By Osman Shabir, M.Sc. Reviewed by Dr. Jennifer Logan, MD, MPH Chronic anxiety is the long-term negative psychological experience to environmental stressors, characterized by prolonged and inappropriately excessive worrying, fatigue, restlessness, concertation, and sleep issues. Often the terms stress and anxiety are used interchangeably. Prolonged stress and anxiety can have a negative impact on one’s...
Scientists find new way to save neurons in Alzheimer’s disease
Neurons die earlier than experts previously thought in Alzheimer’s disease, and stopping the process could prevent the disease from ever developing, finds a new study from Tokyo Medical and Dental University in Japan. Research brings a new understanding of how Alzheimer’s disease develops. Alzheimer’s disease is the leading cause of dementia, and as many as...
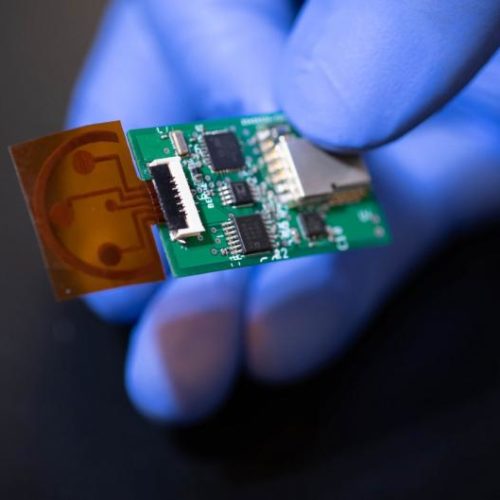
Sweat sensor detects stress levels; May find use in space exploration
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY If someone asked you right now how stressed you are, what would you say? A little? A lot? You do not know? Those are all valid responses, but they are not especially useful to researchers and medical professionals because they are subjective and not easily quantified. Nonetheless, in lieu of a...
Scientists discover new ‘Jekyll and Hyde’ immune cell
TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN Scientists at Trinity College Dublin have identified a rare, new cell in the immune system with “Jekyll and Hyde properties”. These cells play a key protective role in immunity to infection but – if unregulated – also mediate tissue damage in autoimmune disorders. The findings should help us design more effective vaccines...
Existing drugs may offer a first-line treatment for coronavirus outbreak
Broad-spectrum antiviral agents could be a possible quick response to the potential COVID-19 pandemic NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY The number of people infected with the new corona virus continues to skyrocket, with more than 80000 cases worldwide as of the end of February. But there’s no vaccine or cure in sight, meaning that...
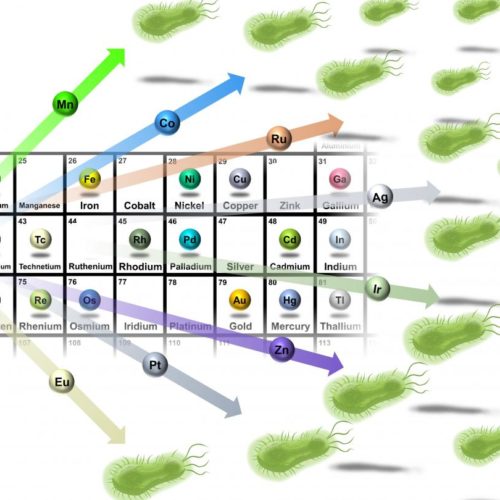
Metals could be the link to new antibiotics
UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Compounds containing metals could hold the key to the next generation of antibiotics to combat the growing threat of global antibiotic resistance. University of Queensland researchers, working with a network of international collaborators, have discovered 23 previously unexplored compounds containing metals such as silver, manganese, zinc, ruthenium and iridium that have antibacterial...
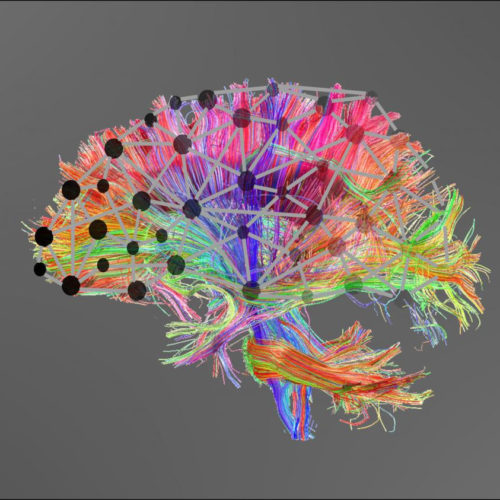
Learning difficulties due to poor connectivity, not specific brain regions
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE Different learning difficulties do not correspond to specific regions of the brain, as previously thought, say researchers at the University of Cambridge. Instead poor connectivity between ‘hubs’ within the brain is much more strongly related to children’s difficulties. Between 14-30% of children and adolescents worldwide have learning difficulties severe enough to require...
Mount Sinai researchers discover new approach for use of stem cells to improve bone marrow transplantation
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Mount Sinai researchers have discovered a way to enhance the potency of blood-forming stem cells, potentially opening the door to a new approach for bone marrow transplantation, according to a study published on February 27 in Cell Stem Cell. The scarcity of blood-forming stem cells,...
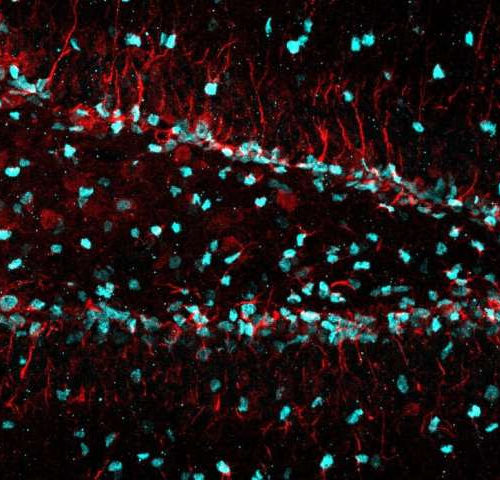
Newly identified cellular trash removal program helps create new neurons
by Eric Hamilton, University of Wisconsin-Madison New research by University of Wisconsin-Madison scientists reveals how a cellular filament helps neural stem cells clear damaged and clumped proteins, an important step in eventually producing new neurons. The work provides a new cellular target for interventions that could boost neuron production when it’s needed most, such as...
Early intervention following traumatic brain injury reduces epilepsy risk
by Iqbal Pittalwala, University of California – Riverside A research team led by a scientist at the University of California, Riverside, has found that brains treated with certain drugs within a few days of an injury have a dramatically reduced risk of developing epilepsy later in life. The development of epilepsy is a major clinical...