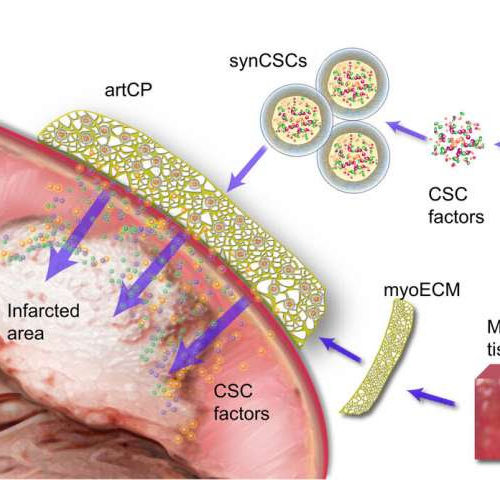
by Yale University A drug used for cancer therapy has shown promise in reversing kidney damage caused by systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, or lupus), according to a Yale-led study published April 8 in the journal Science Translational Medicine. “Kidney damage affects about half of the patients with lupus, sometimes leading to renal failure with a...
Experimental anti-malarial drug shows promise in first clinical trial
by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital A fast-acting anti-malarial compound discovered at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital was well tolerated and showed promising anti-malarial effects in the first study in humans. The findings appear online first this week in the journal Lancet Infectious Diseases. “The results support further development of the compound SJ733 as a...
New tool helps gather useful genetic information obtained from blood, skin tissues
Researchers at CHOP and University of Pennsylvania developed an online tool to refine results from RNA sequencing obtained from clinically accessible tissues CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA Philadelphia, March 31, 2020 – DNA sequencing is becoming a more commonplace method for detecting diseases and improving precision medicine. Because DNA sequencing does not detect all possible disease-causing...
McGill researchers identify correlation between MBI and Alzheimer’s
Study could serve as screening tool for early diagnosis of dementia MCGILL UNIVERSITY In recent years, scientists have conducted more than 100 clinical trials in the hopes of finding new indicators capable of diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease prior to the manifestation of clinical symptoms such as memory loss. Though MBI, characterized by changes in the normal...
UCI-led study finds modifiable risk factors could play a role in Alzheimer’s disease
Amyloid accumulation not the only risk factor in Alzheimer’s risk UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – IRVINE Irvine, Calif. – April 8, 2020 – Amyloid is a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease, but the accumulation of these sticky proteins may not be the only risk factor for developing Alzheimer’s disease, according to a new study published this...
Canadian clinical trial tests plasma therapy for COVID-19
by McMaster University Can those who survive COVID-19 provide blood to treat others hospitalized by the disease? That’s the question driving a Canadian consortium that has launched one of the world’s largest clinical trials of a potential treatment for COVID-19 —one that goes as far back as the Spanish flu a century ago. The treatment...
Neuropsychological and psychological methods are essential for neurorehabilitation
by IOS Press Clinical neuropsychology and psychology have evolved as diagnostic and treatment-oriented disciplines necessary for individuals with neurological, psychiatric, and medical conditions. In this collection of articles in the journal NeuroRehabilitation experts highlight medical advances in neuropsychological and psychological applications in neurorehabilitation. “Neuropsychology and psychology are practical disciplines that provide the underpinnings for understanding...
World-first trial to test benefit of intravenous zinc in COVID-19 fight
by University of Melbourne A world-first trial will see researchers from Austin Health and the University of Melbourne use intravenous zinc to fight the symptoms of coronavirus (COVID-19). The trial will be led by Dr. Joseph Ischia from Austin Health, along with Dr. Oneel Patel from the Department of Surgery at the University of Melbourne,...
First in-human study of drug targeting brain inflammation supports further development
University of Kentucky UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY LEXINGTON, Ky. (April 9, 2020) — Linda J. Van Eldik, director of the Sanders-Brown Center on Aging at the University of Kentucky, co-authored a paper reporting the first human clinical study of a drug candidate that suppresses injury and disease-induced inflammation of the brain. The paper was accepted in...
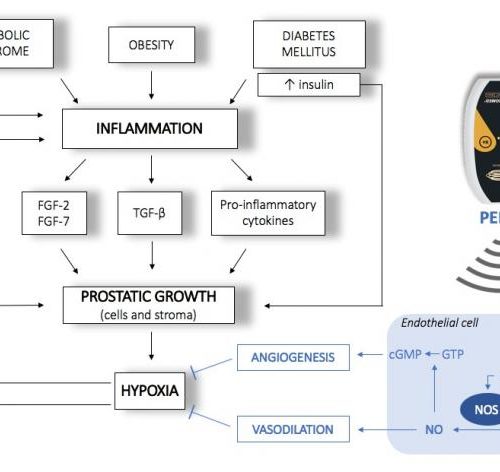
Noninvasive treatment for men suffering from enlarged prostate
Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy decreased prostate volume and improved the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia, cites research published in Andrology PARSEMUS FOUNDATION Physicians from Sapienza University in Rome have published promising results of a small prospective interventional trial using noninvasive pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (PEMF) to treat men suffering from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). After...