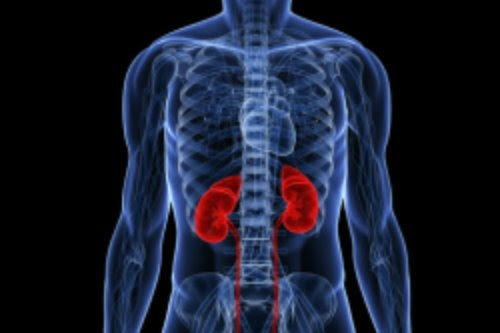
A new UK-wide clinical trial is looking to recruit around 500 patients aged over 65-years with low kidney function and other health problems to better understand the pros and cons of different options should their kidneys fail. The study is announced on World Kidney Day. Current evidence around treatment options for patients with the advanced...
How T cells make sure they have quiet time
All cells, like all people, need “quiet” time to function properly, and this is particularly true of T cells, one of the immune system’s main weapons. They must be ready for activation at all times, and primed to divide more rapidly than almost any cell in the body. When T cells are overworked, people can...
Altered potassium levels in neurons may cause mood swings in bipolar disorder
Salk researchers also find additional differences between the neurons of people with bipolar disorder who respond to lithium and those who don’t People with bipolar disorder experience dramatic shifts in mood, oscillating between often debilitating periods of mania and depression. While a third of people with bipolar disorder can be successfully treated with the drug...
Drug combo reverses arthritis in rats
A combination of two previously studied osteoarthritis drugs works better than either drug alone, Salk researchers discovered People with osteoarthritis, or “wear and tear” arthritis, have limited treatment options: pain relievers or joint replacement surgery. Now, Salk researchers have discovered that a powerful combination of two experimental drugs reverses the cellular and molecular signs of...
Is Appendectomy Linked to Parkinson’s Disease?
By Osman Shabir, M.Sc. Reviewed by Dr. Mary Cooke, Ph.D. Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder clinically characterized by resting tremor, bradykinesia (slow movements), dyskinesia (impairment of movement), dystonia (stiffness of muscles including facial muscles), a stooped posture, sexual and urinary dysfunction, drooling, and in some cases psychiatric symptoms including psychosis, dementia, and depression Pathologically,...
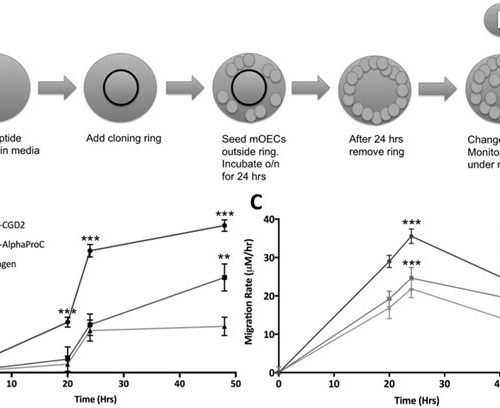
Peptide Hydrogels for Prevention of Esophageal Strictures
Sponsored Content by Manchester BIOGEL Barrett’s esophagus requires endoscopic treatment and can often result in further damage of healthy tissue leading to fibrotic tissue formation, referred to as strictures. This study demonstrates that synthetic, self-assembling peptide hydrogels(PeptiGelDesign) support the activity and function of primary oesophageal cells, and, in turn, epithelialization and stratification occur during in...
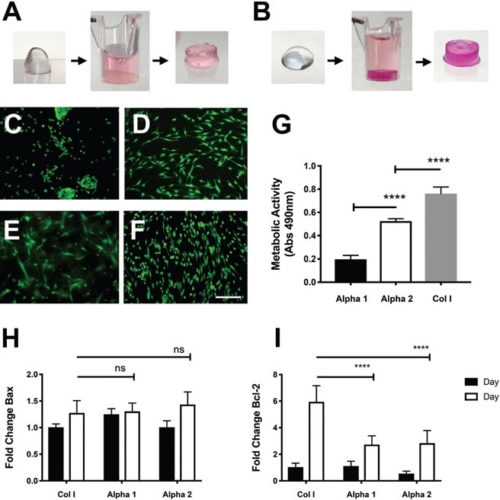
Peptigel Hydrogels Improve Neurotrophic Potential of hADSCs
Although there have been advances in microsurgical procedures, options for treatment to restore prior function after peripheral nerve injury are still unavailable. Currently, autologous nerve grafting remains the favored therapy. However, experimental researchers recently have concentrated efforts on artificial constructs development, specifically to combine smart biomaterials and stem cells, with the aim of enhancing the...
Ultrasound can temporarily increase mood, study suggests
Researchers find that targeting specific regions of the brain with ultrasound may increase a person’s mood. Could ultrasound, one day, be used to boost mood? A study recently published in the journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience suggests that targeting a region of the prefrontal cortex with transcranial focused ultrasound (tFUS) — a new ultrasound technique...
How brain cells lay down infrastructure to grow and create memories
by Center for Genomic Regulation Research published today in Science Advances sheds new light on the molecular machinery that enables the shape, growth and movement of neurons. It is the first time scientists have revealed how the brain shuttles genetic code within its cells, a process believed to be crucial for the formation and storage...
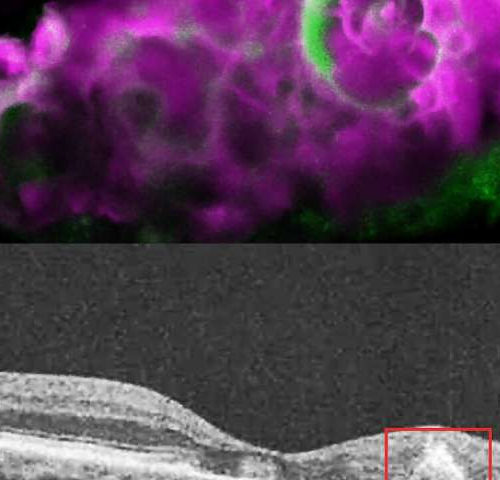
Researchers discover tooth-enamel protein in eyes with dry AMD
by National Eye Institute A protein that normally deposits mineralized calcium in tooth enamel may also be responsible for calcium deposits in the back of the eye in people with dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD), according to a study from researchers at the National Eye Institute (NEI). This protein, amelotin, may turn out to be...