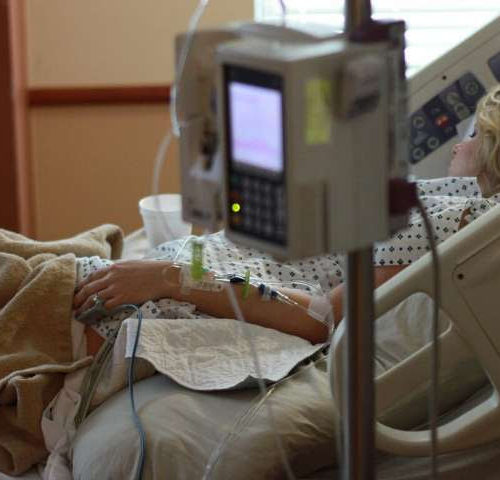
Despite lack of obvious symptoms, high blood pressure should not be ignored, researchers urge AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY While it typically has no symptoms, high blood pressure–or hypertension–has serious health consequences. Rates of deaths related to hypertension have risen by 72% and 20% in rural and urban areas of the U.S., respectively, according to research...
Everlywell Utilizes Telemedicine and At-Home Lab Testing to Diagnose COVID-19
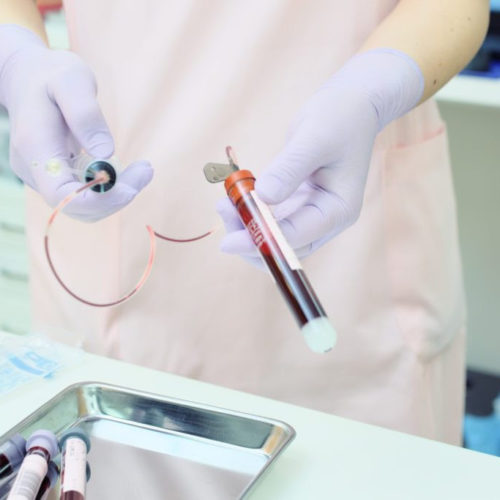
SCOTT JUNGDIAGNOSTICS, EMERGENCY MEDICINE, MEDICINE, PUBLIC HEALTH One of the biggest hurdles for America in its fight against the growing COVID-19 pandemic is a massive shortage of tests to diagnose for the virus. To help in the battle, one of the nation’s leading at-home lab testing companies, Everlywell, has developed an in-home test for COVID-19...
COVID-19 detection in under 20 mins – Iceni Diagnostics offers new approach
The emergence of COVID-19 has exposed a frailty in our ability to rapidly detect and screen new infectious diseases. Iceni Diagnostics is developing a new approach that identifies the virus – not by its genetic code, which can mutate, but by using its reliance on chains of sugars which are constant and unchangeable. The existing...
When coronavirus kills, the lung condition ARDS can be the culprit. Here’s what you need to know.
by Stacey Burling When she was 33, Eileen Rubin learned firsthand what it’s like to have acute respiratory distress syndrome or ARDS, a life-threatening condition she had never heard of. It’s about to become more widely known. ARDS is one of the most severe complications caused by the new coronavirus, and early estimates show it...
Can an old method help doctors fight COVID-19?
Researchers say that a decades-old approach could help fight SARS-CoV-2 infections. It involves collecting antibodies from the blood of people who have recovered from COVID-19. To fight COVID-19, researchers and doctors are trying an old technique: treating patients with antibodies from people who have recovered. For live updates on the latest developments regarding the novel...
FDA OKs Golodirsen (Vyondys 53) for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Megan Brooks The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved golodirsen injection (Vyondys 53, Sarepta Therapeutics), the first treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients with a confirmed mutation amenable to exon 53 skipping. Last summer, the agency declined to approve of the drug on an accelerated basis, sending a complete response letter...
Difficulty breathing and COPD key predictors for severe COVID-19
by Rowan Walker, University College London Shortness of breath (dyspnoea) is the only symptom of COVID-19 significantly associated with severe cases of the disease and admission to intensive care units (ICU), according to a new systematic review and meta-analysis led by UCL. The findings, published in MedRxiv as a pre-print prior to peer-review, also showed...
New study finds immune cells can defend against multiple viruses
by Brita Belli, Yale University An underlying virus does not stop the body’s immune system from launching a strong defense against a second, newly introduced virus, according to a Yale-led study that appears in the March 9 online edition of the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. For the study, Yale researchers obtained blood samples from...
Health forums: Style of language influences credibility and trust
German psychologists investigate advice given on the internet UNIVERSITY OF MÜNSTER More and more, people are using internet forums as first place to look for information on health issues. However, the scientific medical information being provided there is often so complex that laypeople are barely able to form considered judgements on the content of much...
Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde — Enzyme targeted by TB antibiotic later stops the drug destroying it
THE FRANCIS CRICK INSTITUTE Crick and Imperial researchers have found that a key antibiotic widely used to treat drug-resistant tuberculosis does not work as expected – a finding which could be used to develop new drugs. The study was part-funded by the Francis Crick Institute and the Wellcome Trust. The research, published in Nature Chemical...