Paramedic Patricia Rodriguez fills out reports on a laptop after a 12-hour shift on April 6, 2020 in Yonkers, New York. (Credit: John Moore/Getty Images) SHARE THIS ARTICLE Facebook Twitter Email You are free to share this article under the Attribution 4.0 International license. TAGS COVID-19 DEATHS PANDEMICS PREDICTION STATES UNITED STATES UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY OF...
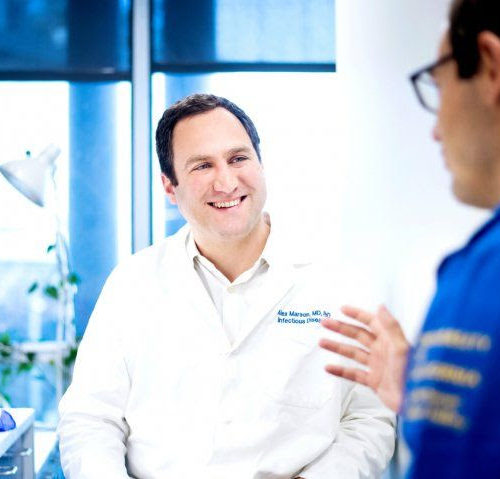
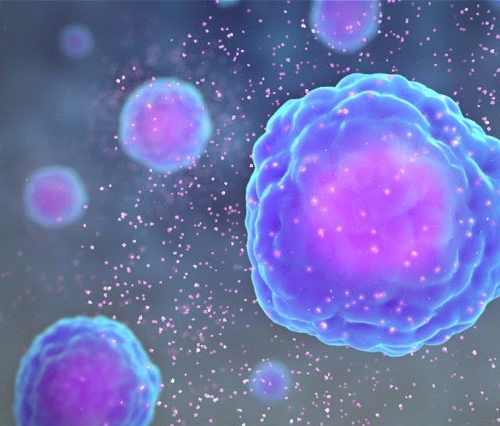
CRISPR-Based ‘Discovery Engine’ for New Cell Therapies to Advance Cancer Treatments
Despite centuries-long efforts to develop cures for cancer, various forms of the disease will kill about 630,000 people in the U.S. in 2020. But hopes are rising for cell therapies – sometimes called “living medicines” – that can boost and adapt the natural cancer-fighting potential of the immune system in ways that conventional cancer treatments...
Proteins may halt the severe cytokine storms seen in Covid-19 patients
Team designs antibody-like receptor proteins that can bind to cytokines, as possible strategy for treating coronavirus and other infections. One of the defining features of Covid-19 is the excessive immune response that can occur in severe cases. This burst of immune overreaction also called a cytokine storm, damages the lungs and can be fatal. A...
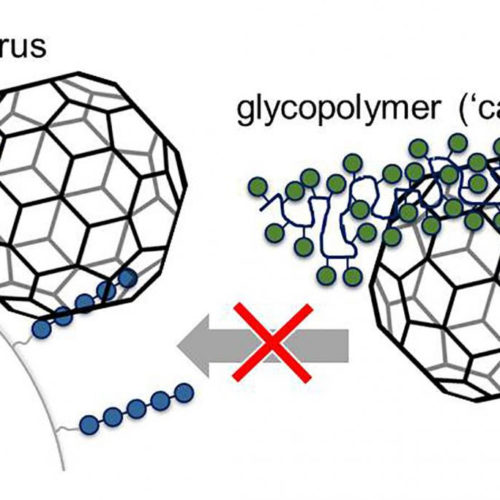
Artificial ‘candy canes’ block viruses
By: L. HARTMANN, M. SCHELHAAS Viruses are part of the human experience throughout our lives. They cause lots of different illnesses with the current coronavirus pandemic as just one example. While a vaccine does provide effective protection from viral infections, vaccines are only available for a select number of viruses. This is why antiviral drugs...
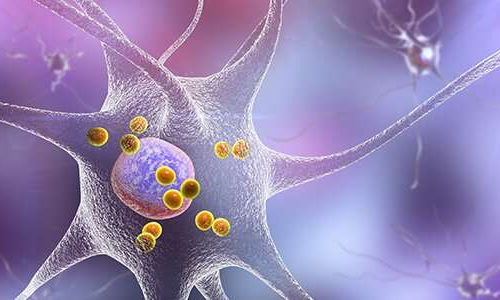
New research gives further evidence that autoimmunity plays a role in Parkinson’s disease
by La Jolla Institute for Immunology roducing brain cells of patients with Parkinson’s disease. T cells that react to alpha-synuclein are most abundant when patients are first diagnosed with the disease. Credit: La Jolla Institute for Immunology A new study co-led by scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) adds increasing evidence that...
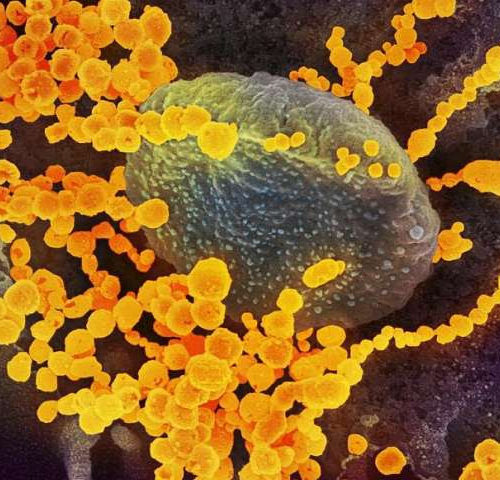
Antiviral remdesivir prevents disease progression in monkeys with COVID-19
by National Institutes of Health image shows SARS-CoV-2 (round gold objects) emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab. SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV, is the virus that causes COVID-19. The virus shown was isolated from a patient in the U.S. Credit: NIAID-RML Early treatment with the experimental antiviral drug remdesivir significantly reduced...
Slower clearance of coronavirus infection may explain why men fare worse than women
by Albert Einstein College of Medicine Researchers at Montefiore Health System and Albert Einstein College of Medicine may have solved a mystery surrounding the novel coronavirus pandemic: Why men infected by the virus generally show more severe symptoms and are more likely than women to die from COVID-19. In collaboration with the Kasturba Hospital for...
Researchers use live virus to identify 30 existing drugs that could treat COVID-19
by Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute, the University of Hong Kong, Scripps Research, UC San Diego School of Medicine, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and UCLA have identified 30 existing drugs that stop the replication of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Almost...
DNA Damage During Cell Replication is Probably Not Important in Mammalian Aging
The size of the contribution of stochastic nuclear DNA damage to aging is debated. It causes cancer, when rare combinations of cancerous mutations occur and suppression of those early cancerous cells fails, but can it give rise to a meaningful degree of tissue dysfunction otherwise? The present consensus is that most such damage is irrelevant,...
Using the CellAge Database to Find Genes Associated with Inhibition of Cellular Senescence
A senescent cell ceases replication and secretes inflammatory and pro-growth signals. The process serves a useful function when such cells are present for a short time and then destroyed, aiding in suppression of cancer and in wound healing. When senescent cells linger, they cause chronic inflammation and significant disruption to tissue function, however. This is...