Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Sharon Clark is able to get her life-sustaining cancer drug, Pomalyst — priced at more than $18,000 for a 28-day supply — only because of the generosity of patient assistance foundations. Clark, 57, a former insurance agent who lives in Bixby, Oklahoma, had to stop working in 2015 and go...
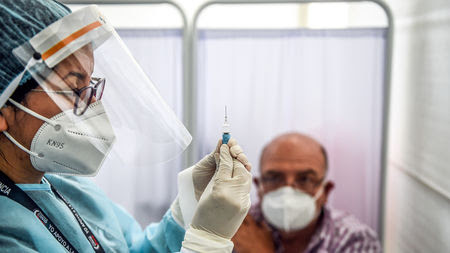
‘It’s crazy.’ Upbeat COVID-19 vaccine news from China and U.K. leaves scientists wanting more details
A health care worker prepares to inoculate a volunteer with China National Biotec Group’s vaccine at Cayetano Heredia University in Lima, Peru, on 9 December. ERNESTO BENAVIDES/AFP VIA GETTY IMAGES In what has become a familiar pattern, the COVID-19 vaccine landscape has changed overnight, simultaneously raising hopes that more people may soon get vaccinated and triggering confusion....
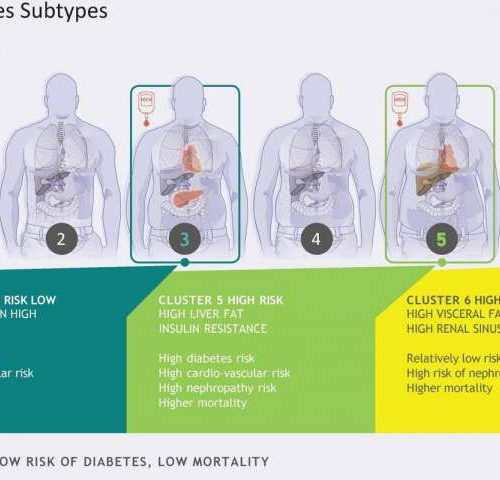
Prediabetes subtypes identified
by Deutsches Zentrum fuer Diabetesforschung DZD In people with prediabetes, there are six clearly distinguishable subtypes (clusters), which differ in development of the diseases, risk for diabetes, and development of complications. Credit: IDM All prediabetes is not the same: in people in the preliminary stages of type 2 diabetes, there are six clearly distinguishable subtypes,...
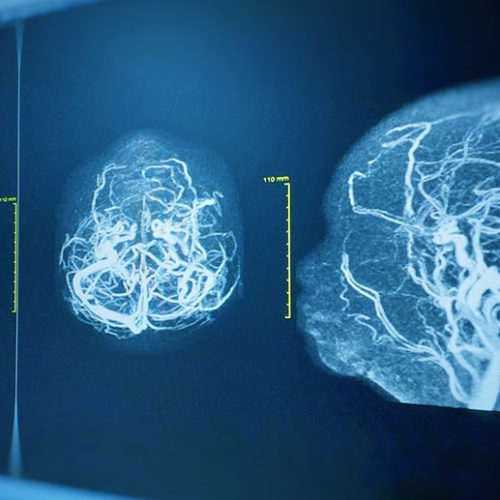
Thinning, Leaky Brain Blood Vessels Seen in COVID-19
by Judy George, Senior Staff Writer, MedPage Microvascular brain injury was seen in COVID-19 patients who died, but no evidence of a direct viral attack on the brain was detected, a pathology report showed. Damage caused by thinning and leaky brain blood vessels consistently appeared on high-resolution MRI, but there were no signs of SARS-CoV-2 infection...
SCIENTISTS ARE WORRIED VACCINES WON’T PROTECT AGAINST NEW COVID STRAINS
BY VICTOR TANGERMANN According to several UK experts, there’s a chance that vaccines currently being administered in the country won’t provide sufficient immunity against new strains of the coronavirus emerging in both the UK and South Africa, Reuters reports. The scientists are most concerned about several mutations in the spike protein, the part of the virus that...
Single dose of the vaccine may be better than nothing at all
by Yale University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Researchers from Yale School of Public Health used a previously published model of a COVID-19 vaccination program to quantify the speed-versus-efficacy tradeoff of vaccination deployment. The model accounted for transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), COVID-19 disease severity, and recovery or vaccination leading to protective immunity....
Nostrum expands recall of diabetes drug metformin after carcinogen concerns
Conner Mitchell Associate Editor Generic metformin has been a thorn in drugmakers’ sides for months after a probable human carcinogen was found in tested lots. Now, one of the companies is expanding its recall to another lot of the drug. Nostrum Laboratories out of Kansas City, MO voluntarily recalled one lot of metformin HCl extended release...
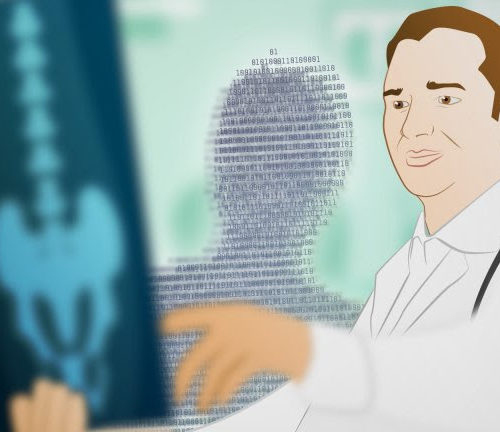
Simple Algorithms vs. A.I. And What They Mean For Medicine
The Medical Futurist Artificial intelligence (A.I.), machine learning (ML) and algorithms; if you are a regular at The Medical Futurist, you’ve come across these terms more than once whether it’s in our articles, videos or e-books. Indeed, our latest e-book about investment in digital health has a dedicated section about A.I. Even The Medical Futurist Institute’s latest peer-reviewed...
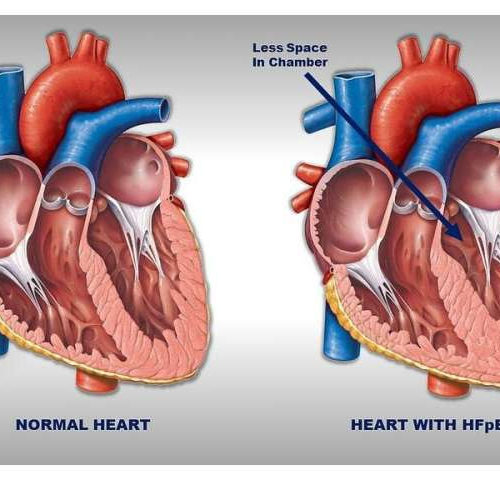
Obesity weakens heart muscle in patients with a common type of heart failure
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Two hearts, a normal on the left and one with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) on the right. The heart with HFpEF has a thicker, stiffer left ventricular wall and therefore, less room in the ventricle chamber to fill with an adequate amount of blood to be...
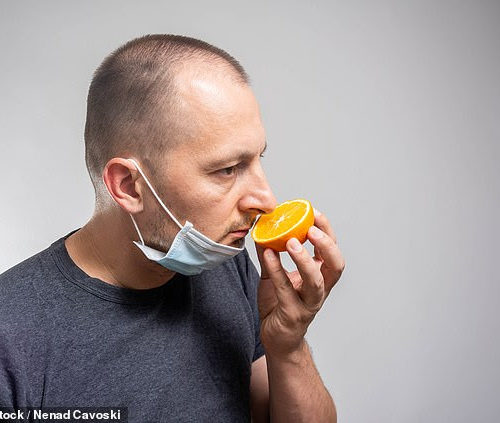
Nearly a quarter of patients who suffered loss of smell from coronavirus did not see it return two months later
By JOE PINKSTONE FOR MAILONLINE Losing the senses smell and taste are common symptoms of Covid-19 and new data shows it affects 86 per cent of individuals with mild cases. However only 4.5 per cent of people with moderate cases and 6.9 per cent in severe-to-critical cases say they have these symptoms. The study from Paris Saclay University...