JANUARY 31ST, 2020 POSTED BY LAURA BAILEY-MICHIGAN (Credit: Getty Images) After an injury, mature bone marrow stromal cells morph to perform in ways similar to their bone-healing stem cell cousins, according to new research in mice. Conventional thinking is that bone regeneration is left to a small number of mighty cells called skeletal stem cells,...
Biophysicists find ‘extra’ component in molecular motor
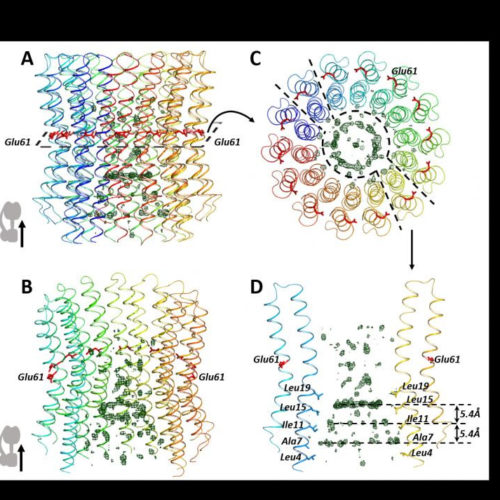
MOSCOW INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS AND TECHNOLOGY Researchers from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology have discovered an additional component in ATP synthase, a molecular machine that produces the energy-conserving compound in all cellular organisms. The new unique features of the ATP synthase structure are described in detail in a paper in Scientific Reports. In...
Mutation’s role in blood cancers revealed by ideal team-up
by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory A genetic mutation that disrupts how DNA sends messages to the rest of a cell has been linked to a large number of blood cancers. Thanks to a collaboration between biologists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) and an oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), we now know...
Could Colchicine Be the New Aspirin?
Jean-Claude Tardif, MD; Michel Zeitouni, MD, MSc DISCLOSURES January 27, 2020 This interview is a translation of a video discussion posted on Medscape France. It has been edited for clarity. Michel Zeitouni, MD, MSc: Hello. I am Michel Zeitouni, a cardiologist at the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital and a researcher with the organization ACTION Cœur (Allies in...
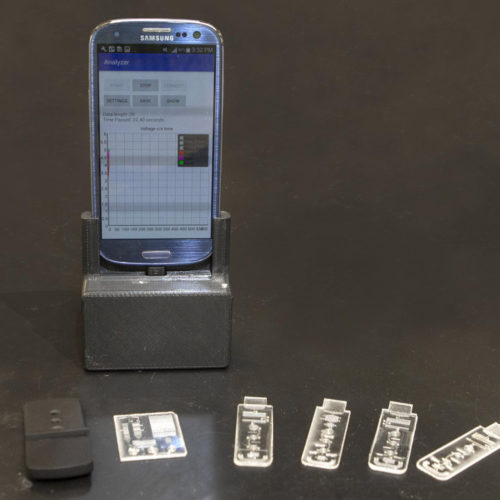
Portable lab you plug into your phone can diagnose illnesses like coronavirus
Smartphone lab delivers test results in ‘spit’ second UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI Engineers with the University of Cincinnati have created a tiny portable lab that plugs into your phone, connecting it automatically to a doctor’s office through a custom app UC developed. The lab the size of a credit card can diagnose infectious diseases such as...
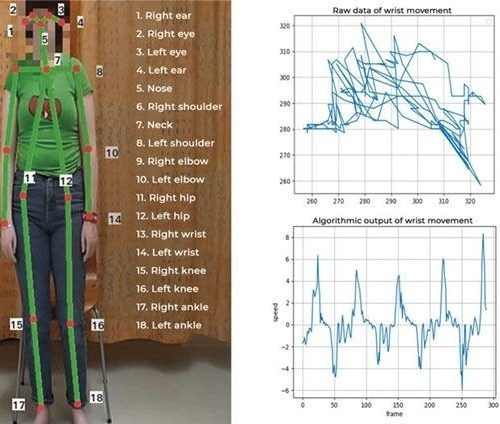
Automatic method to assess severity of myoclonic jerks from video footage
Fast, reliable and automatic assessment of the severity of myoclonic jerks from video footage is now possible, thanks to an algorithm using deep convolutional neural network architecture and pretrained models that identify and track key points in the human body. Published in Seizure, the study is a joint effort by the Epilepsy Centre at Kuopio...
Pioneering SFU research customizes vaccines to reduce bacterial disease
The invention of vaccines for disease prevention is often cited as one of the miracles of modern medicine. New research from Simon Fraser University suggests that tailoring vaccines based on geography and other factors could substantially reduce overall rates of bacterial disease. Professor Caroline Colijn, who holds a Canada 150 Research Chair in Mathematics for...
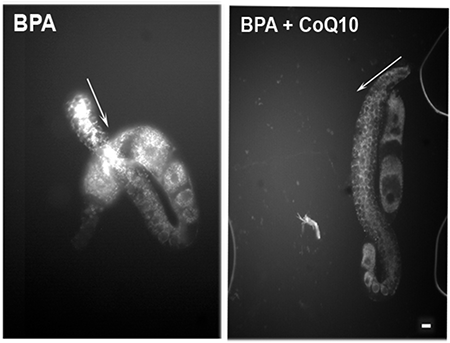
Rescue Attempt
From plastics to pesticides, it seems like every week delivers fresh news about the dangers of endocrine disruptors—chemicals in the environment that alter the body’s hormones and can lead to reproductive, developmental, neurologic and immune problems and cancer. Industry regulation and individual consumer choice can reduce exposure to such chemicals, but there are few options...
Differences between deep neural networks and human perception
Stimuli that sound or look like gibberish to humans are indistinguishable from naturalistic stimuli to deep networks. When your mother calls your name, you know it’s her voice — no matter the volume, even over a poor cell phone connection. And when you see her face, you know it’s hers — if she is far...
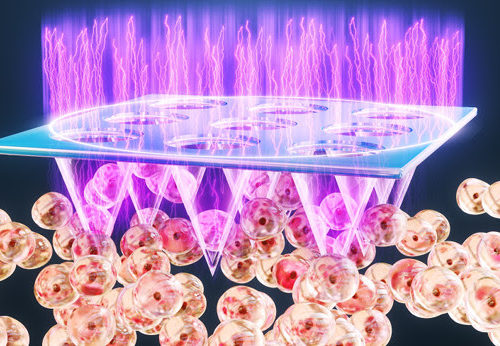
Cold plasma patch could make immunotherapy more effective for treating melanoma Share
An interdisciplinary team of researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has developed a medicated patch that can deliver immune checkpoint inhibitors and cold plasma directly to tumors to help boost the immune response and kill cancer cells. The thumb-sized patch has more than 200 hollow microneedles that can penetrate the skin and enter...