Currently, cancers are detected and diagnosed using more invasive methods such as surgical biopsies of suspected tumours and blood draws. Urinalysis has long been used to detect and manage many diseases and disorders, but not cancer. Image credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) via Wikimedia, Public Domain Researchers investigated whether fragments of cell-free DNA...
Fine-tuning device performance with swarms of swimming cells
Scientists use acoustic microfluidic devices to separate and sort components in fluids, such as red and white blood cells, platelets and tumour cells in the blood, to better understand diseases or to develop new treatments. However, technologies developed in research labs often lack the consistent performance needed for use in clinical and industrial settings. A team of researchers at...
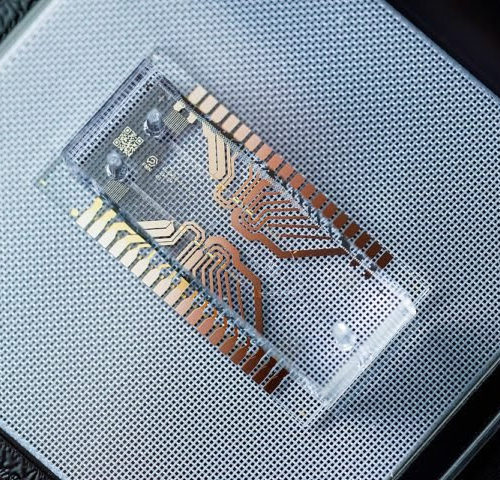
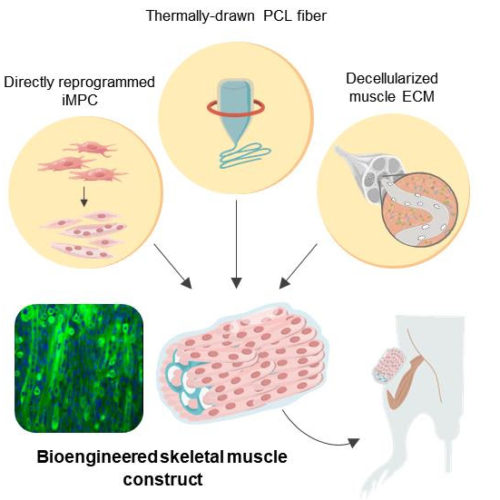
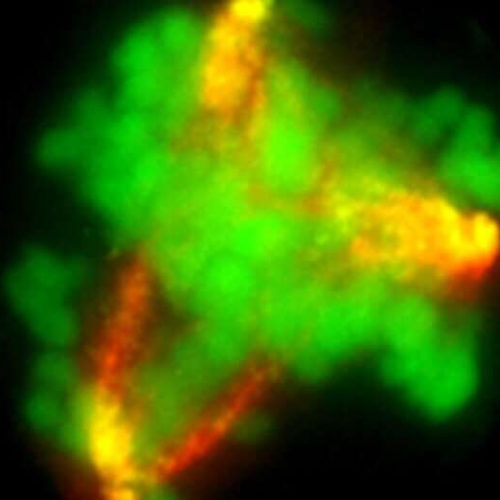
Bioengineered hybrid muscle fiber for regenerative medicine
INSTITUTE FOR BASIC SCIENCE IMAGE: SCHEMATIC ILLUSTRATION OF THE 3D SKELETAL MUSCLE-LIKE BIOENGINEERED CONSTRUCTS CREDIT: INSTITUTE FOR BASIC SCIENCE Muscle is the largest organ that accounts for 40% of body mass and plays an essential role in maintaining our lives. Muscle tissue is notable for its unique ability for spontaneous regeneration. However, in serious injuries...
Improving immunotherapies for blood cancers: real-time exploration in the tumor
INSTITUT PASTEUR Monoclonal antibodies are part of the therapeutic arsenal for eliminating cancer cells. Some make use of the immune system to act and belong to a class of treatment called “immunotherapies.” But how do these antibodies function within the tumor? And how can we hope to improve their efficacy? Using innovative in vivo imaging...
Psychological ‘signature’ for the extremist mind uncovered by Cambridge researchers
by University of Cambridge Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers have mapped an underlying “psychological signature” for people who are predisposed to holding extreme social, political or religious attitudes, and support violence in the name of ideology. A new study suggests that a particular mix of personality traits and unconscious cognition—the ways our brains take in basic information—is...
Cancer cell vulnerability points to potential treatment path for aggressive disease
by Larner College of Medicine at the University of Vermont Image of a triple negative breast cancer cell undergoing abnormal division after inhibition of KIF18A (red = microtubules; green = chromosomes; yellow = spindle poles). Credit: Cindy Fonseca, M.S., Stumpff Lab, UVM Larner College of Medicine Unravelling the unique characteristics of cancer cells and finding...
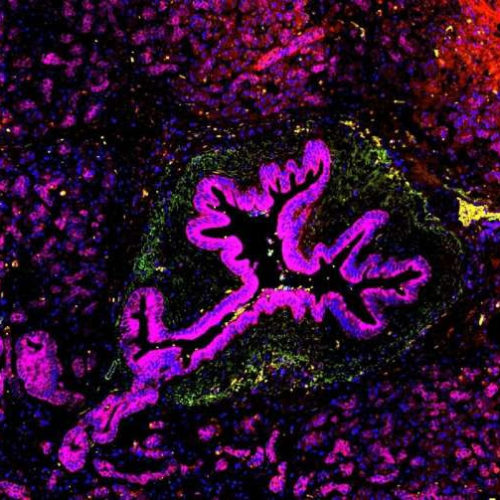
New insights on how inflammatory molecule contributes to skin and pancreatic cancers
by Massachusetts General Hospital Pancreatic cells can become cancerous (magenta) when an inflammatory molecule called IL-33 activates signals within the pancreatic cells that promote their abnormal growth, investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital have found. The research, which is published in The EMBO Journal, could lead to new strategies to prevent certain cancers. Credit: Jong Ho Park, PhD...
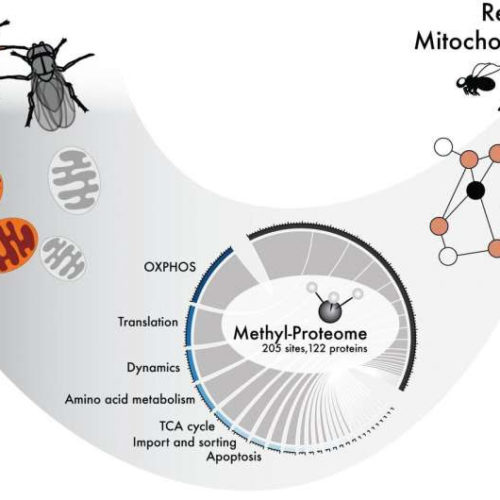
New research on mitochondrial function can play significant part in serious disease
by Karolinska Institutet Methylation is a small protein modification that uses SAM as a co-factor. This study shows how SAM is required for mitochondrial function in various organisms. Credit: Karolinska Institutet. Disorders of cellular energy supply can cause a number of serious diseases, but also seem to be connected to aging. More research is needed on mitochondrial function...
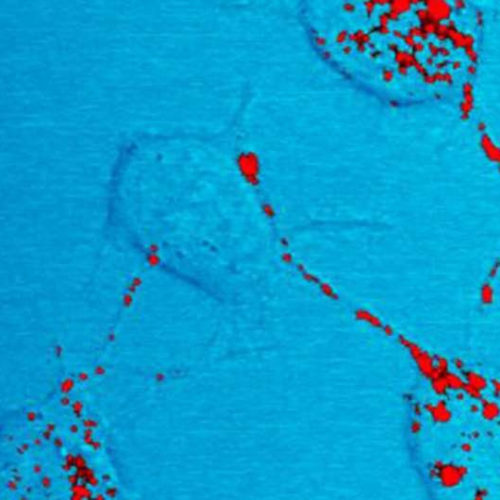
Prion diseases: New clues in the structure of prion proteins
by International School of Advanced Studies (SISSA) Photomicrograph of a neural tissue specimen, harvested from a scrapie affected mouse, revealing the presence of prion protein stained in red. Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases(NIAID) Prion diseases are a group of rapidly progressive, fatal and infectious neurodegenerative disorders affecting both humans and animals. Bovine spongiform...
What happens to immunity levels post COVID-19 infection?
by Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity Credit: CC0 Public Domain Australian scientists have described the evolution of immunity levels up to four months following COVID-19 infection, finding that while antibody levels drop dramatically in the first one to two months, the decrease then slows down substantially. The findings suggest that protective COVID-19 vaccines should...