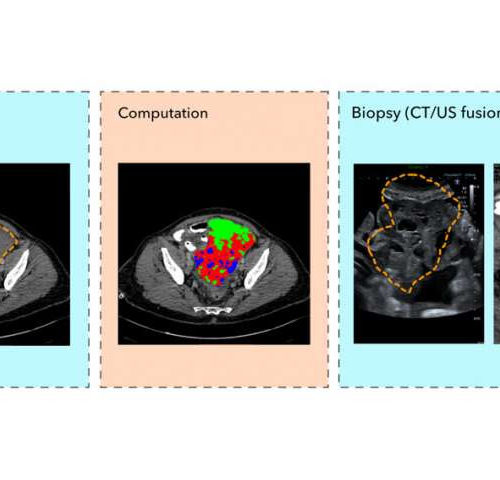
by Craig Brierley, University of Cambridge Illustration of a patient with a pelvic tumour. a Routine contrast-enhanced CT images were used to manually segment the pelvic tumour (dashed line). b Spatial radiomic feature extraction and generation of habitat maps. For this patient, three tumour habitats are feasible and highlighted in blue, red, and green, respectively. c...
New drug form may help treat osteoporosis, calcium-related disorders
by Purdue University Elizabeth Topp, a Purdue professor of physical and industrial pharmacy, helped develop a stabilized form of human calcitonin, which is a peptide drug already used for people with osteoporosis. Credit: Chris Adam/Purdue University A novel form of a drug used to treat osteoporosis that comes with the potential for fewer side effects may...
Microbiome study: Gum disease-causing bacteria borrow growth molecules from neighbors to thrive
by Marcene Robinson, University at Buffalo Credit: CC0 Public Domain The human body is filled with friendly bacteria. However, some of these microorganisms, such as Veillonella parvula, may be too nice. These peaceful bacteria engage in a one-sided relationship with pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis, helping the germ multiply and cause gum disease, according to a new University...
Immune response to COVID-19 reduced in patients with blood cancers
by The Francis Crick Institute Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Patients with blood cancers such as leukemia vary in their immune response to COVID-19 and can struggle to clear infection for very many weeks, according to new research published in Cancer Cell. By contrast, most patients with solid tumors, even those with advanced cancer, can mount an effective and lasting...
Bone fracture risk may increase when critical enzymatic processes decline
RENSSELAER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE TROY, N.Y. — A loss of enzymatic processes within the body can increase a person’s risk of bone fracture. This new insight was recently published in eLife by an international team of scientists and engineers led by Deepak Vashishth, the director of the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies (CBIS) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute....
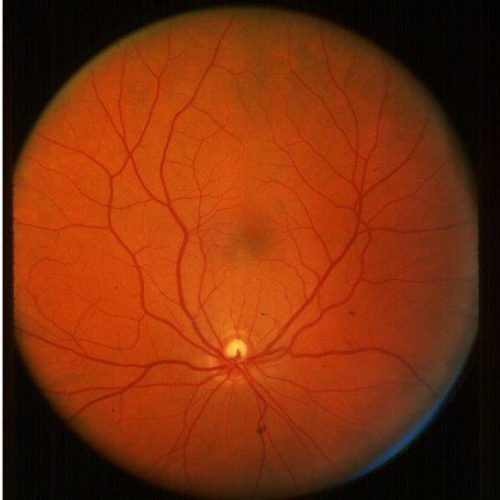
Routine eye scans may give clues to cognitive decline in diabetes
JOSLIN DIABETES CENTER IMAGE: OPHTHALMOLOGY EXAM OF PATIENT WITH DIABETES CREDIT: BEETHAM EYE INSTITUTE/JOSLIN DIABETES CENTER BOSTON – (January 4, 2021) – As they age, people with diabetes are more likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders than are people without diabetes. Scientists at Joslin Diabetes Center now have shown that routine eye...
Repeated ketamine infusions reduce PTSD symptom severity
by The Mount Sinai Hospital Adriana Feder, MD, Associate Professor of Psychiatry at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and lead author of the study Credit: Mount Sinai Health System Repeated intravenous (IV) ketamine infusions significantly reduce symptom severity in individuals with chronic post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the improvement is rapid and maintained...
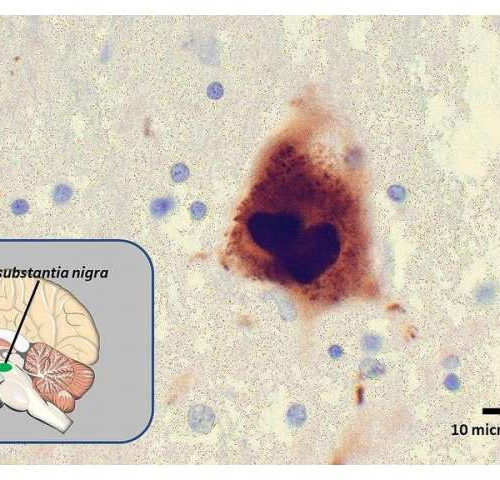
Artificial enzyme may be first step toward treatment for Parkinson’s disease
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Photomicrograph showing a Lewy body (center), a clump of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins believed to be a factor in Parkinson’s disease. The inset shows the location of the substantia nigra, an area of the brain that influences movement and cognition, where this Lewy body was found. A Johns Hopkins Medicine...
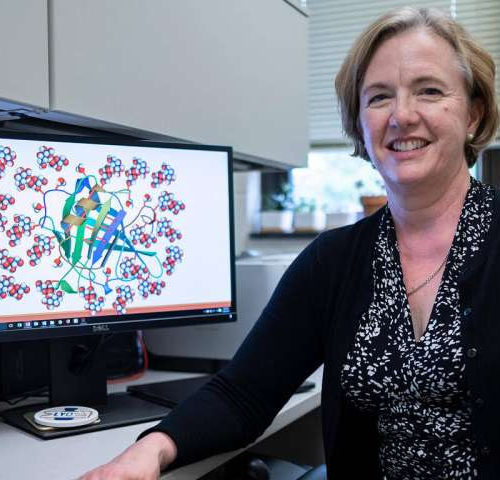
Can a new protein bring RNA drugs where they can’t reach?
Amber Tong Senior Editor Sue Dillon remembers the uncertainty when she first left J&J to start her own biotech around a new kind of molecules called centyrins. Sue Dillon J&J had already licensed the tech, which was developed by her co-founder Karyn O’Neil at the pharma giant’s Centyrex unit, to two companies for use in CAR-T and...
Hopping electrons help re-route harmful diseases
The simple act of breathing is among the most familiar ways we convert nutrients to energy – inhaling molecules of oxygen and harmlessly breathing out unwanted material. But when our usual disposal mechanisms fail, the accumulated electrons can produce the kind of toxic event that causes many diseases, including cancer. Illustration by Israel Palacio on...