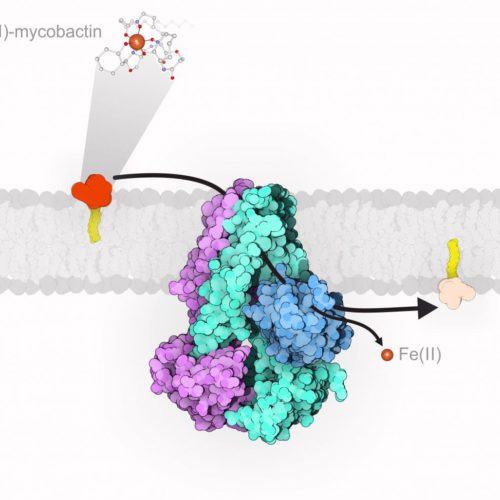
UNIVERSITY OF ZURICH One of the most devastating pathogens that lives inside human cells is Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacillus that causes tuberculosis. According to the World Health Organization, 1.5 million people died in 2019 from this disease that generally affects the lungs. The rise of multidrug resistant M. tuberculosis strains, which are resistant to many...
Scientists discover gene that increases risk of Alzheimer’s disease
by University of British Columbia Researchers from the University of British Columbia (UBC) and the Central South University (CSU) in China have for the first time identified a gene that increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. In the study, published recently in the journal JCI Insight, the researchers found two mutations in the gene endothelin-converting...
Solving a molecular mystery may have opened new class of cancer drugs
By Michael Irving Researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have solved a molecular mystery that might lead to new treatments for cancer. The team has uncovered just how a strange molecule works to kill cancer by inducing a little-known type of cell death, and identified other molecules that may work even better....
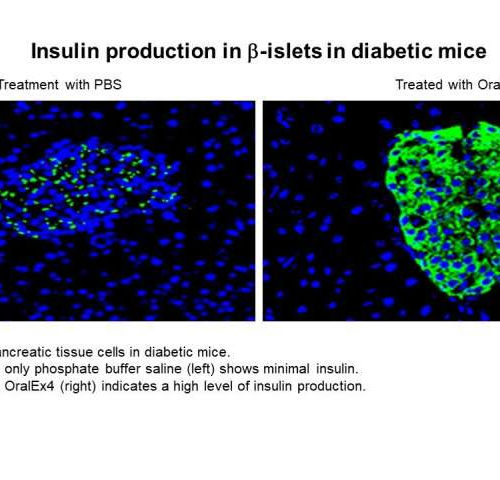
Fatty acid in triglycerides proves an effective platform for biological drug delivery
by Houston Methodist We’ve all been warned about the dangers of triglycerides, the fat stored in your blood. But what if that unhealthy fat could effectively transport oral medication to your body and eliminate the need for some injections or IV treatment? Houston Methodist nanomedicine researchers are studying this new drug delivery system for a...
Suspect cells’ ‘neighbor’ implicated in colorectal cancer
by Bill Hathaway, Yale University Colorectal cancer kills more than 50,000 people a year in the United States alone, but scientists have struggled to find the exact mechanisms that trigger the growth of tumors in the intestine. Cancer researchers have zeroed in on a tightly sequestered group of stem cells within the intestine as suspects...
COVID-19 vaccine candidate shows promise in first peer-reviewed research
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH PITTSBURGH, April 2, 2020 – University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists today announced a potential vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus causing the COVID-19 pandemic. When tested in mice, the vaccine, delivered through a fingertip-sized patch, produces antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 at quantities thought to be sufficient for neutralizing the virus....
Researchers find that nicotinamide may help treat fibrotic eye diseases and mitigate vision loss
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Nicotinamide, a form of vitamin B3, can inhibit aggressive cell transformations during wound healing and may be key to the development of therapies to treat fibrotic eye diseases that impair vision, according to a new Mount Sinai study published on Thursday, April 2, in Stem...
Is the coronavirus airborne? Experts can’t agree
The World Health Organization says the evidence is not compelling, but scientists warn that gathering sufficient data could take years and cost lives. Dyani Lewis Since early reports revealed that a new coronavirus was spreading rapidly between people, researchers have been trying to pin down whether it can travel through the air. Health officials say...
Tracking Tau
Understanding how the protein tau moves between neurons yields insight into possible treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. In the fight against neurodegenerative diseases such as frontotemporal dementia, Alzheimer’s and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, the tau protein is a major culprit. Found abundantly in our brain cells, tau is normally a team player — it maintains structure and...
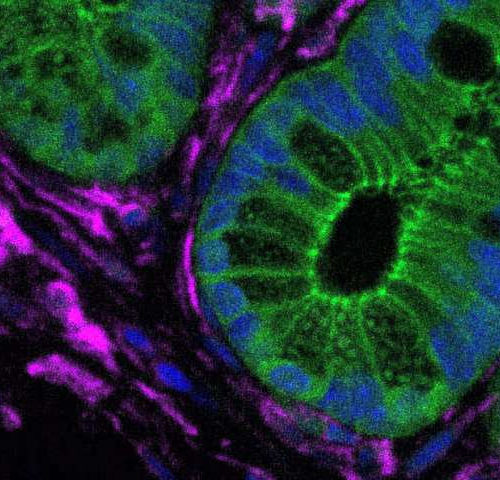
Turning colon cancer cells around
Using a modified natural substance along with current clinical approaches could improve colon cancer treatment, according to findings by the University of California, Irvine biologists. The discovery comes from their research into the role of an amino acid in tumor development and a potential method for reversing the process. Their study appears in Nature Cancer....