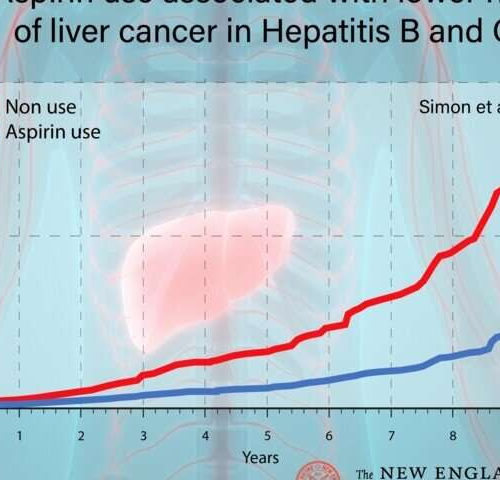
by Felicia Lindberg, Karolinska Institutet Among adults with chronic viral hepatitis at high risk of liver cancer, those who took low-dose aspirin long-term were less likely to develop liver cancer or to die from liver-related causes. The findings come from a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine and conducted by a team...
Popular painkiller ibuprofen affects liver enzymes in mice
by Andy Fell, UC Davis The popular painkiller ibuprofen may have more significant effects on the liver than previously thought, according to new research from the University of California, Davis. The study in laboratory mice also shows marked differences between males and females. The popular painkiller ibuprofen may have more significant effects on the liver...
How brain biology promotes starvation in patients with anorexia nervosa
by University of California – San Diego Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have discovered differences in brain circuitry that contribute to starvation and weight loss in people with anorexia nervosa (AN). The findings, published in the March 12, 2020 online issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry, shed new light...
Protective brain-cell housekeeping mechanism may also regulate sleep
Penn Medicine study may point to new strategies for improving sleep and preventing neurodegenerative disease UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE An important biological mechanism that is thought to protect brain cells from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s may also be involved in regulating sleep, according to new research from the Perelman School...
Mayo Clinic research discovers how stem cells repair damage from heart attacks
MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic researchers have uncovered stem cell-activated mechanisms of healing after a heart attack. Stem cells restored cardiac muscle back to its condition before the heart attack, in turn providing a blueprint of how stem cells may work. The study, published in NPJ Regenerative Medicine, finds that human cardiopoietic cells...
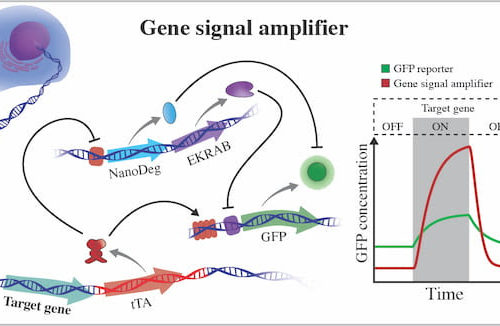
Strong signals show how proteins come and go
A novel system to amplify gene expression signals could be a game-changer for scientists who study the regulatory processes in cells that are central to all life. The Rice University lab of bioscientist Laura Segatori has developed a versatile gene signal amplifier that can do a better job of detecting the expression of target genes...
Study Reveals a Delicate Dance of Dynamic Changes in the Conscious Brain
Using anesthesia, Michigan Medicine researchers uncover how moment-to-moment brain changes may reflect consciousness. Imagine you’re at work: you’re focused on a task when suddenly your mind starts to wander to thoughts of the weekend–that is until you catch your boss walking by out of the corner of your eye. This back and forth in consciousness...
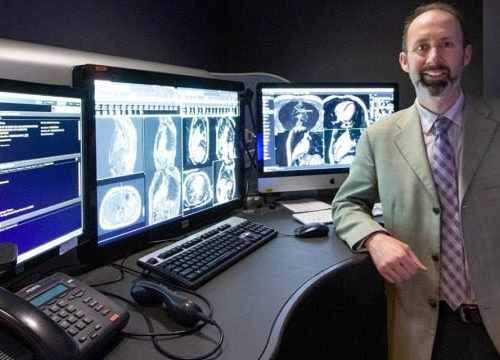
MRI scans unnecessary to diagnose heart failure, new study suggests
A new study from the University of Alberta cardiac researchers casts doubt on the standard practice of using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help diagnose the causes of heart failure not related to a heart attack. In a study published in the journal Circulation, 500 patients with heart failure from Canada and Finland were randomly...
New drug combination may improve cold sore treatment
by Sam Wood, University of Kent Research from Kent’s School of Biosciences and the Goethe-University Frankfurt am Main, has found a drug combination that may improve treatment for diseases caused by herpes simplex viruses such as cold sore, genital herpes, and keratitis. The research is published in Frontiers in Microbiology. Researchers tested different drugs on...
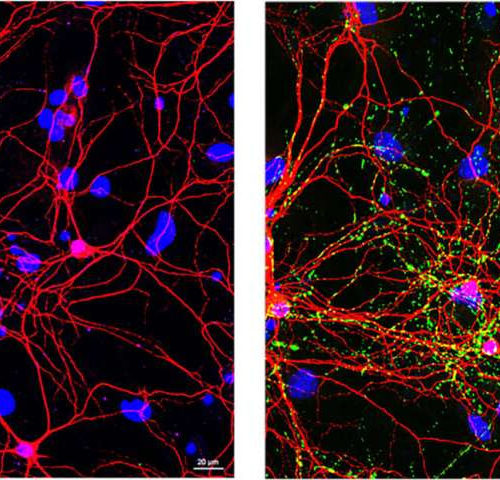
‘Natural killer’ cells could halt Parkinson’s progression
by University of Georgia Researchers at the University of Georgia’s Regenerative Bioscience Center and their colleagues have found that “natural killer” white blood cells could guard against the cascade of cellular changes that lead to Parkinson’s disease and help stop its progression. Natural killer (NK) cells are white blood cells that can kill tumors without...