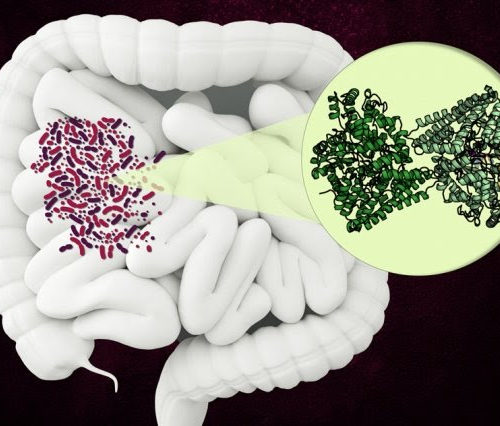
Scientists discover the structure of an enzyme, found in the human gut, that breaks down a component of collagen. MIT and Harvard University chemists have discovered the structure of an unusual bacterial enzyme that can break down an amino acid found in collagen, which is the most abundant protein in the human body. The enzyme,...
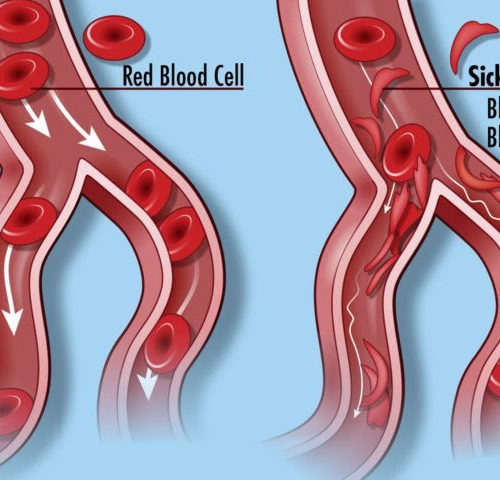
Viruses for the Good: Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
While the world worries about novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, other viruses continue to be used for the good – as vectors that ferry in healing genes for gene therapy and editing. Charles Hough calls himself “reborn” after lentiviruses – disabled versions of HIV – gave his blood cells the gene that overrides the mutant one that...
Exploring cells’ path to build cholesterol and finding a future drug target
Researchers based at UTokyo and RIKEN in Japan, and the University of New South Wales in Australia have uncovered a new aspect of one of the molecules involved in cells’ production line to build cholesterol. This understanding could provide a new target for high-cholesterol medications and other drugs that kill pests like athlete’s foot fungus...
Could disease pathogens be the dark matter behind Alzheimer’s disease?
by Richard Harth, Arizona State University For researchers investigating Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), a devastating neurodegenerative illness afflicting close to 6 million Americans, it is the best and worst of times. Scientists have made exponential advances in understanding many aspects of the mysterious disease since it was first diagnosed over 100 years ago. Nevertheless, every effort...
How gene therapy may hold key to treating life-threatening cardiac disease
by University of California – San Diego Danon disease is a very rare, life-threatening condition where the fundamental biological process of removing and recycling proteins does not work. This impairment results in dysfunction of the heart, skeletal muscle, neurologic system, eyes, and liver. Most patients die or require heart transplants by the third decade of...
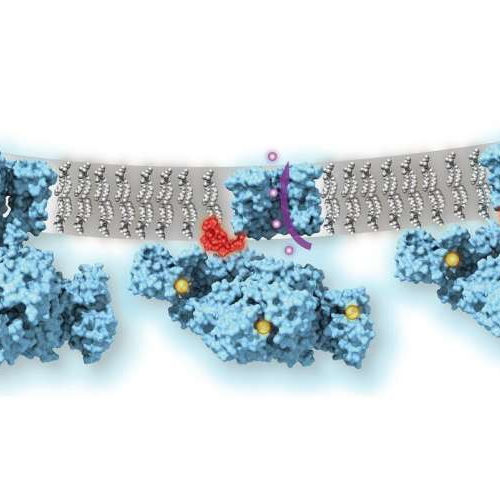
Ball-and-chain inactivation of ion channels visualized by cryo-electron microscopy
by Weill Cornell Medical College Ion channels, which allow potassium and sodium ions to flow in and out of cells, are crucial in neuronal ‘firing’ in the central nervous system and for brain and heart function. These channels use a “ball-and-chain” mechanism to help regulate their ion flow, according to a new study led by...
In NIH trial, selumetinib shrinks tumors, provides clinical benefit for children with NF1
Findings from a phase 2 clinical trial show that the drug selumetinib improves outcomes for children with the genetic disorder neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). In the trial, selumetinib shrank the inoperable tumors that develop with NF1 called plexiform neurofibromas, and children experienced reduced pain, improved function, and better overall quality of life after receiving the...
How to slow down ageing?
ESTONIAN RESEARCH COUNCIL Healthy ageing has become one of the priorities of research in Europe. University of Tartu researchers looked for differences in the immune systems of young and old people. They focused on monocytes and found that the monocytes of the elderly do not seem to produce as much energy, and there is an...
New technique ‘prints’ cells to create diverse biological environments
Take a neural stem cell in the brain: Whether this cell remains a stem cell or differentiates into a fully formed brain cell is ultimately determined by a complex set of molecular messages the cell receives from countless neighbors. Understanding these messages is key for scientists hoping to harness these stem cells to treat neurological...
Clinical trial shows HIV drugs ineffective against COVID-19
by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress A team of doctors and researchers in China has found that drugs that are effective in treating patients with HIV are ineffective against COVID-19. In their paper published in The New England Journal of Medicine, the group describes the clinical trial they conducted with patients in Wuhan, China, and...