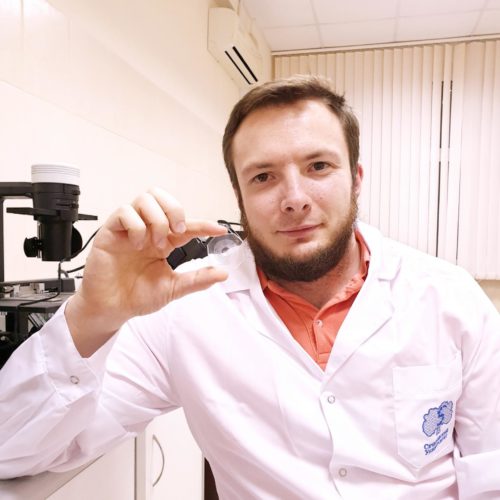
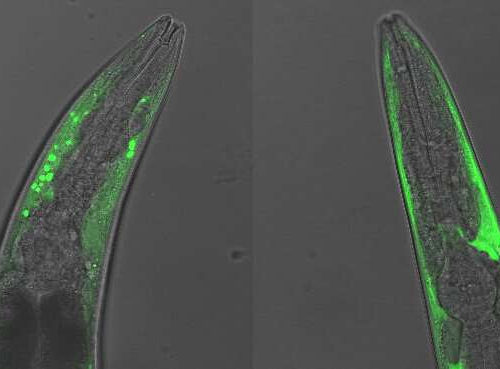
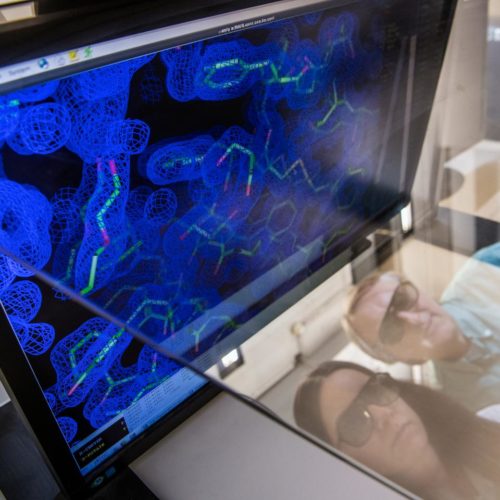
by University of Leeds A master control region of a protein linked to Parkinson’s disease has been identified for the first time. The finding, made by scientists from the University of Leeds’ Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology, provides a new target for the development of therapies to try and slow down or even prevent...
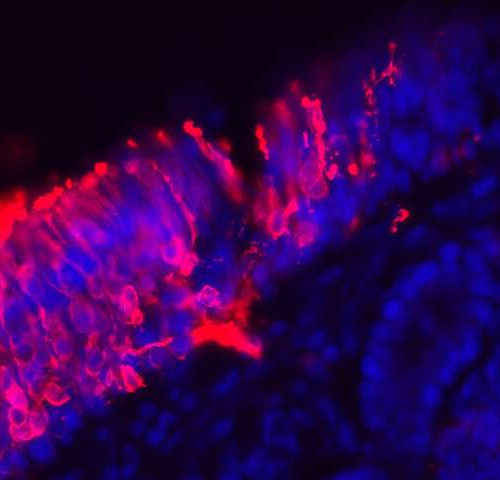
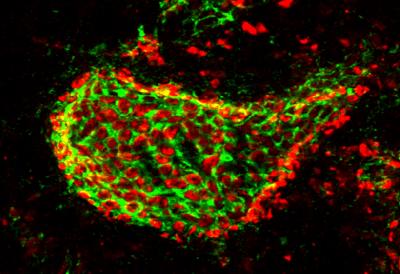
Thriving neuron ‘nursery’ found in a section of adult human nose tissue
by Duke University Is it possible for an adult brain to make new nerve cells? Scientists have debated this question for decades, with many concluding that neuron-making stops after childhood, or around the age of 13. However, a research team recently rocked the debate again after finding a thriving neuron ‘nursery’ in a section of...
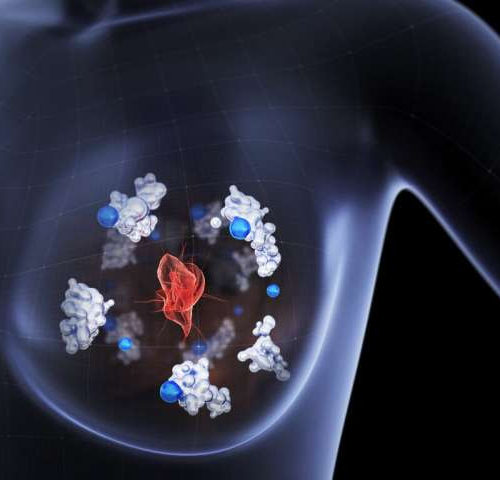
Cancer cells spread using a copper-binding protein
by Chalmers University of Technology Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have shown that the Atox1 protein, found in breast cancer cells, participates in the process by which cancer cells metastasize. The protein could therefore be a potential biomarker for assessing the aggressiveness of the disease, as well as a possible target for new...
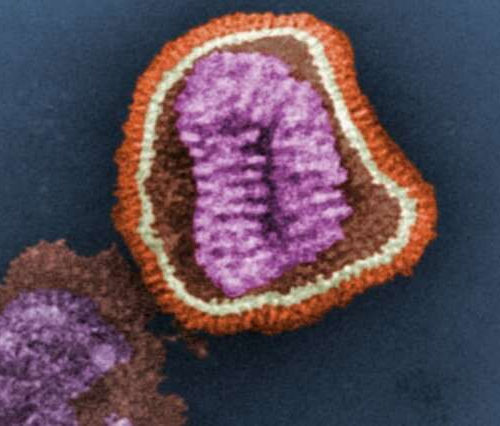
A single dose of universal flu vaccine, FLU-v, may provide long-lasting protection against influenza
by American College of Physicians A single dose of adjuvanted FLU-v, a synthetic universal flu vaccine, may provide long-lasting protection across a broad spectrum of influenza viruses. Findings from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial are published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Currently, the best available prophylactic treatment against influenza is annual vaccination with inactivated or...
Fatal overproduction of antibodies
Mutations in plasma cells play a key role in light chain amyloidosis TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF MUNICH (TUM) Bone marrow plasma cells produce antibodies. These comprise two long and two short protein chains. The pathological proliferation of plasma cells can lead to an overproduction of the short chains. These associate to fibrils and deposit in organs....
Chip for liquid biopsy will help to detect prostate cancer
SECHENOV UNIVERSITY Researchers of Sechenov University together with their colleagues from Australia used the microfluidics technology to develop a device able to isolate cancer cells from urine of patients with prostate cancer. The study showed high sensitivity and specificity of the new method in diagnosing prostate cancer. The results obtained were published in Cancers. Prostate...
More than a nice coating
NETHERLANDS INSTITUTE FOR NEUROSCIENCE – KNAW Researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience (NIN) have shown that specialized aggregates of molecules enwrapping nerve cells in the brain, the perineuronal nets, are crucial for regulating the connections between nerve cells that control motor memories. The discovery, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences...
The Lancet HIV: Study suggests a second patient has been cured of HIV
Long-term follow-up of the London patient suggests no detectable active HIV virus remains in the patient. THE LANCET Long-term follow-up of the London patient suggests no detectable active HIV virus remains in the patient. Although the treatment is high-risk and only suitable for certain patients, the results provide evidence that this patient is the second...
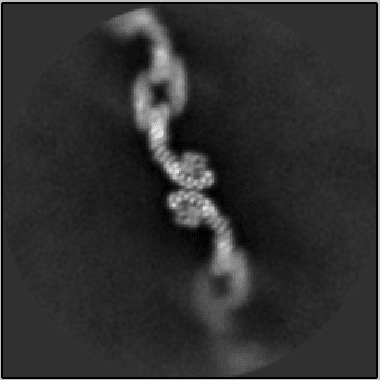
Biology researchers capture shape-shifting delivery structures in body’s cellular “FedEx system”
A new cellular biology study, published in the journal Structure by scientists at Vanderbilt, reports a shape-shifting structure in the human body that plays an important role in the timely delivery of fats and proteins. Led by Lauren Jackson, assistant professor of biological sciences and biochemistry at Vanderbilt, the work is the first to visualize...
Brain-doping produced by your own body
Erythropoietin, or Epo for short, is a notorious doping agent. It promotes the formation of red blood cells, leading thereby to enhanced physical performance – at least, that is what we have believed until now. However, as a growth factor, it also protects and regenerates nerve cells in the brain. Researchers at the Max Planck...