by Catherine Williams, Emory University Orange represents tumor cells displaying the HPV antigen p16, while green represents B cells with the arrows indicating germinal center-like structures. Immunotherapies have transformed the treatment of several types of cancer over the last decade. Yet they focus on reactivating one arm of the immune system: cytotoxic T cells, which sniff...
Undesirable rejection mechanism identified in stem cell transplantation
by Medical University of Vienna In the treatment of leukemia, stem cell transplantation subsequent to chemotherapy and radiation can often engender severe adverse inflammatory reactions—especially in the skin or in the gut, since these so-called barrier organs are more frequently affected. Up until now, the reason for this was unclear. A MedUni Vienna team led by...
Tau protein changes correlate with Alzheimer’s disease dementia stage
by Alice McCarthy, Children’s Hospital Boston PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Research into Alzheimer’s disease has long focused on understanding the role of two key proteins, beta amyloid and the tau protein. Found in tangles in patients’ brain tissue, a pathological form of the tau protein contributes to propagating the disease in the...
Scientists identify possible COVID-19 treatment
by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (L-R) Bhesh Sharma, Ph.D., Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti, Ph.D., Rajendra Karki Ph.D., of the Kanneganti Lab at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital The COVID-19 pandemic continues to cause significant illness and death while treatment options remain limited. St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists have discovered a potential strategy to prevent life-threatening inflammation, lung damage and organ...
Revolutionary CRISPR-based genome editing system treatment destroys cancer cells
by Tel Aviv University Cancer cell during cell division. Researchers at Tel Aviv University (TAU) have demonstrated that the CRISPR/Cas9 system is very effective in treating metastatic cancers, a significant step on the way to finding a cure for cancer. The researchers developed a novel lipid nanoparticle-based delivery system that specifically targets cancer cells and destroys them by genetic...
Vitamin D supplements may reduce risk of developing advanced cancer
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital For many years, investigators have been trying to pin down the tantalizing connection between vitamin D and cancer. Epidemiological studies have found that people who live near the equator, where exposure to sunlight produces more vitamin D, have lower incidence and death rates from certain cancers. In cancer cells in the...
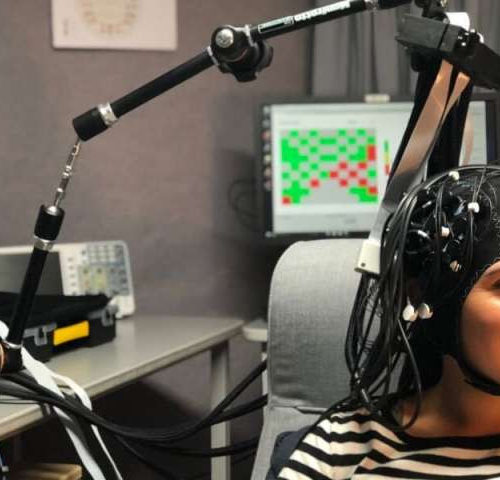
Technology lets clinicians objectively detect tinnitus for first time
by Public Library of Science A person set up for an fNIRS recording (the brain imaging technique used in this paper). A technology called functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) can be used to objectively measure tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, according to a new study published November 18 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Mehrnaz Shoushtarian of...
Alzheimer’s disease drug may help fight against antibiotic resistance
by University of Queensland UQ’s Dr David De Oliveira in the lab, testing the efficacy of PBT2 in disrupting and killing antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. An experimental Alzheimer’s disease treatment is proving effective at treating some of the most persistent, life-threatening antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Researchers from The University of Queensland, The University of Melbourne and Griffith University have discovered...
Cellular pathway of genetic heart disease similar to neurodegenerative disease
MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER, Minn. — Research on a genetic heart disease has uncovered a new and unexpected mechanism for heart failure. This landmark discovery found a correlation between the clumping of RNA-binding proteins long linked to neurodegenerative disease ? and the aggregates of protein found in the heart tissue of patients with RBM20 dilated cardiomyopathy. Dilated cardiomyopathy...
UTHSC researchers identify three drugs as possible therapeutics for COVID-19
UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER IMAGE: BASED ON VIRTUAL AND IN VITRO ANTIVIRAL SCREENING THAT BEGAN IN THE EARLIER MONTHS OF THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC, THE RESEARCHERS LED AT UTHSC BY COLLEEN JONSSON, PHD, IDENTIFIED ZUCLOPENTHIXOL, NEBIVOLOL AND AMODIAQUINE AS A PROMISING THERAPEUTICS FOR TEH VIRUS IN ITS EARLY STAGES. Memphis, Tenn. (November 18, 2020)–Researchers at...