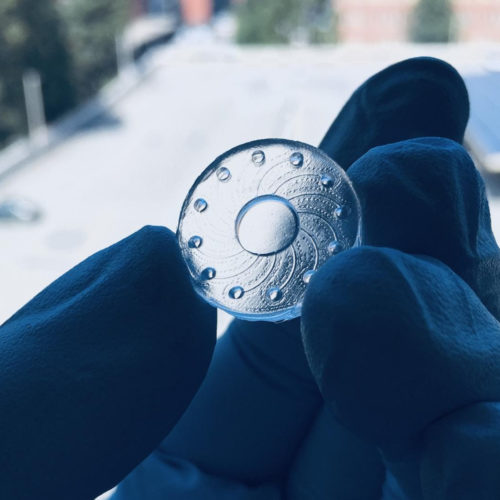
UNIVERSITY OF BIRMINGHAM Scientists at the University of Birmingham have developed a new sensor to measure weak magnetic signals in the brain, which has the potential to increase understanding of connectivity in the brain, and detect signs of traumatic brain injury, dementia and schizophrenia. Magnetic signals in the brain are measured by magnetoencephalography (MEG). They...
Contact lenses for diagnostic and therapeutic use
TERASAKI INSTITUTE FOR BIOMEDICAL INNOVATION IMAGE: ENLARGED PROTOTYPE OF BIOSENSOR LENS WITH RESERVOIRS. (LOS ANGELES) – Human bodily fluids and secretions contain molecules known as biomarkers that contain a wealth of information about the body’s health and the presence of disease. Among secretions such as tears, sweat and saliva, tears are considered the best source...
Targeting calcium overload could improve stroke outcomes, research suggests
UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA HEALTH SYSTEM IMAGE: PETR TVRDIK, PHD, HAS FOUND THAT IMMUNE CELLS CALLED MICROGLIA ARE FLOODED WITH WAVES OF CALCIUM IN THE WAKE OF ISCHEMIC STROKES Excessive calcium contributes to harmful inflammation in ischemic stroke, and targeting it may provide doctors with a new way to improve patient outcomes, new research from the University of...
Vegans, vegetarians and pescetarians may be at higher risk of bone fractures
BMC (BIOMED CENTRAL) Compared with people who ate meat, vegans with lower calcium and protein intakes on average, had a 43% higher risk of fractures anywhere in the body (total fractures), as well as higher risks of site-specific fractures of the hips, legs and vertebrae, according to a study published in the open access journal BMC...
Folding of SARS-CoV2 genome reveals drug targets — and preparation for ‘SARS-CoV3’
GOETHE UNIVERSITY FRANKFURT The genetic code of the SARS-CoV2 virus is exactly 29,902 characters long, strung through a long RNA molecule. It contains the information for the production of 27 proteins. This is not much compared to the possible 40,000 kinds of protein that a human cell can produce. Viruses, however, use the metabolic processes...
New treatments for hot flashes target neurons
As many as 75 percent of the women in North American experience hot flashes, and many of these women still look to hormone therapy to relieve the surge of hormones, otherwise known as vasomotor symptoms, or VMS. But new research, shared recently at the Annual North American Menopause Society Conference, shows the direction of VMS therapy is turning toward new...
Psilocybin & migraine: First of its kind trial reports promising results
By Rich Haridy; November 22, 2020 An exploratory trial found a single dose of psilocybin cut migraine frequency by half in the two weeks following taking the drug A first-of-its-kind exploratory study, led by researchers from Yale School of Medicine, has found a single dose of the psychedelic psilocybin can reduce migraine frequency by 50 percent for...
Super-porous material transports cancer-killing CRISPR inside cells
By Michael Irving; November 22, 2020 A new study has shown how metal organic frameworks (MOFs) can be used to carry the CRISPR gene-editing tool into cancer cells The CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing tool has shown promise in treating a wide range of diseases, but getting it into cells in the first place can be challenging. Now, researchers in...
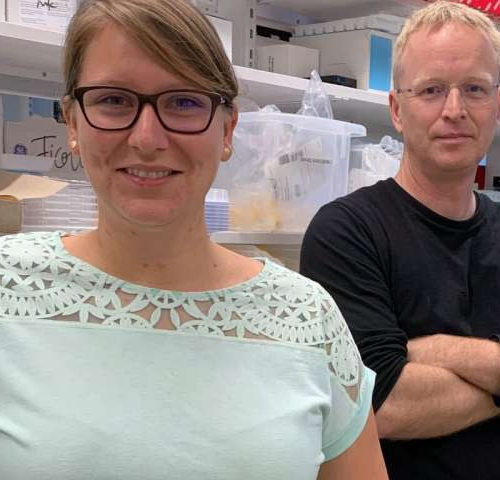
New type of immunotherapy may pave the way for better cancer treatments
by Karolinska Institutet From left: First author Silke Eisinger and last author Mikael Karlsson from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden. Immunotherapy for cancer has made great advances and many patients can now receive effective treatments that were not available 10 years ago. However, there are certain types of cancer that do not respond to existing immunotherapy. A...
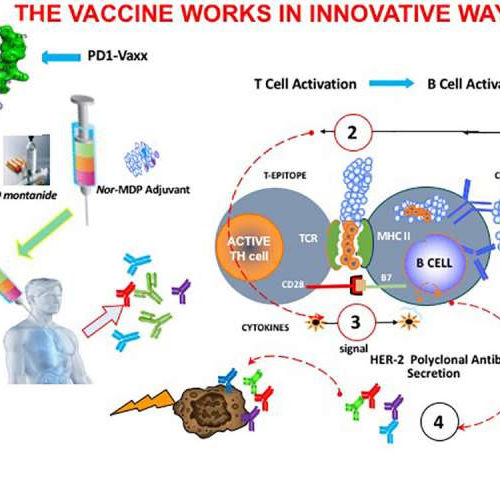
Therapeutic PD-1 cancer vaccine shown to be safe and effective in animal study
by Ohio State University Medical Center A study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center—Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC—James) described a potential therapeutic anticancer vaccine that frees suppressed cancer-killing immune cells, enabling them to attack and destroy a tumor. Published in the journal Oncoimmunology, on October 1, 2020, the findings...