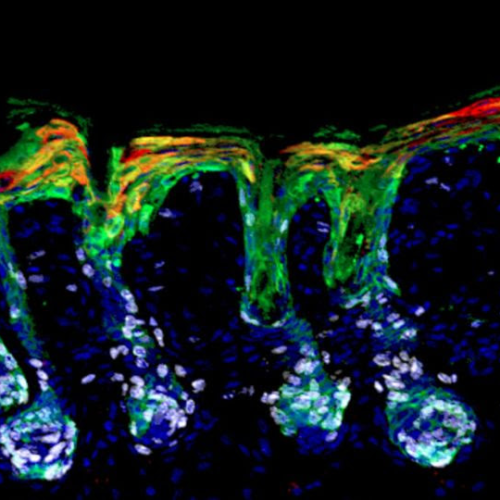
The new study investigated the role of vitamin A in skin cells’ lineage plasticity. Sarah Whelan, PhD Hair follicle stem cells (green) mobilize and expand (white) to help repair the skin’s barrier by differentiating into epidermal lineages (red). Credit: Robin Chemers Neustein Laboratory of Mammalian Cell Biology and Development at The Rockefeller University. Retinoic acid,...
Thousands of Previously Unknown Bile Acids Discovered
Researchers have uncovered thousands of bile acids that the gut microbiome uses to communicate with the rest of the body. University of California, San Diego Researchers from Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at the University of California San Diego have uncovered thousands of previously unknown bile acids, a type of molecule used by...
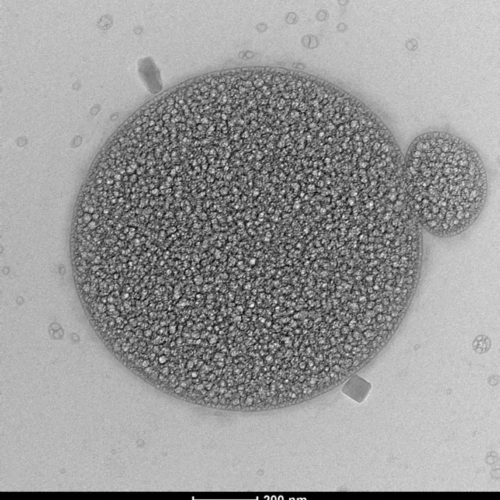
Possible ‘Trojan Horse’ found for treating stubborn bacterial infections
Peer-Reviewed Publication WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) IMAGE OF THE BACTERIAL CELL WITH AN EXTRACELLULAR VESICLE ATTACHED.CREDIT: WSU PULLMAN, Wash. – Bacteria can be tricked into sending death signals to stop the growth of their slimy, protective homes that lead to deadly infections, a new study demonstrates. The discovery by Washington State University...
Low iron levels resulting from infection could be key trigger of long COVID
Peer-Reviewed PublicationUNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Problems with iron levels in the blood and the body’s ability to regulate this important nutrient as a result of SARS-CoV-2 infection could be a key trigger for long COVID, new research has discovered. The discovery not only points to possible ways to prevent or treat the condition, but could help...
Double trouble at chromosome ends
Peer-Reviewed Publication ROCKEFELLER UNIVERSITY CST–Polα/primasE, THE ENZYME THAT SOLVES THE NEWLY DISCOVERED END-REPLICATION PROBLEM CREDIT: CREDIT SARAH CAI Double Trouble at Chromosome Ends Half a century ago, scientists Jim Watson and Alexey Olovnikov independently realized that there was a problem with how our DNA gets copied. A quirk of linear DNA replication dictated that telomeres...
Normal-appearing tissue offers insights into lesion formation in multiple sclerosis
by Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience Microglia nodules in MS are more frequent than in stroke but are similar in size. IHC stainings with HLA and PLP shown in brown. Quantifications performed on n = 8 MS and n = 8 stroke donors. a PLP and HLA staining of (NA)WM matter in MS and in stroke shows no sign of demyelination...
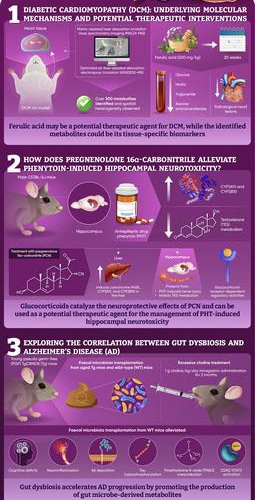
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis articles provide novel insights into previously unknown disease mechanisms
Researchers decode underlying mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM), hippocampal neurotoxicity, and dysbiosis mediated Alzheimer’s disease (AD) progressionPeer-Reviewed Publication CACTUS COMMUNICATIONS INVESTIGATION OF THREE DISEASES SHARING COMMON THEMES OF METABOLIC DYSREGULATION REVEAL COMMON UNDERLYING MECHANISMS AND MOLECULAR PATHWAYS. CREDIT: JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS DCM is the leading cause of heart failure in patients with chronic diabetes....