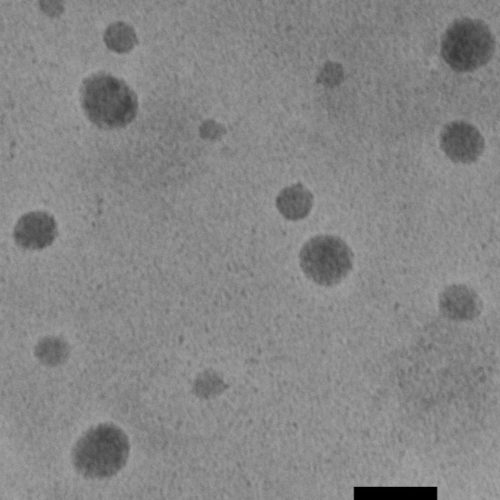
UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD PDT does not always kill cells deep within a cancerous tumour, allowing tumours to grow back again. The new compound uses penetrating infrared light to damage cells directly and potentially improve the success rate of PDT Researchers at the University of Sheffield have synthesized a new compound which could improve the success...
KAT6A syndrome: Advances on the genetic bases and clinical picture of a rare disease
UNIVERSITY OF BARCELONA A research team has described five new cases of a rare disease -known as KAT6A syndrome- of which there are only eighty dominant cases worldwide. This neurological and developmental disorder, caused by alterations in the lysine acetyltransferase 6A gene (KAT6A), involves intellectual disability, language impairment, low muscle tone, cardiovascular malformation and eye...
Fur-friendly ‘wearable for pets’ developed at Imperial
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Imperial College London researchers have invented a new health tracking sensor for pets and people that monitors vital signs through fur or clothing. The new type of sensor, which can detect vital signs like heart and breathing rates through fur and up to four layers of clothing, could help make everyday wearables...
International group of scientists found new regulators of blood supply to the brain
The data obtained can be used in the treatment of hypertension, occurring without an obvious reason IMMANUEL KANT BALTIC FEDERAL UNIVERSITY Only about ten years ago theories began to appear that astrocytes, along with neurons, are actively involved in processing information and in supporting the activity of the brain. Recently, an article by an international...
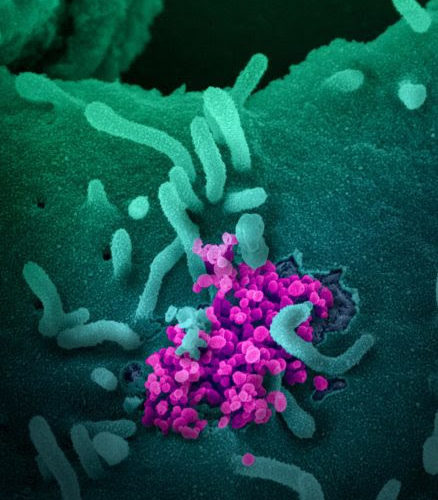
Nanosize device ‘uncloaks’ cancer cells in mice and reveals them to the immune system
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE Scientists at Johns Hopkins report they have designed and successfully tested an experimental, super small package able to deliver molecular signals that tag implanted human cancer cells in mice and make them visible for destruction by the animals’ immune systems. The new method was developed, say the researchers, to deliver an immune...
Researchers make asthma breakthrough
TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have made a breakthrough that may eventually lead to improved therapeutic options for people living with asthma. The researchers have uncovered a critical role for a protein (Caspase-11), which had previously never been implicated in the disease. They report their findings today [Wednesday 26th February 2020] in...
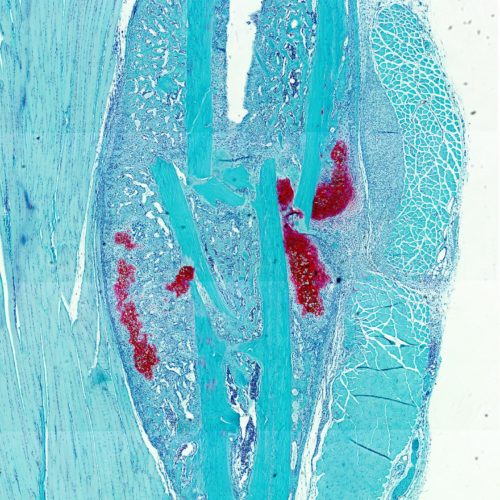
Bone or cartilage? Presence of fatty acids determines skeletal stem cell development
KU LEUVEN In the event of a bone fracture, fatty acids in our blood signal to stem cells that they have to develop into bone-forming cells. If there are no blood vessels nearby, the stem cells end up forming cartilage. The finding that specific nutrients directly influence the development of stem cells opens new avenues...
NIH clinical trial of remdesivir to treat COVID-19 begins
A randomized, controlled clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the investigational antiviral remdesivir in hospitalized adults diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has begun at the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) in Omaha. The trial regulatory sponsor is the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National...
New Clue Behind Age-Related Diseases and Food Spoilage Discovered
Exotic molecule linked to ozone also at work in chronic diseases and cancers, and even the decomposition of food. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have made a surprising discovery that could help explain our risk for developing chronic diseases or cancers as we get older, and how...
‘PAIN SENSOR’ DISCOVERY COULD LEAD TO NEW PAINKILLERS
MCGILL UNIVERSITY “Now that we have identified the sensor associated with mechanical pain, we can start designing new powerful analgesic drugs that can block its action. This discovery is really exciting and brings new hope for novel pain treatment,” says Reza Sharif-Naeini. A protein in the membrane of our sensory neurons is involved in our...