WILEY Consuming a diet high in fiber was linked with a reduced incidence of breast cancer in an analysis of all relevant prospective studies. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society (ACS). Because studies have generated inconsistent results regarding the potential relationship between fiber intake and...
A new way to deliver drugs in MOFs
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Scientists from the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS) in cooperation with the Faculty of Chemistry of the Warsaw University of Technology (WUT) have developed a new, solvent-free method for the encapsulation of drug molecules in MOF (Metal-Organic Framework)...
CORONAVIRUS VACCINE PATCH SHOWS PROMISE IN MICE
Scientists have produced a potential vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus causing the COVID-19 pandemic. When tested in mice, the vaccine—delivered through a fingertip-sized patch—produces antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 at quantities thought to be sufficient for neutralizing the virus. The paper appears in EBioMedicine and is the first study describing a candidate vaccine for COVID-19...
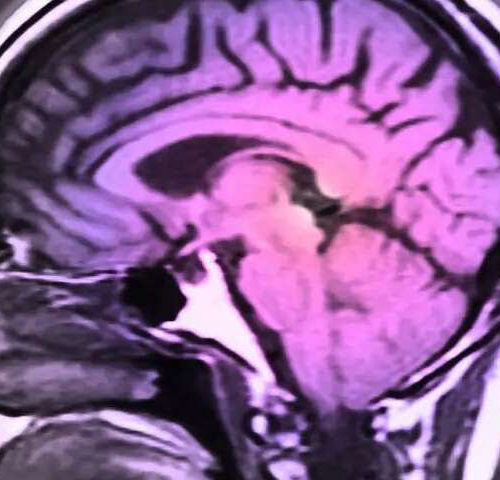
Brain changes from multiple sclerosis may occur in preteens
(HealthDay)—Greater genetic predisposition for multiple sclerosis (MS) is associated with altered brain white matter development at an early age, according to a study published online March 12 in the Annals of Neurology. C. Louk de Mol, from the Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam in the Netherlands, and colleagues evaluated the association between MS polygenic risk...
Brown fat can burn energy in an unexpected way
by Joslin Diabetes Center When we are exposed to sufficient cold or exercise, small clusters of brown fat cells in our bodies begin to burn up energy. Since 2009, when researchers at Joslin Diabetes Center and other institutions discovered that this helpful form of fat can be active in adults, scientists have sought to turn...
Potential therapy for rare neurologic disease
by University of Cincinnati A targeted therapy, currently being studied for treatment of certain cancers including glioblastoma, may also be beneficial in treating other neurologic diseases, a study at the University of Cincinnati shows. The study, being published online April 6 in the journal EBioMedicine, revealed that the effects of a therapy delivery system using...
Scientist proposes clinical trials with low-dose rapamycin to protect elderly from COVID-19
by Impact Journals The Biogerontology Research Foundation, a registered UK charity supporting and promoting aging and longevity research worldwide since 2008, today announced the publication of a paper titled “Geroprotective and senoremediative strategies to reduce the comorbidity, infection rates, severity, and lethality in gerophilic and gerolavic infections” in the leading journal Aging. Vaccines and therapeutic...
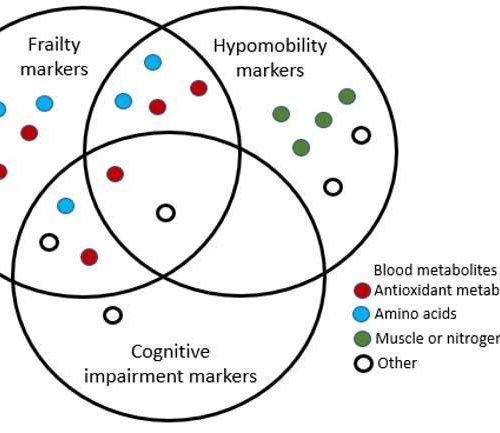
Leaving its mark: How frailty impacts the blood
by Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Globally, human society is aging. A side-effect of this is that age-related disorders, such as frailty, are becoming increasingly common. Frailty includes not only physical disabilities, but also a decline in cognitive function and an increase in various social problems. The prevalence of this disorder among those aged...
Hangover drug shows wider benefits in research
by Gary Polakovic, University of Southern California A well-known hangover drug not only helps soothe pounding headaches but also triggers profound changes that protect the liver, USC scientists report in new findings that could help prevent alcohol-related harm. The study focuses on dihydromyricetin (DHM), also known as ampelopsin, an over-the-counter herbal remedy. When researchers at...
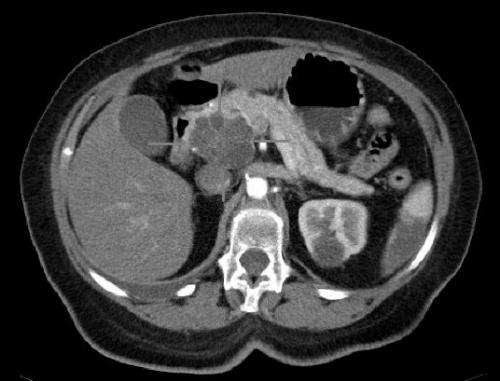
Pancreatic cancer blocked by disrupting cellular pH balance
by Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys have found a new way to kill pancreatic cancer cells by disrupting their pH equilibrium. The study, published in Cancer Discovery, reports how depleting an ion transport protein lowers the pH to a point that compromises pancreatic cancer cell growth. Pancreatic cancer cells—like...