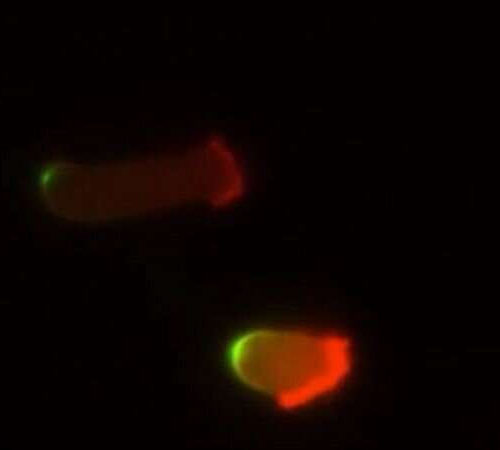
Neurology RUHR-UNIVERSITY BOCHUM The short-chain fatty acid propionic acid influences the intestine-mediated immune regulation in people with multiple sclerosis (MS). This has been shown by a team from the Department of Neurology of Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) at St. Josef-Hospital in an international study headed by Professor Aiden Haghikia. The application of propionic acid in addition...
Contact Lenses to Correct Color Blindness
Deuteranomaly is a color blindness that causes green light photoreceptors to react to redder light. Red objects seem greener for patients with the condition, but it has been known for a while that blocking some of the light in the red color range can improve proper color perception. There are glasses that do this, a...
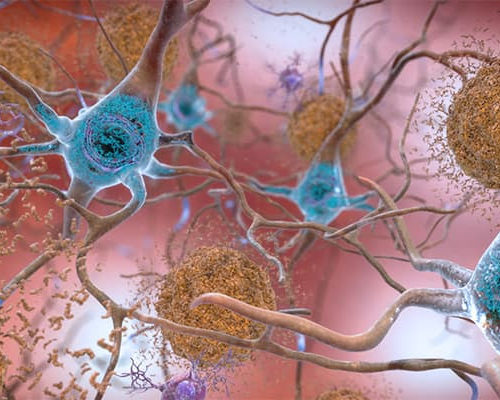
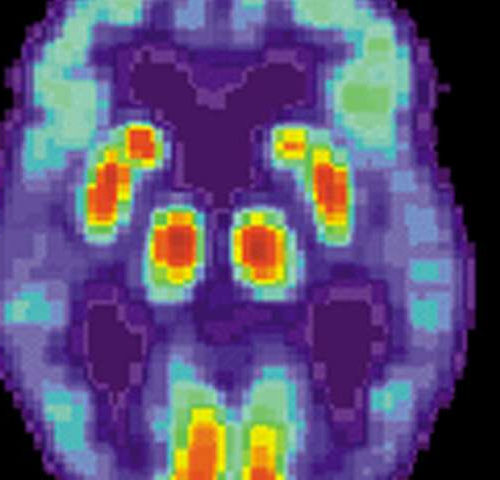
Scientists design new model to further understand causes of Alzheimer’s disease
The Multiplex Model is a new way of looking at Alzheimer’s disease developed by Professor Julie Williams, Dr Rebecca Sims and Dr Matt Hill of the University’s UK Dementia Research Institute (UKDRI) and unveiled in the Journal Nature Neuroscience. The model was produced by looking at all known genetic risk factors to further understanding of...
NEUROTRANSMITTER MAP MAY LEAD TO NEW DRUGS
ANDERS BUCH-LARSEN-COPENHAGEN A new map of a neurotransmitter may lead to better drugs for ADHD, depression, epilepsy, and more, researchers report. The discovery also adds to the researchers’ knowledge of neurotransmitters in the brain. The map is of a new conformation of LeuT, a bacterial protein that belongs to the same family of proteins as...
Like patching a flat tire: New fix heals herniated discs
by Cornell University A new two-step technique to repair herniated discs uses hyaluronic acid gel to re-inflate the disc and collagen gel to seal the hole, essentially repairing ruptured discs like you’d repair a flat tire. After a rupture, a jelly-like material leaks out of a herniated disc, causing inflammation and pain. The injury is...
Giving common muscle relaxant via nose shows potential to treat neurodegenerative diseases
by Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Delivering the medication dantrolene through the nose rather than the mouth may help the medication penetrate the brain more effectively, potentially maximizing its therapeutic benefits in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer’s disease. In a first-of-its-kind study, researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine...
Immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory bowel disease does not increase women’s risk of vulvar or vaginal cancer
by Elsevier In a new retrospective study, researchers found that the use of immunosuppressive therapy does not increase the occurrence or recurrence of vulvar or vaginal cancer in women with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). However, earlier onset of cancer was reported, and lymphomas were found in some patients, which is very rare in the genital...
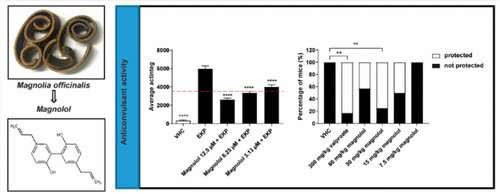
Magnolia bark compound could someday help treat drug-resistant epilepsy
by American Chemical Society In patients with epilepsy, normal neurological activity becomes disrupted, causing debilitating seizures. Now, researchers report in ACS Chemical Neuroscience that they have found a potential new treatment for this disorder by turning to traditional Chinese medicine. Tests of extracts from plants used in these ancient remedies led the team to one...
Statins starve cancer cells to death
by Johns Hopkins University More than 35 million Americans take statin drugs daily to lower their blood cholesterol levels. Now, in experiments with human cells in the laboratory, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine have added to growing evidence that the ubiquitous drug may kill cancer cells and have uncovered clues to how they do it....
Scientists describe new molecules that form direct link between gut microbiome and brain function
by University of Glasgow Scientists at the University of Glasgow have described new molecules which form a direct link between the gut microbiome and the brain, leading to inhibition of brain cell function in pre-clinical investigations in mice. In the study, conducted in collaboration with AstraZeneca and published today in Science Advances, scientists were able...