by Monash University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Communication, serendipity and an enzyme called DOT1L have all combined to produce some exciting findings into the immune system’s B cells and T cells by two groups of Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute (BDI) scientists. These could result in further studies into a target for asthma and allergies, and fundamental...
New study links cadmium to more severe flu, pneumonia infections
by Nardy Baeza Bickel, University of Michigan A 3-D image of a flu virus. Credit: Center for Disease Control High levels of cadmium, a chemical found in cigarettes and in contaminated vegetables, are associated with higher death rates in patients with influenza or pneumonia—and may increase the severity of COVID-19 and other respiratory viruses, according to...
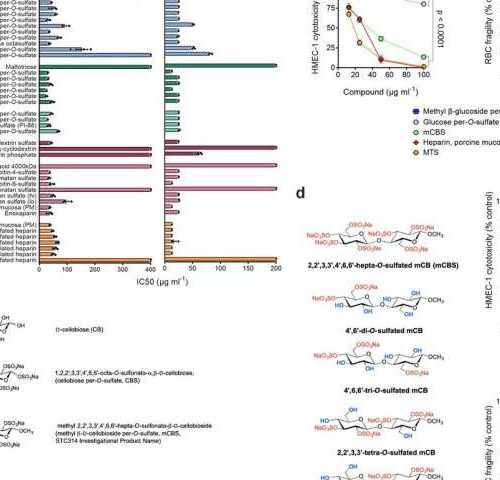
New drug to combat global killer sepsis
by Rachel Curtis, Australian National University Fig. 1: Polyanions inhibit histone-mediated endothelial cell cytotoxicity and RBC fragility with minimal structural requirements for the activity identified. A promising new drug to combat sepsis has been developed by researchers at The Australian National University (ANU), potentially saving millions of lives each year. ANU Professor Christopher Parish and...
Analysis of Human Inheritance of Longevity is not as Straightforward as One Might Think
Here, researchers note some of the challenges inherent in trying to analyze data on human inheritance of longevity; it isn’t as easy as it sounds. Considerable effort has gone into analysis of long-lived families to try to identify genetic variants that might explain why some lineages exhibit greater longevity than others. Nonetheless, so far only a small number...
Researchers identify the origin of a deadly brain cancer
Researchers at McGill University are hopeful that the identification of the origin and a specific gene needed for tumour growth could lead to new therapeutics to treat a deadly brain cancer that arises in teens and young adults. The discovery relates to a subgroup of glioblastoma, a rare but aggressive form of cancer that typically proves...
Key type of immune cell ‘self-renews’ in humans, new study finds
by Cardiff University Credit: CC0 Public Domain A team of scientists has shown that a key type of immune cell “self-renews” in humans. It is an unexpected discovery, as it was previously thought this specific type of “senescent” killer immune cell had reached “end-stage” and would die following one more stint at helping people fight off—or...
TWEAKED PSYCHEDELIC COULD TREAT DEPRESSION AND ADDICTION
“Psychedelics are some of the most powerful drugs we know of that affect the brain,” says David Olson, assistant professor of chemistry at the University of California, Davis, and senior author of the paper in Nature. “It’s unbelievable how little we know about them.” Ibogaine is extracted from the plant Tabernanthe iboga. There are anecdotal reports that...
Cellular connections found between nervous and immune systems
by Claudia Lopez Lloreda, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard Researchers have found sensory nerve fibers (red) that interact with lymph nodes (green) in mice. Credit: Siyi Huang, John Austin, Najat Mannoun The nervous and immune systems have long been thought to be separate entities in the body, but new research has uncovered a direct cellular...
Novel earwax test could improve diabetes diagnosis
Blood glucose levels are always changing – one minute they can be radically different from the other. This means that assessing chronic glucose levels is quite difficult. Now scientists from UCL and King’s College London determined that a simple earwax self-sampling device could be used to measure chronic glucose levels with 60% more reliability tha...
Could existing drugs be used against COVID-19?
by University of Montreal Credit: CC0 Public Domain Several drugs already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) could potentially be used to alleviate the symptoms of COVID-19, biomedical researchers at Université de Montréal have found. The team—led by doctoral student Nehme El-Hachem, working under the supervision of UdeM pharmcology associate professor Moutih Rafei in collaboration...