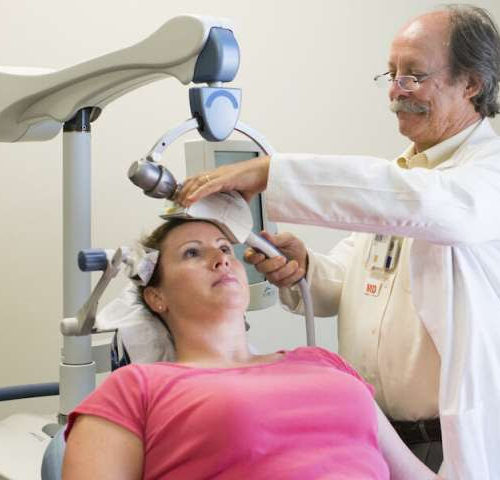
by Medical University of South Carolina In a pilot study in adults with autism and depression, transcranial magnetic stimulation, or TMS, was effective in reducing depressive symptoms and had some effects on autistic symptoms, report researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina in Autism Research. This study suggests that TMS warrants further study as...
Coronavirus patients can benefit from blood of the recovered, new study shows
by Melissa Healy, Los Angeles Times For 10 patients severely ill with the new coronavirus, a single dose of antibodies drawn from the blood of people who had recovered from COVID-19 appeared to save lives, shorten the duration of symptoms, improve oxygen levels and speed up viral clearance, newly published research reports. The preliminary findings...
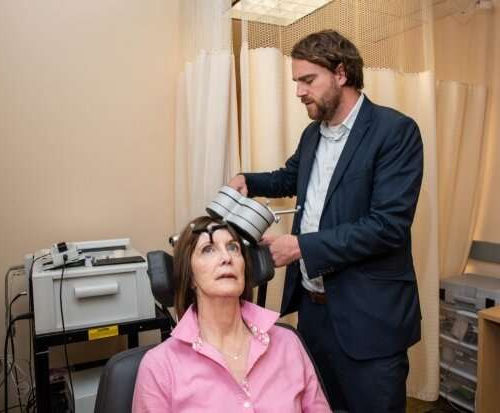
Researchers devise treatment that relieved depression in 90% of participants in small study
by Mandy Erickson, Stanford University Medical Center A new form of magnetic brain stimulation rapidly relieved symptoms of severe depression in 90% of participants in a small study conducted by researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine. The researchers are conducting a larger, double-blinded trial in which half the participants are receiving fake treatment....
Compound in fruit peels halts damage and spurs neuronal repair in multiple sclerosis
by Thomas Jefferson University Multiple sclerosis (MS), characterized by increasing muscle weakness and paralysis, has a number of treatments that help stall progression of the disease when used early on in the disease. But the current treatments can hardly reverse damage that has already occurred in brain cells called neurons. New research suggests that a...
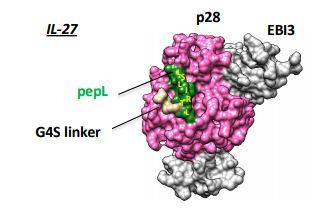
Cancer scientists at Purdue aim to use protein power to stop tumor growth
PURDUE UNIVERSITY WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – In 2018, approximately 324,000 men died from cancer in the United States. The combination of lung cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer equated to half of those deaths. Large percentages of each of these cancers can be prevented or treated if caught early. Now, Purdue University scientists have created...
Researchers suggest a special diet against asthma
Study by the University of Bonn proves success of a so-called ketogenic diet UNIVERSITY OF BONN Can a special diet help in certain cases of asthma? A new study at the University of Bonn at least points to this conclusion. According to the study, mice that were switched to a so-called ketogenic diet showed significantly...
Researchers reveal new understandings of synthetic gene circuits
ASU professors use synthetic biology to discover new relationships between engineered gene circuits and biological host cells ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY Recent discoveries by two research teams in the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering at Arizona State University are advancing the field of synthetic biology. Assistant Professor Xiaojun Tian and Associate Professor Xiao Wang conducted...
MANY COVID-19 PATIENTS ARE DYING FROM CARDIAC ARREST
THE DISCOVERY HAS DOTORS MYSTIFIED.BY VICTOR TANGERMANN A recent study by Chinese researchers found that as many as one in five COVID-19 patients experienced cardiac damage, heart failure — and, in some instances, death. Out of 416 hospitalized patients, 19 percent showed signs of heart damage. About half of those with heart damage succumbed to...
Seeking COVID cures: Scientists find promising first step in antiviral treatment
by Cornell University Researchers from Cornell University have identified a possible target for antiviral treatment for COVID-19. The researchers initially set out to analyze the structure and characteristics of SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) and MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus), with a focus on the spike protein—specifically the fusion peptide—that allows these viruses...
Common protein in skin can ‘turn on’ allergic itch
by Tracey Peake, North Carolina State University A commonly expressed protein in skin—periostin—can directly activate itch-associated neurons in the skin, according to new research from North Carolina State University. The researchers found that blocking periostin receptors on these neurons reduced the itch response in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis, or eczema. The findings could...