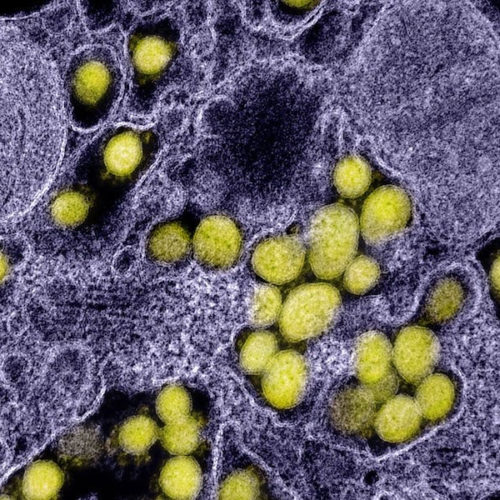
Most adults with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are not at increased risk of hospitalization from COVID-19 due to medications used to dampen their altered immune system, the cause of their disease. Nor are most people with more common types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid, psoriatic and spondyloarthritis, at greater risk of hospitalization from COVID-19, a...
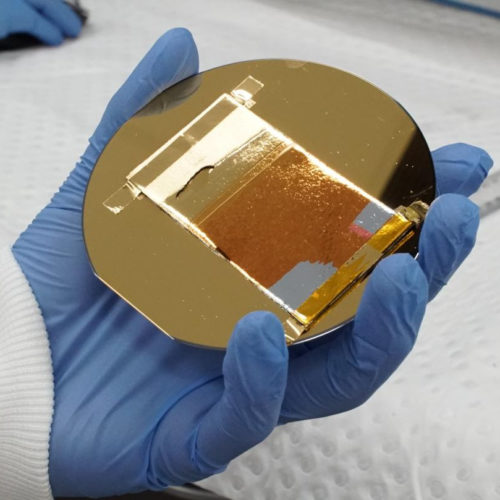
Pot of gold engineered to help with early disease detection
UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND University of Queensland researchers have developed biosensors that use nanoengineered porous gold which more effectively detect early signs of disease, potentially improving patient outcomes. Most diagnostic methods use costly materials and are time-consuming and expensive to run, but PhD candidate Mostafa Masud and research supervisors Professor Yusuke Yamauchi and Dr MD Shahriar...
Compared to placebo, vitamin D has no benefit for severe asthma attacks
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH CHIEF OF PEDIATRIC PULMONARY MEDICINE AT UPMC CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL OF PITTSBURGH, AND THE NIELS K. JERNE CHAIR OF PEDIATRICS AT THE UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH SCHOOL OF MEDICINE view more CREDIT: UPMC PITTSBURGH, Aug. 25, 2020 – Contrary to earlier results, vitamin D supplements do not prevent severe asthma attacks in at-risk children,...
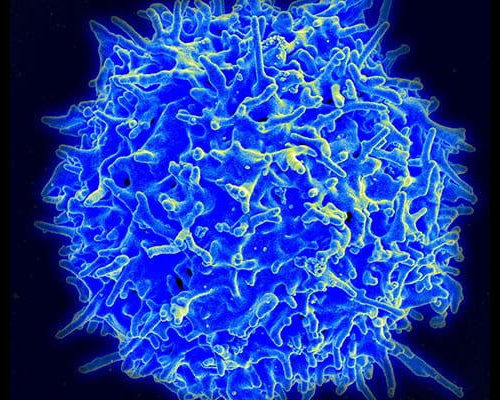
Inflammatory bowel disease linked to an immune cell run amok
New findings may provide new therapeutic target and help explain why IBD and other autoimmune diseases are often chronic and life-long UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO COLORIZED SCANNING ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF A T CELL, A TYPE OF LYMPHOCYTE THAT PLAYS A CENTRAL ROLE IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. view more CREDIT: NIAID Inflammatory bowel disease...
New devices for point-of-care re-constitution and administration of two-component vaccines
GSK is seeking new approaches for simplified point-of-care re-constitution and delivery of vaccines made of two components. The components can either be liquids to be mixed together, or a lyophilized vaccine solid (cake or powder) to be dissolved in a liquid. We are interested in a device that would be as convenient as a pre-filled...
Nanoparticles show promise in defeating antibiotic-resistant bacteria, U of T researchers find
A new therapy developed by researchers at the University of Toronto may bring us one step closer to effectively killing deadly drug-resistant superbugs. “The threat posed by pathogens that are increasingly becoming resistant to all known antibiotics is an alarming and pressing health care problem,” says Ruby Sullan, assistant professor in the department of physical...
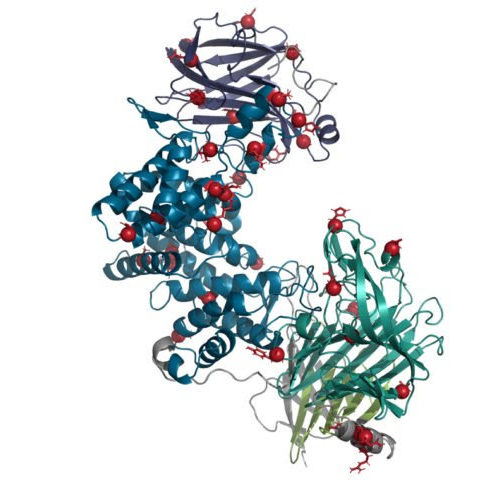
Re-engineered enzyme could help reverse damage from stroke, spinal cord injury: U of T study
A team of researchers from the University of Toronto’s Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering and the University of Michigan has redesigned and enhanced a natural enzyme that shows promise in promoting the regrowth of nerve tissue following injury. The new version of the enzyme is more stable and could lead to treatments for reversing...
Study: MTL deterioration can lead to impulsive decisions
Deterioration of a part of the brain known as the medial temporal lobe can cause an older adult to make more impulsive decisions. One decision-making process — temporal discounting — places a greater value on a smaller and immediate outcome while dismissing a better but delayed outcome: instant gratification, in other words. Researchers at the...
University of Minnesota research team studies neutralizing monoclonal antibodies as possible treatment for COVID-19
Posted Today The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Operation Warp Speed have chosen a University of Minnesota School of Public Health research team to begin a global clinical trial of synthetic versions of natural human antibodies — called neutralizing monoclonal antibodies — as a treatment for COVID-19. The collaborative study, named ACTIV-3, will investigate...
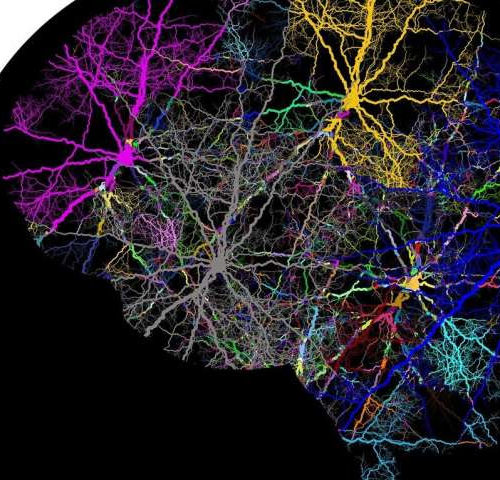
New form of brain analysis engages whole brain for the first time
by Duke University A new method of brain imaging analysis offers the potential to greatly improve the effectiveness of noninvasive brain stimulation treatment for Alzheimer’s, obsessive compulsive disorder, depression, and other conditions. Duke researchers developed the new method, which for the first time analyzed the whole brain network rather than a single region of the...