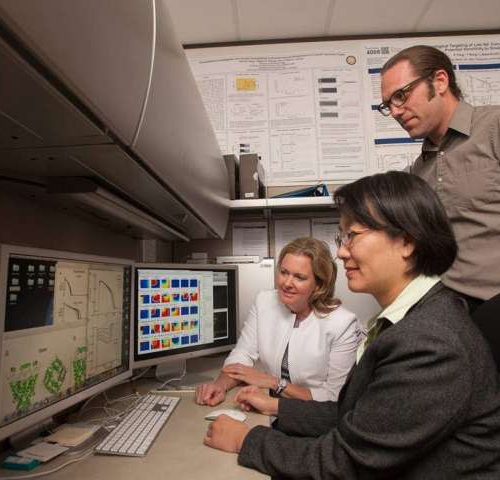
by Karen Finney, UC Davis UC Davis Health researchers have developed a computer model to screen drugs for unintended cardiac side effects, especially arrhythmia risk. Published in Circulation Research, the study was led by Colleen E. Clancy, professor of physiology and membrane biology, and Igor Vorobyov, assistant professor of physiology and membrane biology. Clancy is...
New process to identify existing drugs for potential COVID-19 treatments
by Adrian De Novato, Michigan State University In late January, as the world watched the growing COVID-19 epidemic with increasing unease, a Michigan State University laboratory, which specializes in the use of artificial intelligence and big data to discover therapeutics for cancers, switched gears to face the coming challenge. The Chen Lab, led by Bin...
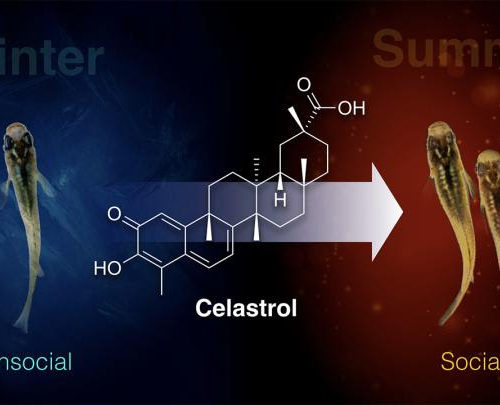
Discovery of a drug to rescue winter depression-like behavior
Celastrol treats SAD-like symptoms in medaka fish INSTITUTE OF TRANSFORMATIVE BIO-MOLECULES (ITBM), NAGOYA UNIVERSITY A group of animal biologists and chemists at the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (WPI-ITbM), Nagoya University, has used a chemical genomics approach to explore the underlying mechanism of winter depression-like behavior and identified a drug that rescues winter depression-like behavior in...
COMPUTER MODEL PREDICTS DRUG ARRHYTHMIA RISK
A new computer model screens drugs for unintended cardiac side effects, especially arrhythmia risk, report researchers. “One main reason for a drug being removed from the market is potentially life-threatening arrhythmias,” says study co-leader Colleen E. Clancy, professor of physiology and membrane biology at the University of California, Davis. “Even drugs developed to treat arrhythmia...
Chinese scientists determine structure of COVID-19 main protease and identify inhibitors
CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS A team of Chinese scientists has reported the high-resolution crystal structure of the main protease (Mpro) of the COVID-19 virus and has identified drugs that may hold promise in combating the virus. Prof. RAO Zihe and Prof. YANG Haitao from the Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies of ShanghaiTech University,...
Large-scale analysis links glucose metabolism proteins to Alzheimer’s disease biology
NIH-funded research reveals protein network changes that may be druggable targets, biomarkers NIH/NATIONAL INSTITUTE ON AGING In the largest study to date of proteins related to Alzheimer’s disease, a team of researchers has identified disease-specific proteins and biological processes that could be developed into both new treatment targets and fluid biomarkers. The findings suggest that...
The building blocks of gum disease
OKINAWA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (OIST) GRADUATE UNIVERSITY Porphyromonas gingivalis is a major bacterial pathogen which leads to periodontitis also known as gum disease. In Japan, 80% of adults aged 35 and over suffer from this disease. What’s more, P. gingivalis has also been linked to rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, pancreatic cancer, and even...
Researchers describe possible mechanism for link between obesity and breast cancer
It is widely accepted that higher levels of body fat increase the risk of developing breast cancer, as well as other cancers. Based on his ongoing research, Bing Li, Ph.D., associate professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology and UofL Health — James Graham Brown Cancer Center at the University of Louisville, has published...
Vaccine skeptics actually think differently than other people
In 2000, the measles virus was declared eliminated from the United States. Despite cases coming in from outside the country, there were few outbreaks because most people were vaccinated against measles. And then 2019 happened. The U.S. saw 1,282 confirmed cases in 31 states — the greatest number reported since 1992, with nearly three-fourths linked...
Potential Stem Cell Therapy for ALS Moving into Phase 3 Trial
BY DAVID MELAMED, PHD Seneca Biopharma announced that work is underway to advance NSI-566, its leading stem cell treatment candidate, into a Phase 3 study in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The decision followed a meeting with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and is supported by data collected from a Phase 1...